©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2019; 7(23): 4084-4090
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4084
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4084
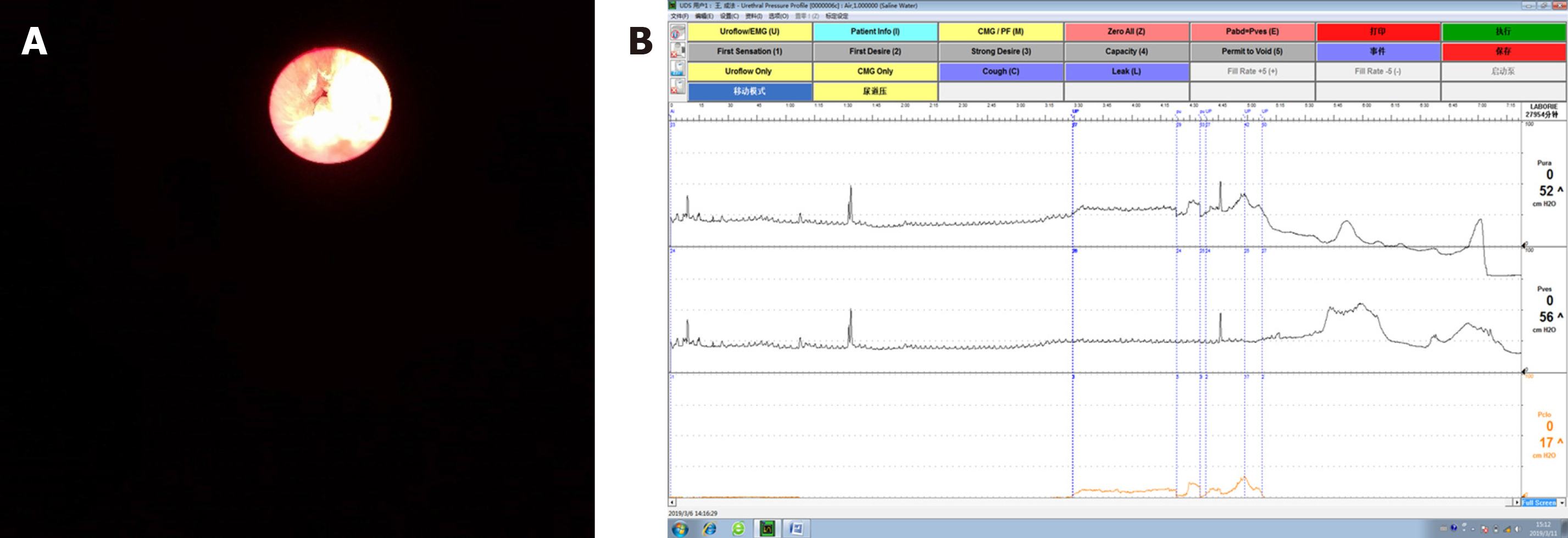
Figure 1 Preoperative examination.
A: Cystoscopy revealed no urethral stricture, and it was observed that the urethra could not close completely; B: Preoperative urethral pressure profilometry showed that the maximum urethral pressure was 52 cmH2O and maximum urethral closure pressure was 17 cmH2O.
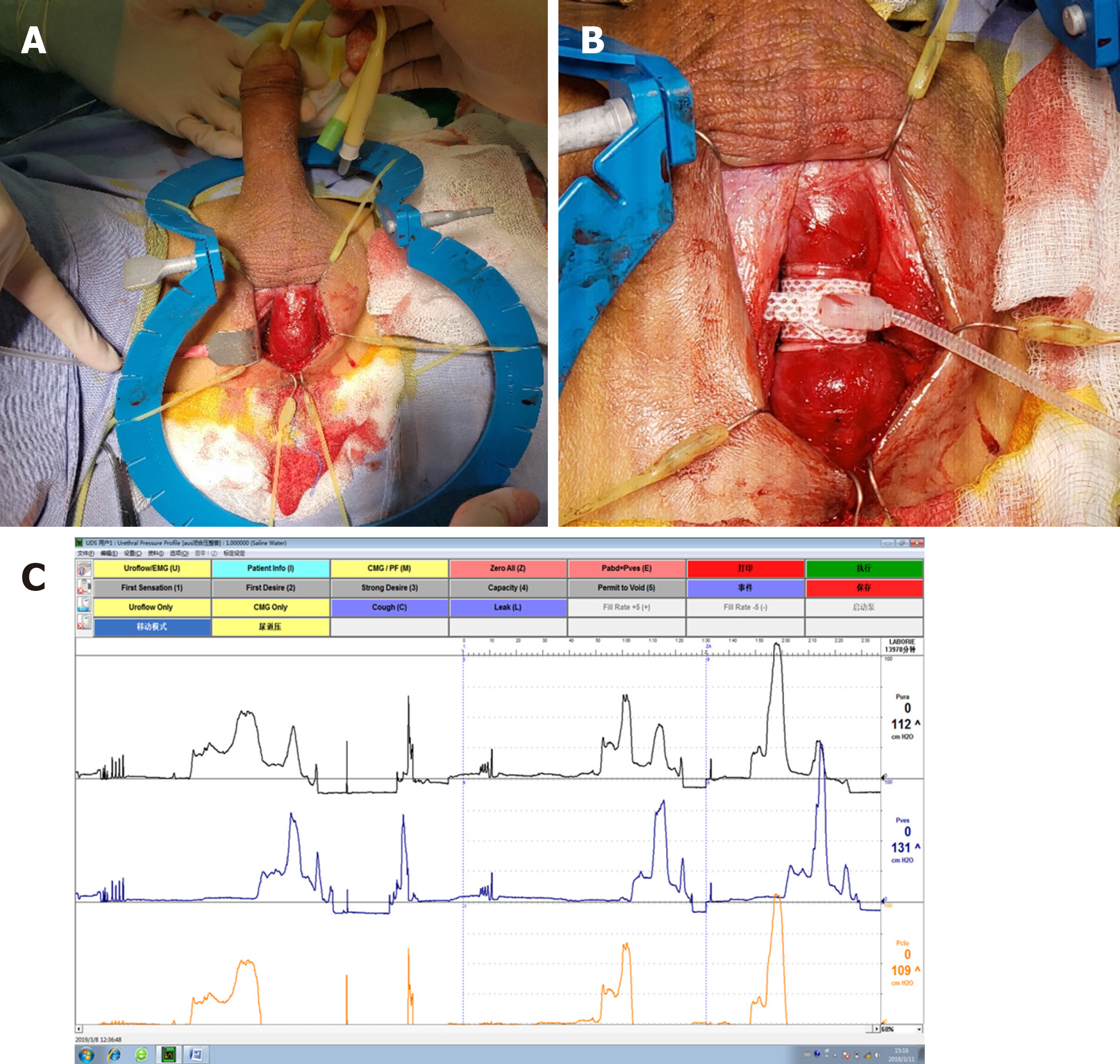
Figure 2 Intraoperative findings.
A: Abnormal erection during operation; B: A 4.5-cm cuff was selected and placed; C: During operation, the maximum urethral pressure (MUP) was 53 cmH2O and maximum urethral closure pressure (MUCP) was 50 cmH2O in the inactivated state; the MUP was 112 cmH2O and MUCP was 109 cmH2O in the activated state.
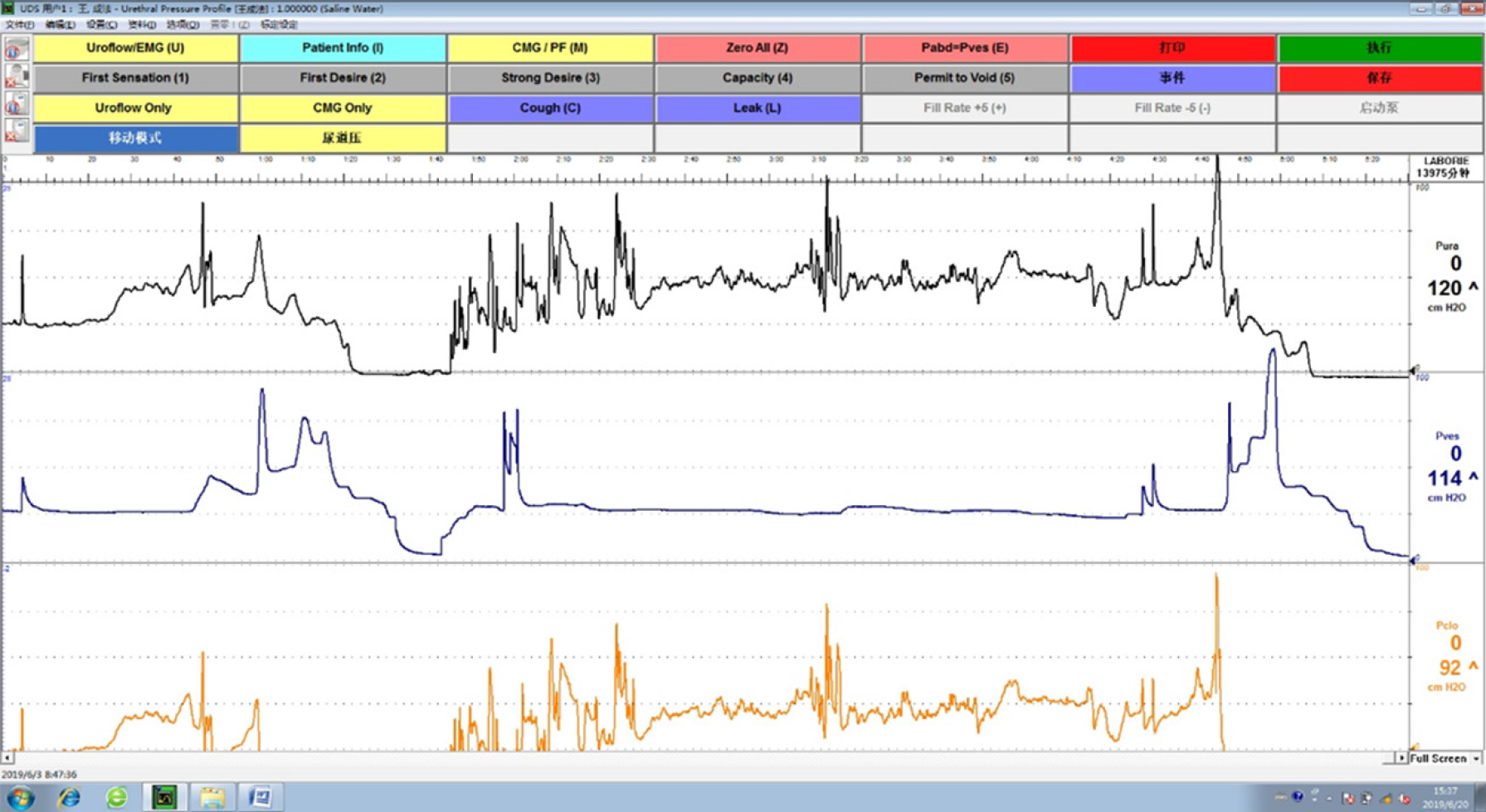
Figure 3 Urethral pressure measured at follow-up.
Six weeks after the operation, the maximum urethral pressure (MUP) was 89 cmH2O and maximum urethral closure pressure (MUCP) was 51 cmH2O in the inactivated state; the MUP was 120 cmH2O and MUCP was 92 cmH2O in the activated state.
- Citation: Meng LF, Liu XD, Wang M, Zhang W, Zhang YG. Urethral pressure profilometry in artificial urinary sphincter implantation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(23): 4084-4090
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i23/4084.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4084