©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2019; 7(14): 1892-1898
Published online Jul 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1892
Published online Jul 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1892
Figure 1 Findings from chest computed tomography scan at the lung window level from our patient.
The characteristic nodulocystic pattern was detected at the time of pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis diagnosis. A: Coronal scanning; B Cross-sectional scanning; C: Coronal scanning at 3 mo after smoking cessation, the lung nodulocystic lesions had disappeared significantly; and D: Cross-sectional scanning at 3 mo after smoking cessation, the lung nodulocystic lesions had disappeared significantly.
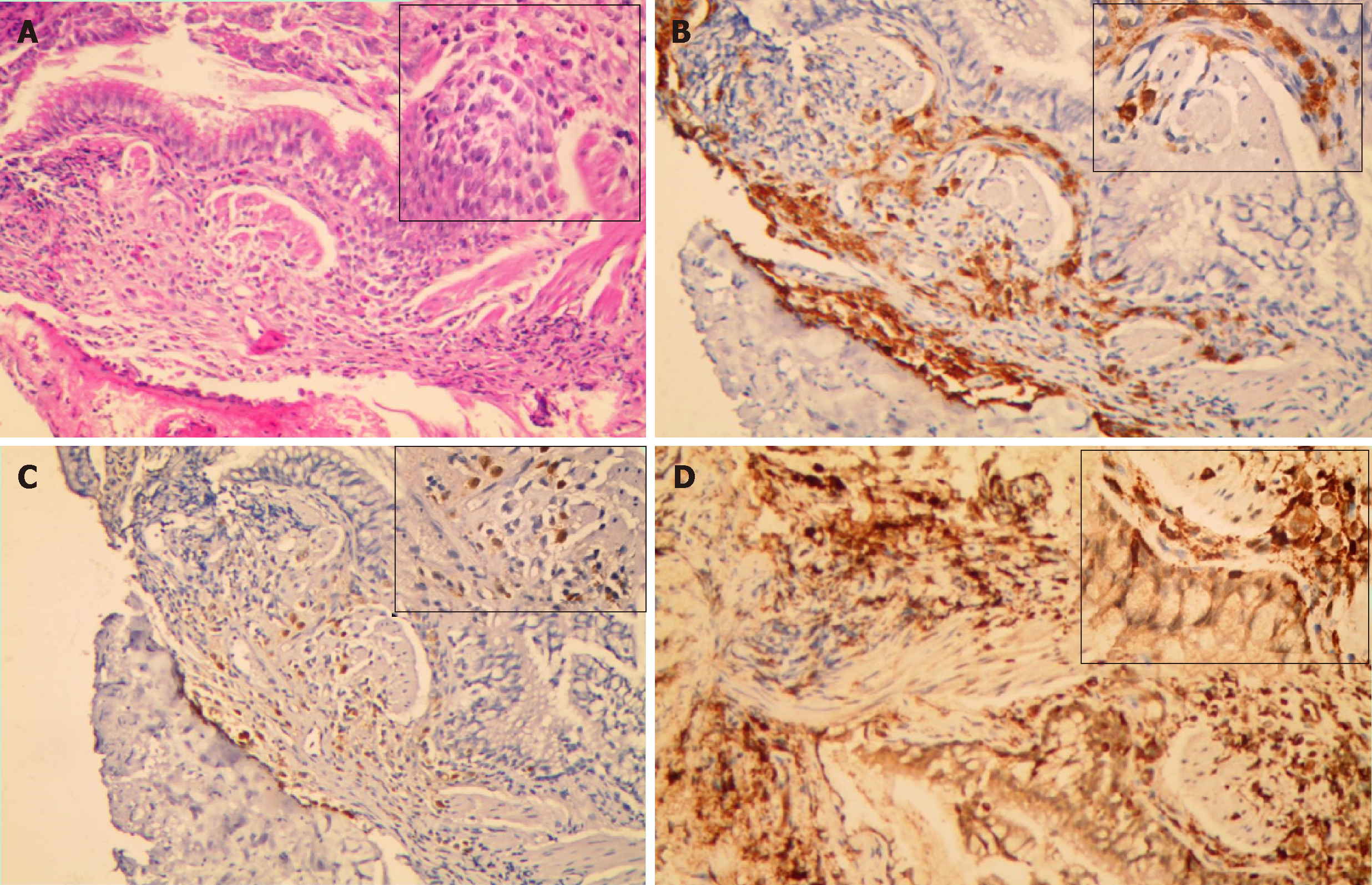
Figure 2 Findings from pathological analyses of lung biopsy from our patient.
A: Haematoxylin-eosin staining showed a large number of typical Langerhans cells in the lung tissue, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, irregular nuclei, and prominent folds and grooves; B: Langerhans cells showed positive staining for CD1a; C: Langerhans cells showed positive staining for S-100; D: Langerhans cells showed positive staining for CD68.
- Citation: Wang FF, Liu YS, Zhu WB, Liu YD, Chen Y. Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis in adults: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(14): 1892-1898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i14/1892.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1892