©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2019; 7(17): 2519-2525
Published online Sep 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i17.2519
Published online Sep 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i17.2519
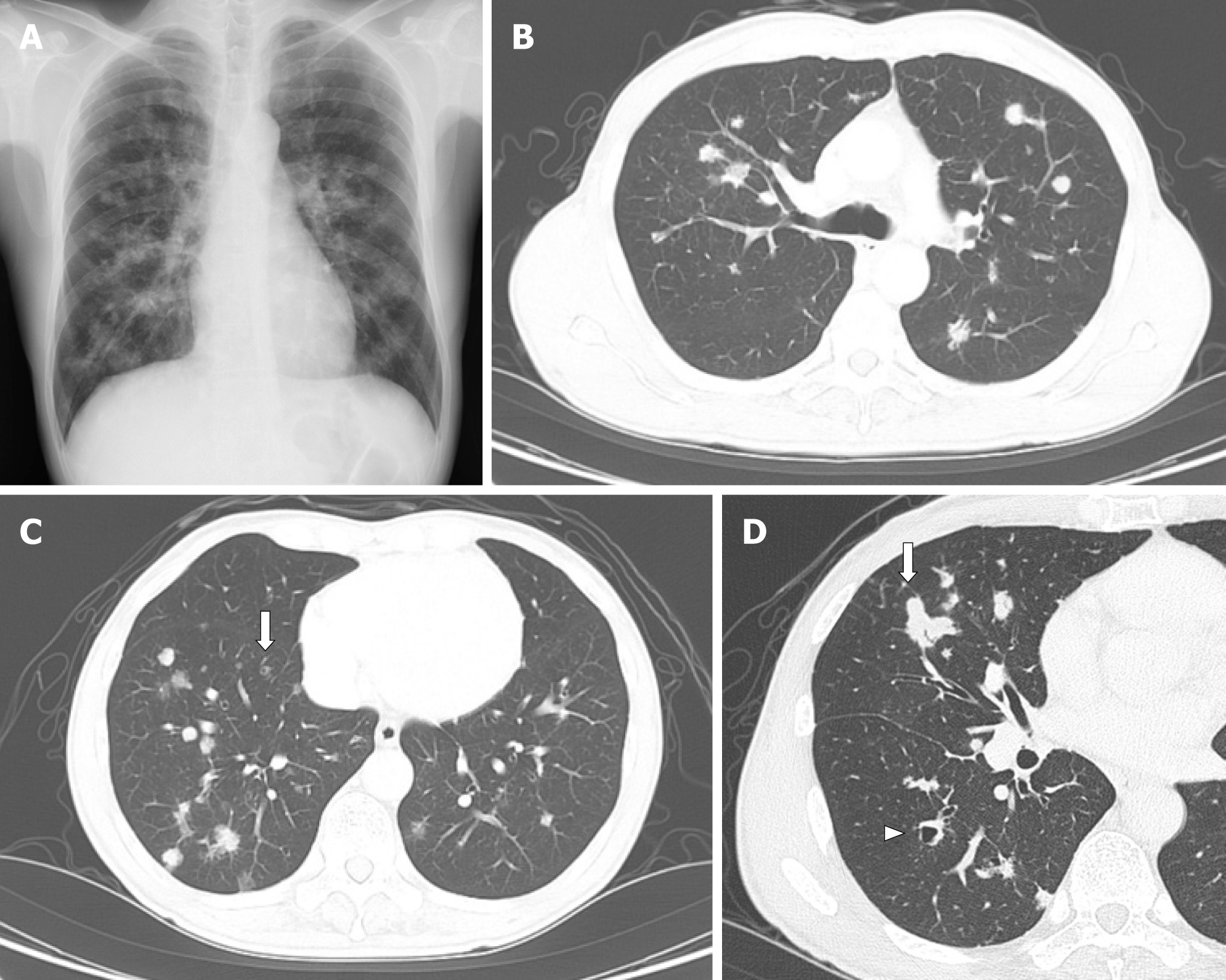
Figure 1 Radiological findings at the initial diagnosis.
A: Chest X-ray at the diagnosis showed multiple nodules in bilateral lung fields; B and C: Chest computed tomography showed multiple nodules, adjacent to the pleura or bronchus, predominantly in the right lower lobe. Some small nodules showed cystic formation (arrow); D: Largest nodule was in the right middle lobe; 22 mm dia. (arrow). Arrowhead: A dilated bronchus, but not a cystic nodule.
Figure 2 Histopathological findings obtained from a nodule in right lower field.
A and B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining showing abnormal cells with notched nuclei with the infiltration of many eosinophils; C and D: Abnormal cells were positive for CD1a and S-100.
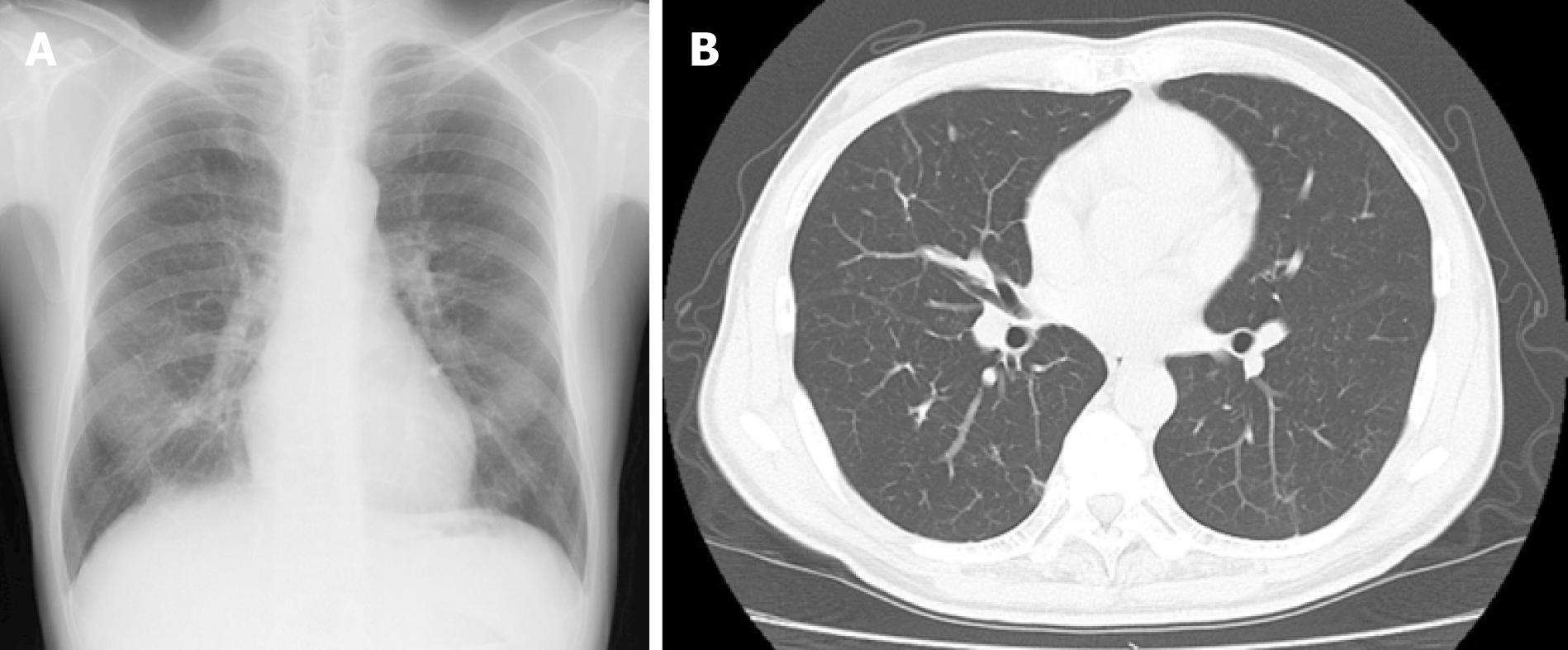
Figure 3 Radiological findings at 6 mo after the patient quit smoking.
A: Chest X-ray; B: Computed tomography scan.
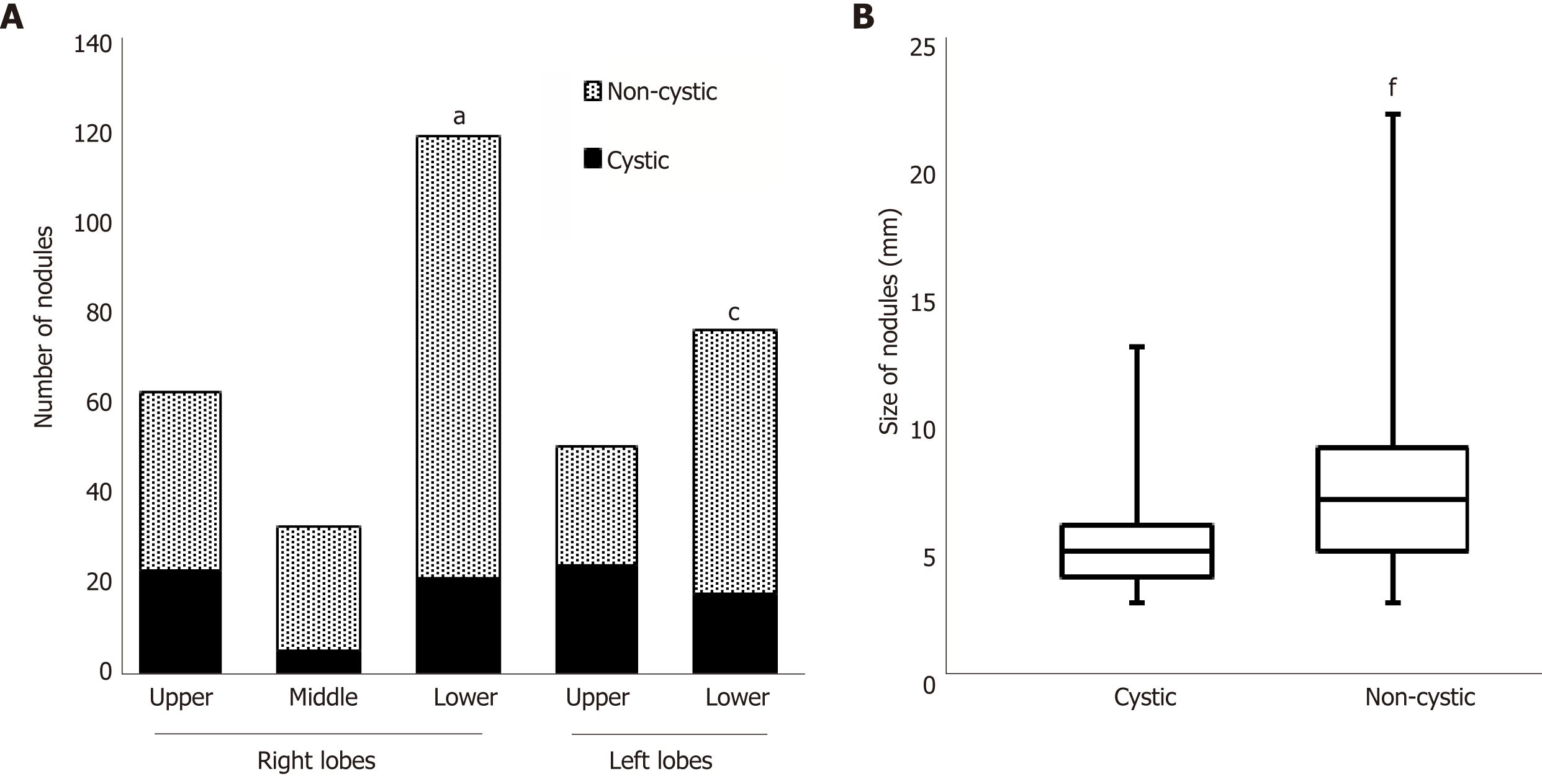
Figure 4 Numbers and sizes of cystic and non-cystic nodules.
A: Number of nodules in each lobe. The prevalence of cystic nodules is compared. aP<0.01 vs the right upper lobe, cP < 0.01 vs the left upper lobe; B: Sizes of the nodules. The data summarize the results of all lung lobes. fP < 0.0001 vs the cystic nodules.
- Citation: Kanaji N, Tokunaga Y, Ishikawa R, Watanabe N, Kadowaki N. Characteristics of multiple nodules in a patient with pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(17): 2519-2525
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i17/2519.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i17.2519