©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2018; 6(8): 176-182
Published online Aug 16, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i8.176
Published online Aug 16, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i8.176
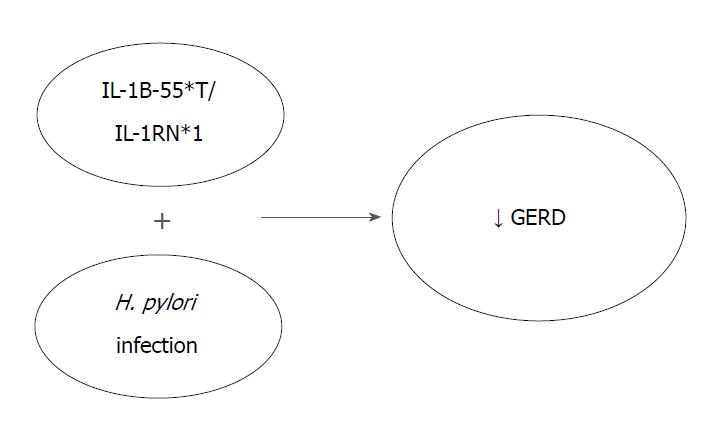
Figure 1 The presence of the genes IL-1B and IL-1RN combined with Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with hypochlorydria and thus reducing the risk for gastroesophageal reflux disease.
GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; IL-1B-511*T: Interleukin-1 beta T allele; IL-1RN: Gene encoding for a non-signaling molecule IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra).
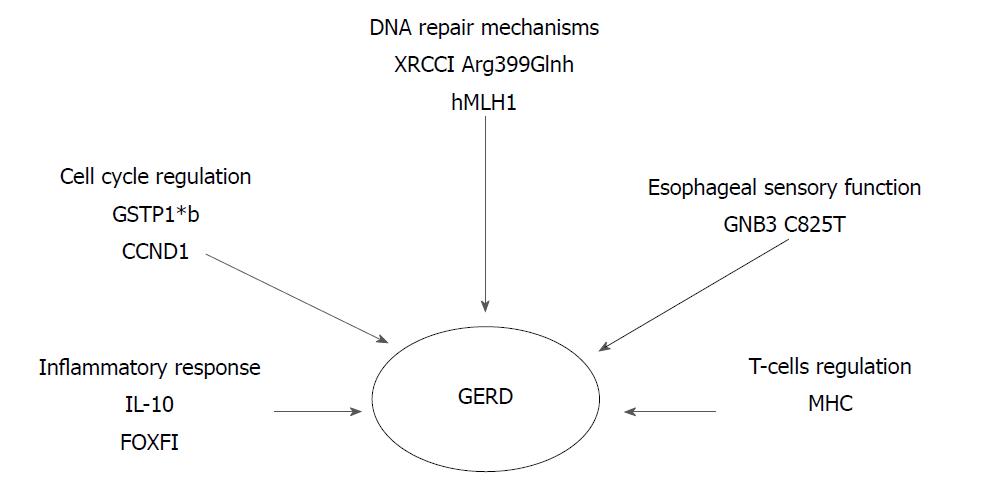
Figure 2 Susceptible risk genes for gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Their increased or reduced (DNA repair genes) expression alters different biological pathways. GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; IL-10: Anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin 10; FOXF1: Forkhead BOX F1; GSTP1*b: Glutathione- S- transferases b allele; CCND1: Cyclin D1 gene; XRCC1: X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 1; Hmlh1: Humal homolog of the E. coli DNA mismatch repair gene mutL; GNB3: Guanine nucleotide binding protein beta polypeptide 3; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex.
- Citation: Argyrou A, Legaki E, Koutserimpas C, Gazouli M, Papaconstantinou I, Gkiokas G, Karamanolis G. Risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease and analysis of genetic contributors. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(8): 176-182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i8/176.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i8.176