©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2019; 7(24): 4407-4413
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4407
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4407
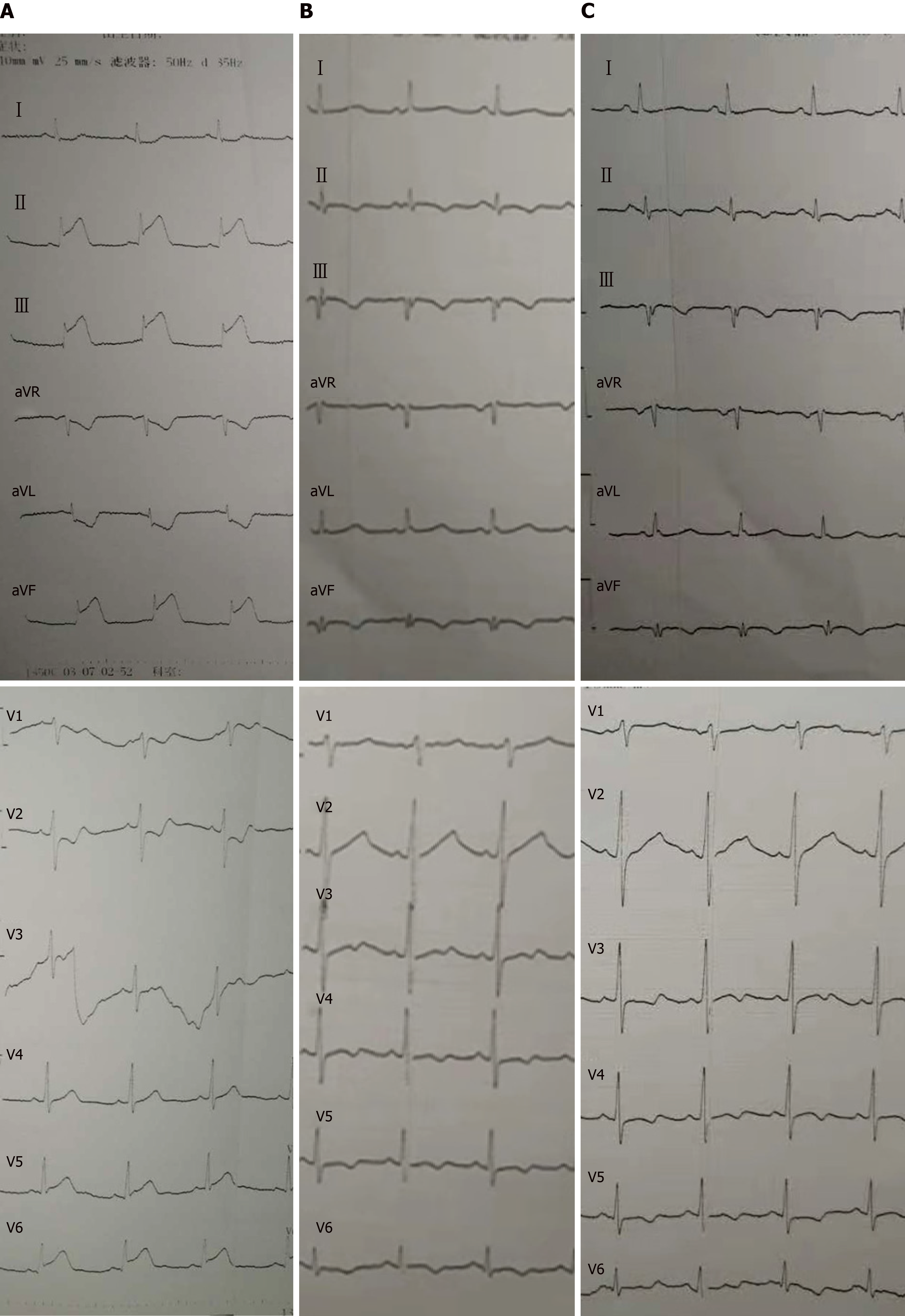
Figure 1 Electrocardiography examinations.
A: Electrocardiography (ECG) on admission; B: ECG after intervention; C: ECG when the patient had the symptoms of vomit, nausea, and chest pain.
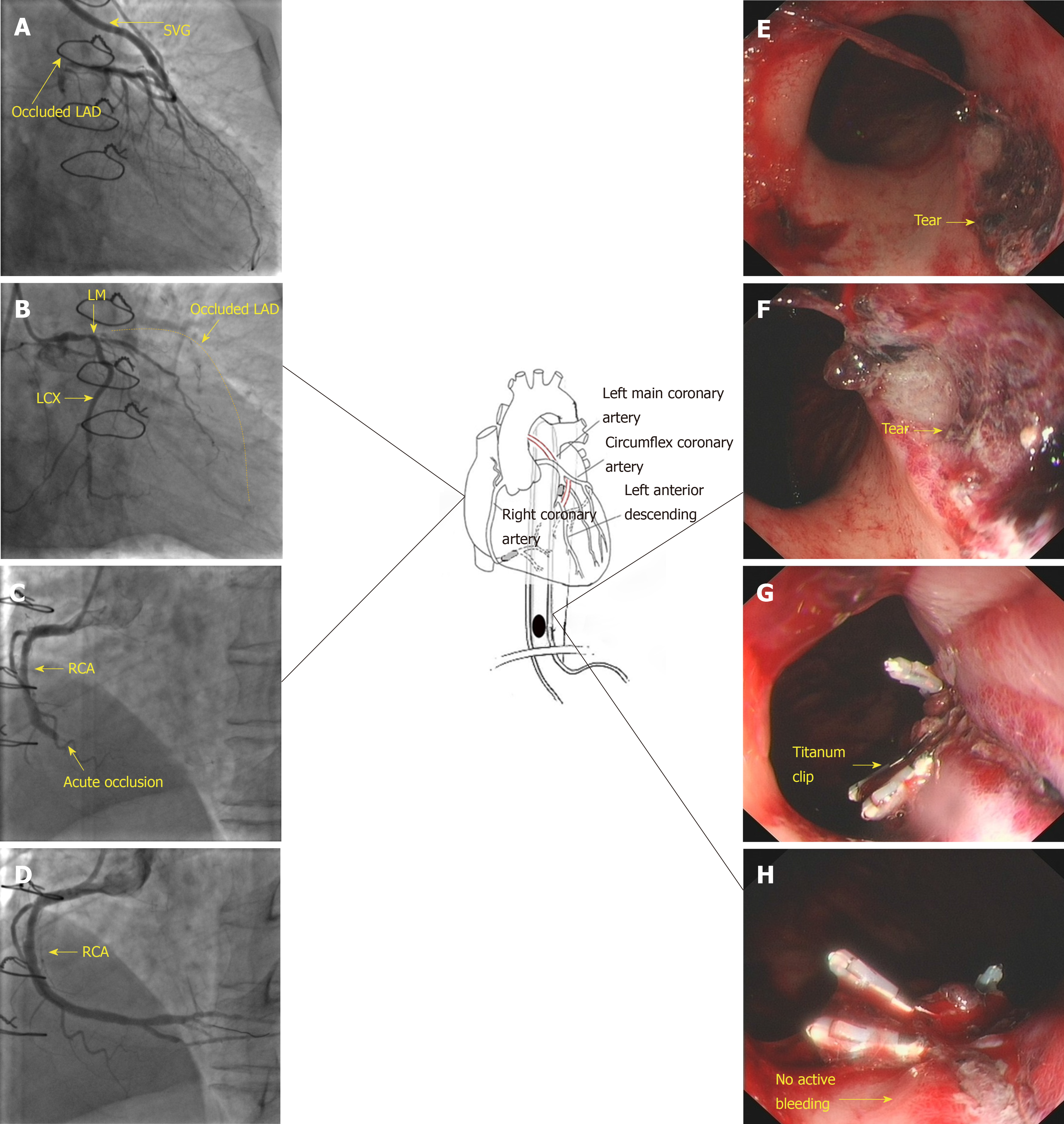
Figure 2 Coronary and esophageal diseases of the patient and subsequent treatments.
A: Occluded left anterior descending artery (LAD) and saphenous vein graft to the LAD; B: Native left coronary of the patient. The dash line indicates the track of the occluded LAD; C: Acute occlusion of the right coronary artery (RCA); D: Post-stenting RCA; E and F: Representative superficial mucosal tear (arrow) due to Mallory-Weiss syndrome; G and H: Hemoclip treatment of the tear and confirmation of no active bleeding. SVG: Saphenous vein graft; LAD: Left anterior descending artery; RCA: Right coronary artery; MWS: Mallory-Weiss syndrome.
- Citation: Du BB, Wang XT, Li XD, Li PP, Chen WW, Li SM, Yang P. Treatment of severe upper gastrointestinal bleeding caused by Mallory-Weiss syndrome after primary coronary intervention for acute inferior wall myocardial infarction: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(24): 4407-4413
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i24/4407.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i24.4407