©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2014; 2(9): 426-431
Published online Sep 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i9.426
Published online Sep 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i9.426
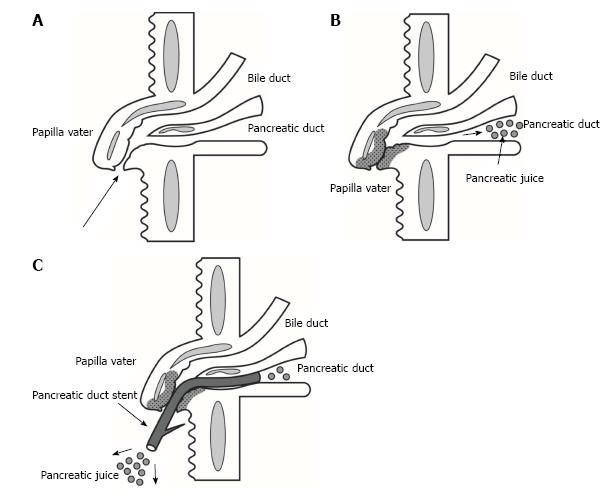
Figure 1 Pancreatic duct stenting for preventing post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis.
A: Duodenal papilla before cannulation is performed; B: Duodenal papilledema occurs by frequent cannulation manipulation; C: Pancreatic duct stent is placed to regulate the passage of pancreatic juice.
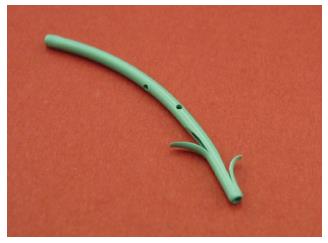
Figure 2 Pancreatic duct stent with the flap in one duodenal side having no flap within the pancreatic duct (Pancreatic duct stent: Geenen®-COOK): Spontaneous dislodgement type.
Figure 3 Pancreatic duct stent with the flap in the pancreatic duct side (Pancreatic duct stent Zimmon®-COOK).
- Citation: Sakai Y, Tsuyuguchi T, Yokosuka O. Clinical usefulness and current problems of pancreatic duct stenting for preventing post-ERCP pancreatitis. World J Clin Cases 2014; 2(9): 426-431
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v2/i9/426.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v2.i9.426