©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2019; 7(22): 3718-3727
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3718
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3718
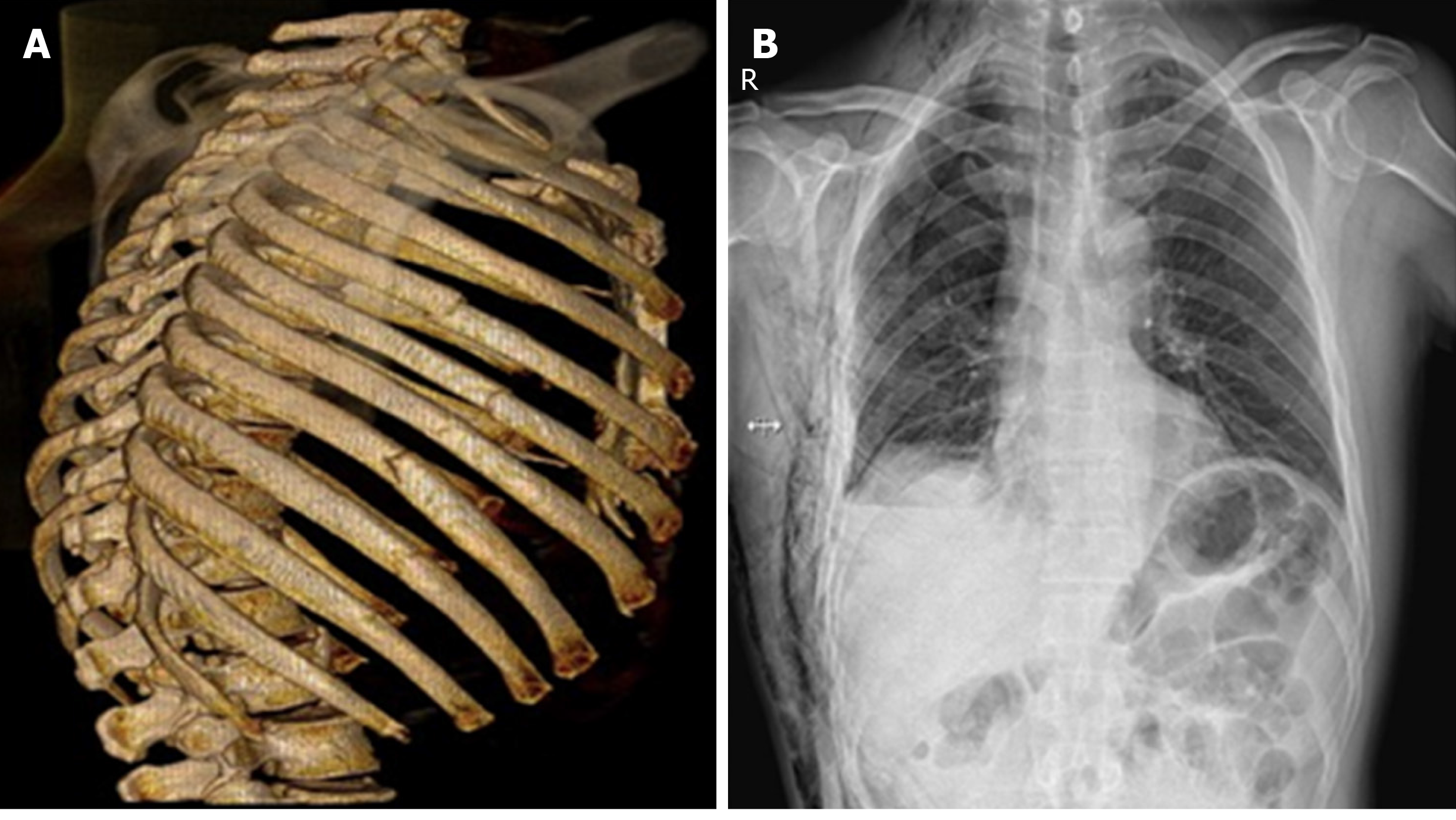
Figure 1 Imaging findings of patients with rib fractures.
A: Three-dimensional reconstruction of the chest computed to mographyimages shows that the patient had rib fractures; B: Chest radiograph indicating the position of the rib.
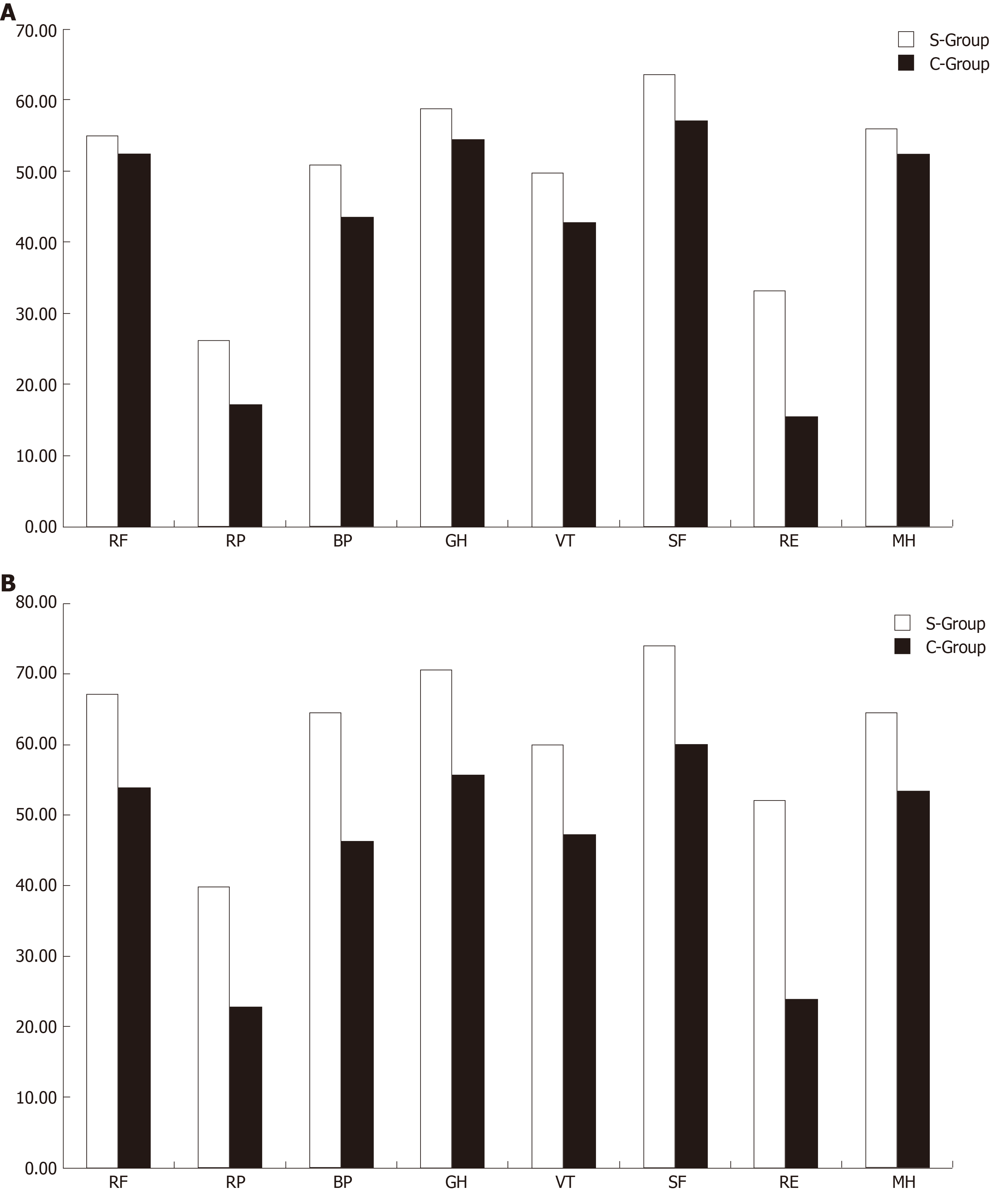
Figure 2 Comparison of the SF-36 scores in each of the dimensions between the two groups after the injury.
A: 3 mo after the injury; B: 6 mo after the injury. S-Group: Surgery group; C-Group: Conservation group; PF: Physical functioning; BP: Bodily pain; RP: Physical role functioning; GH: General health; VT: Vitality; SF: Social functioning; RE: Emotional functioning; MH: Mental health.
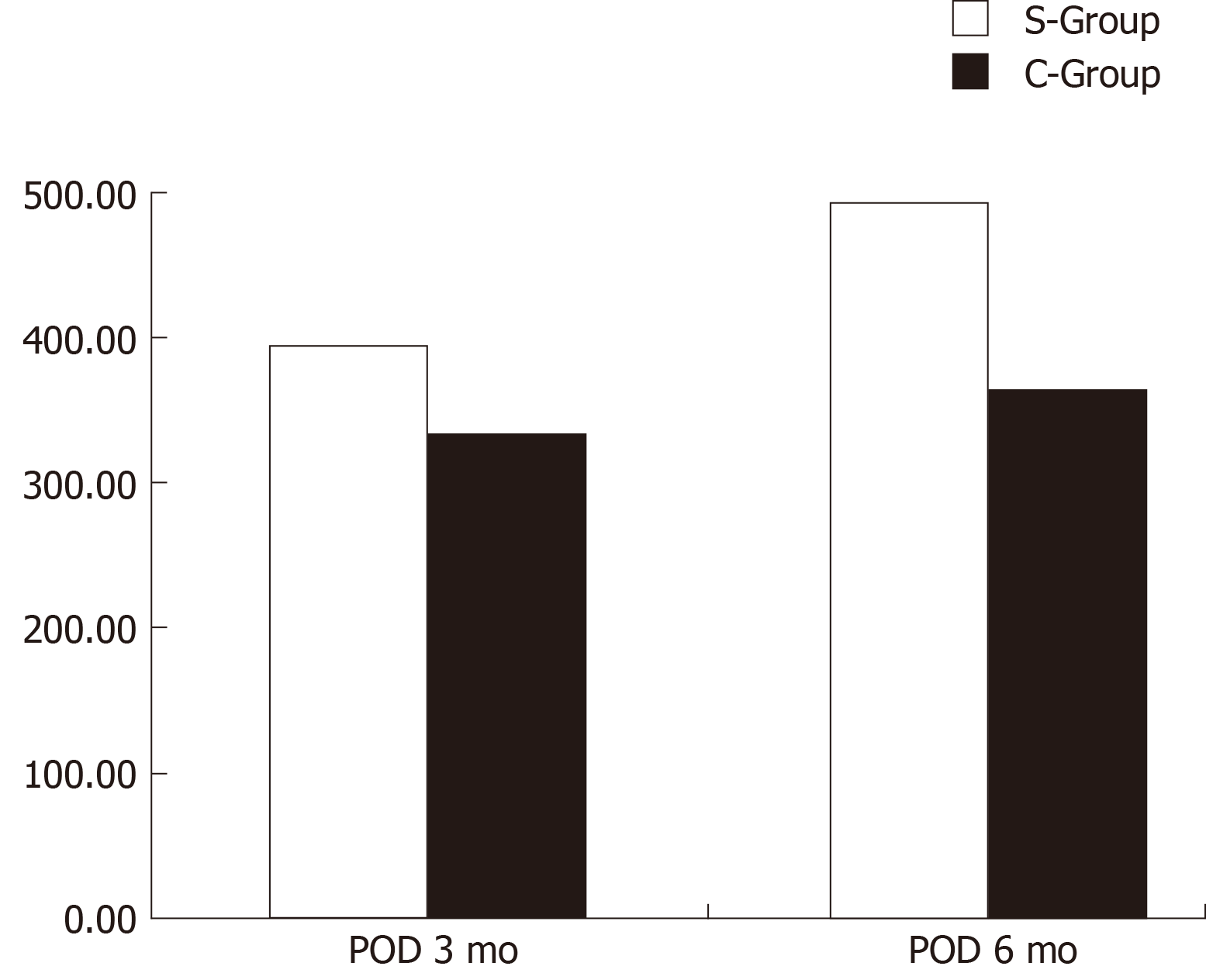
Figure 3 Comparison of total SF-36 scores between the two groups at 3 and 6 mo after surgery/injury.
S-Group: Surgery group; C-Group: Conservation group.
- Citation: Zhang JP, Sun L, Li WQ, Wang YY, Li XZ, Liu Y. Surgical treatment ofpatients with severe non-flail chest rib fractures. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(22): 3718-3727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i22/3718.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3718