©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 16, 2016; 4(12): 385-389
Published online Dec 16, 2016. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v4.i12.385
Published online Dec 16, 2016. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v4.i12.385
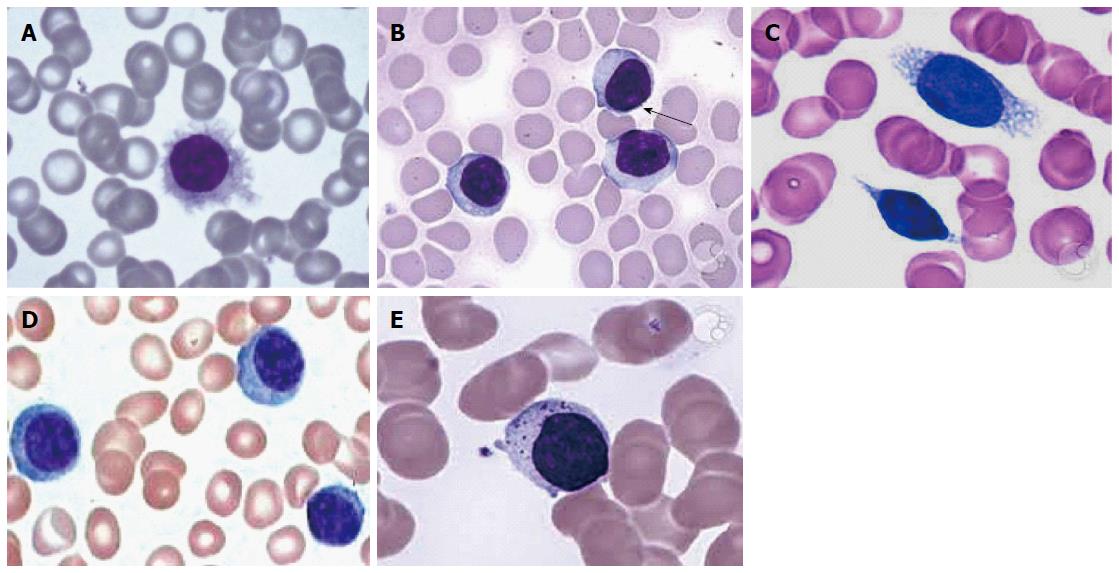
Figure 1 Peripheral blood smear.
A: Hairy cells; B: Prolymphocytes; C: Villous lymphocytes; D: Plasmacytoid lymphocytes; E: Granular lymphocytes.
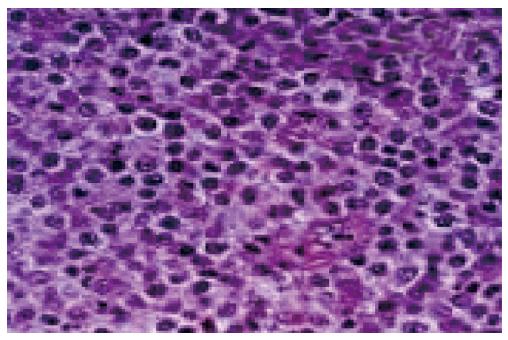
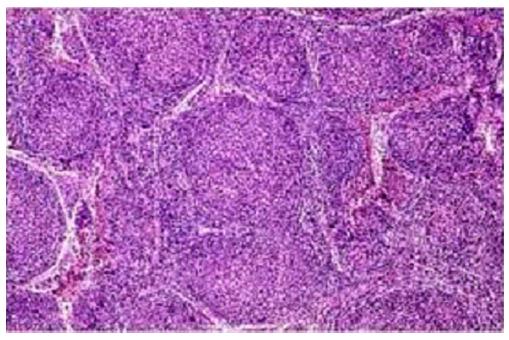
Figure 2 Diffuse large B cell lymphoma showing monotonous population of large neoplastic lymphoid cells.
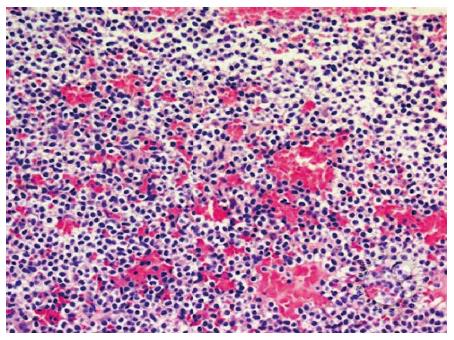
Figure 3 Small to medium sized lymphocytic infiltrate.
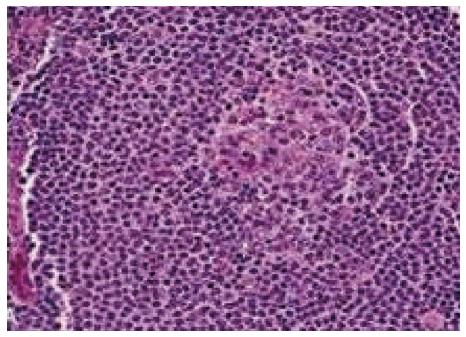
Figure 4 Splenic white pulp are replaced by small neoplastic lymphocytes.
Figure 5 Neoplastic lymphoid cells arranged predominantly in follicular pattern.
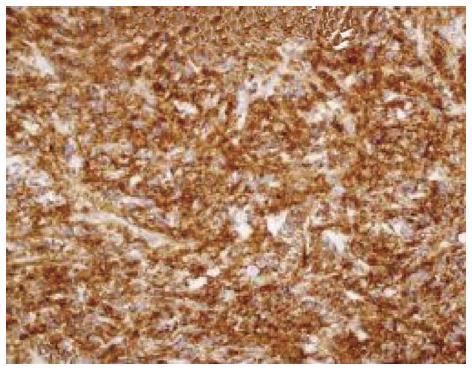
Figure 6 CD20 immunopositivity in neoplastic lymphoid B cells.
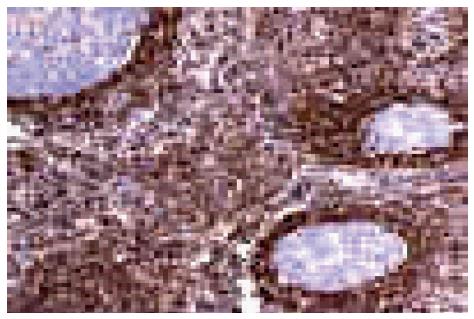
Figure 7 B cell lymphoma-2 expression in follicular lymphoma.
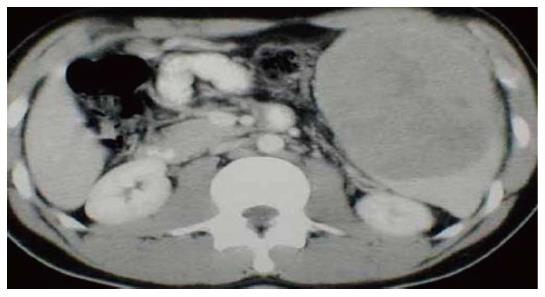
Figure 8 Computed tomography showing massive splenomegaly on ultrasonography.
- Citation: Ingle SB, Hinge (Ingle) CR. Primary splenic lymphoma: Current diagnostic trends. World J Clin Cases 2016; 4(12): 385-389
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v4/i12/385.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v4.i12.385