©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2019; 7(21): 3583-3589
Published online Nov 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3583
Published online Nov 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3583
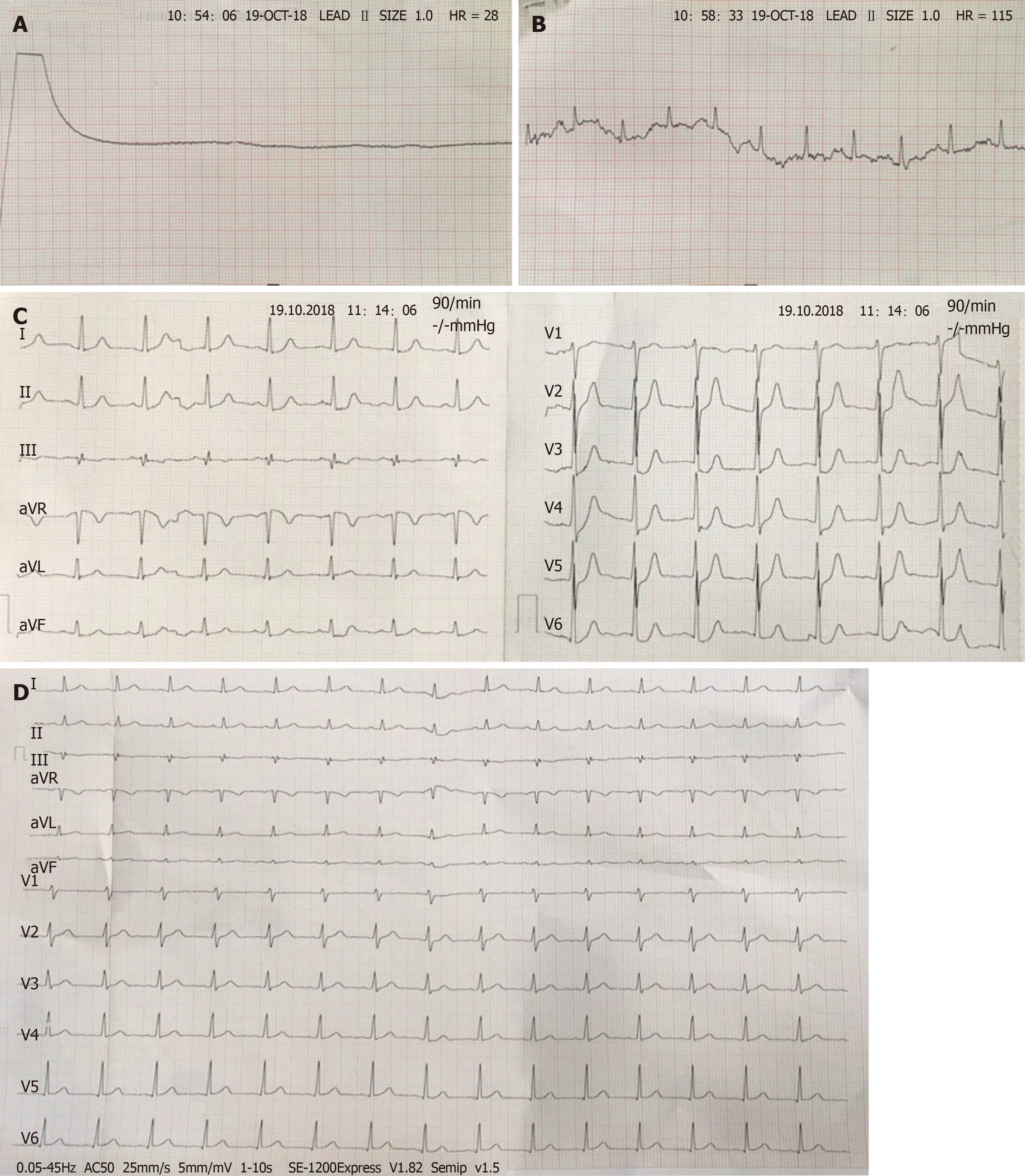
Figure 1 Representative electrocardiograms.
A: Flat line while cardiopulmonary resuscitation; B: Recovery of spontaneous circulation after about 10 min resuscitation; C: Electrocardiogram on admission showing depressed ST-segments in I, II, aVF, and V2-6 leads; D: Normal electrocardiogram parameters 4 hr later.
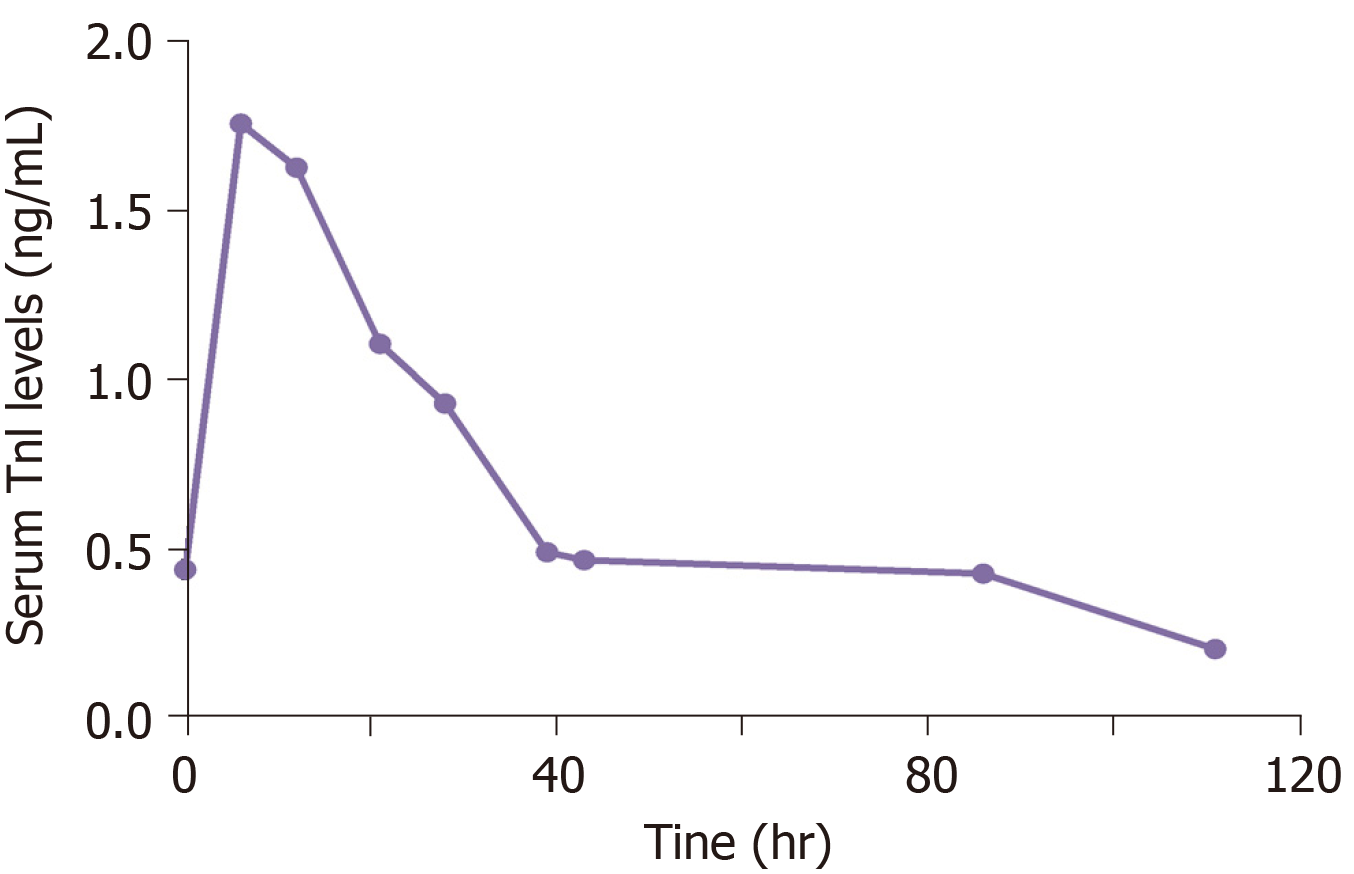
Figure 2 Serum troponin I level on admission.
The levels of troponin I were slightly elevated and reached the highest value at 6 hr (1.76 ng/mL) and then gradually decreased to normal range.
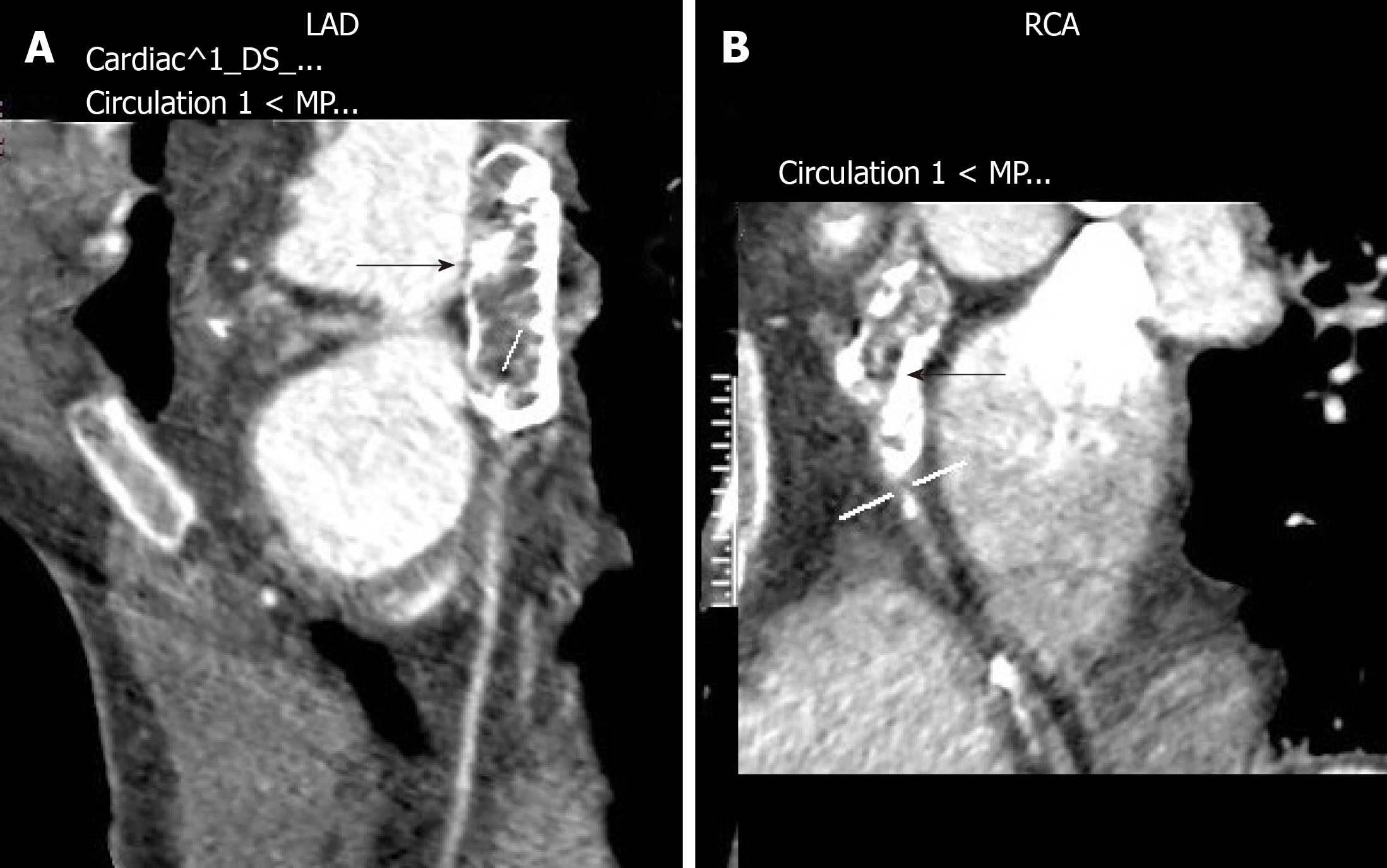
Figure 3 Coronary computed tomography angiography images from a 29-year-old man with a history of Kawasaki disease at age 5 year and coronary artery aneurysms.
A: Aneurysmal dilation of left anterior descending with extensive calcification (black arrow); B: Aneurysmal dilation of right coronary artery with extensive calcification (black arrow). LAD: Left anterior descending; RCA: Right coronary artery.
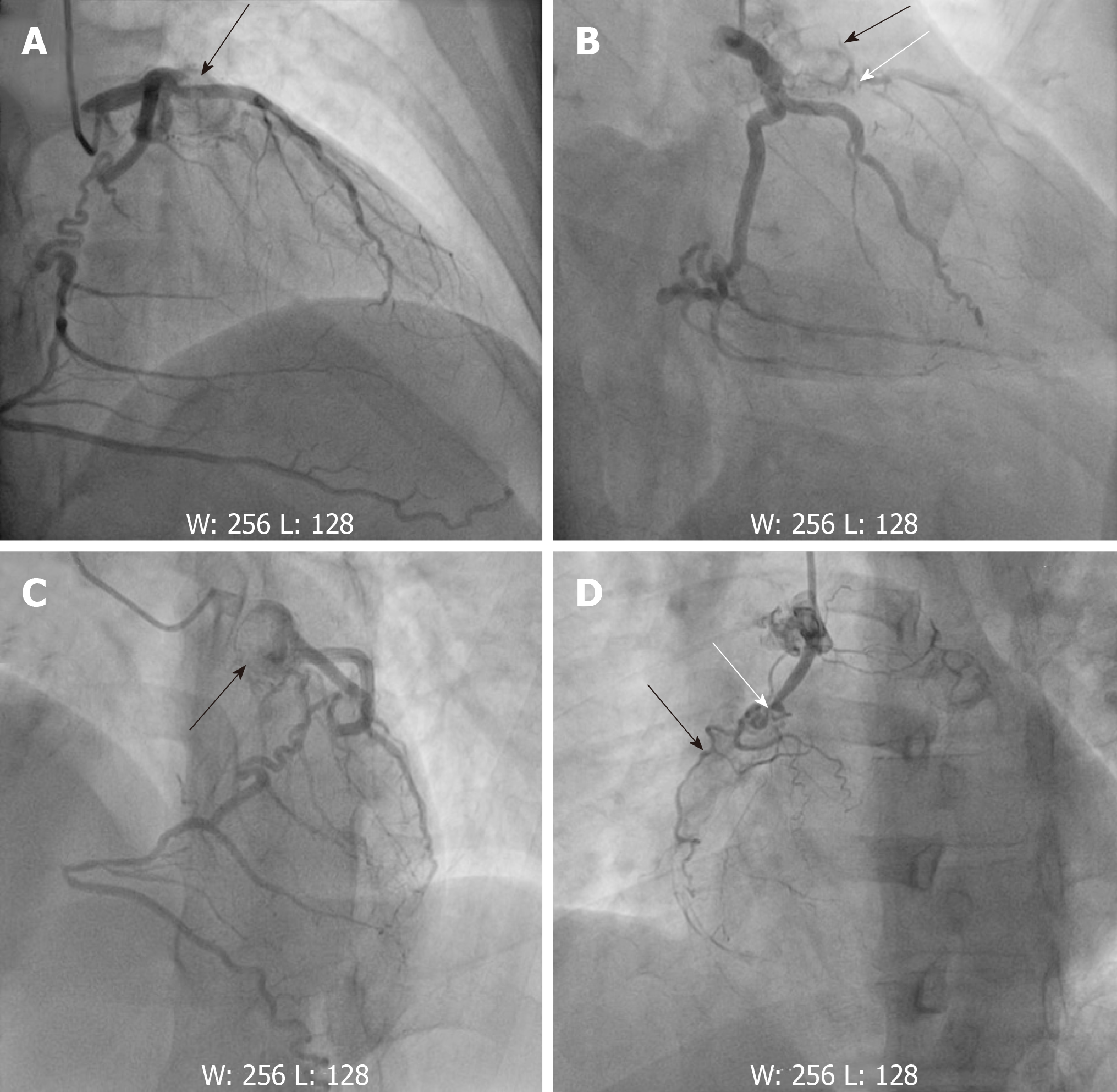
Figure 4 Angiography images.
A, B, C: Showing giant aneurysms (black arrows) of the proximal left anterior descending with subtotal occlusion (white arrows); D: Showing the proximal and mid right coronary artery with chronic total occlusion (white arrows). The right coronary artery received left-to-right epicardial collateral circulation from left circumflex coronary artery.
- Citation: Zhu KF, Tang LJ, Wu SZ, Tang YM. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in a young adult survivor with sequelae of childhood Kawasaki disease: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(21): 3583-3589
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i21/3583.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3583