©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2026; 14(1): 115845
Published online Jan 6, 2026. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v14.i1.115845
Published online Jan 6, 2026. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v14.i1.115845
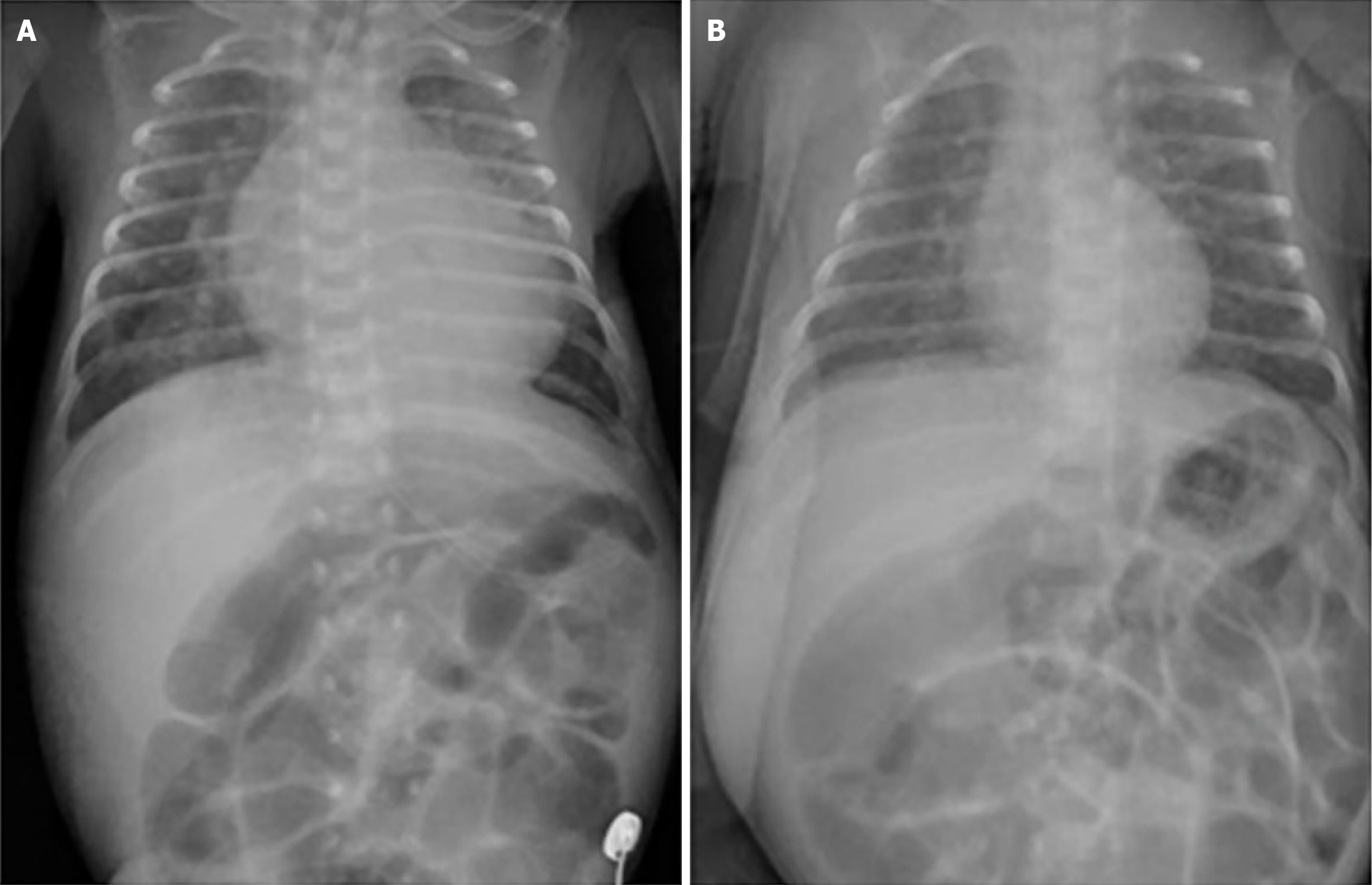
Figure 1 Chest radiography changes before and after levothyroxine treatment.
A: Admission chest radiograph (2 days before levothyroxine) showed cardiomegaly and pulmonary congestion; B: Post-levothyroxine chest radiograph revealed marked improvement.
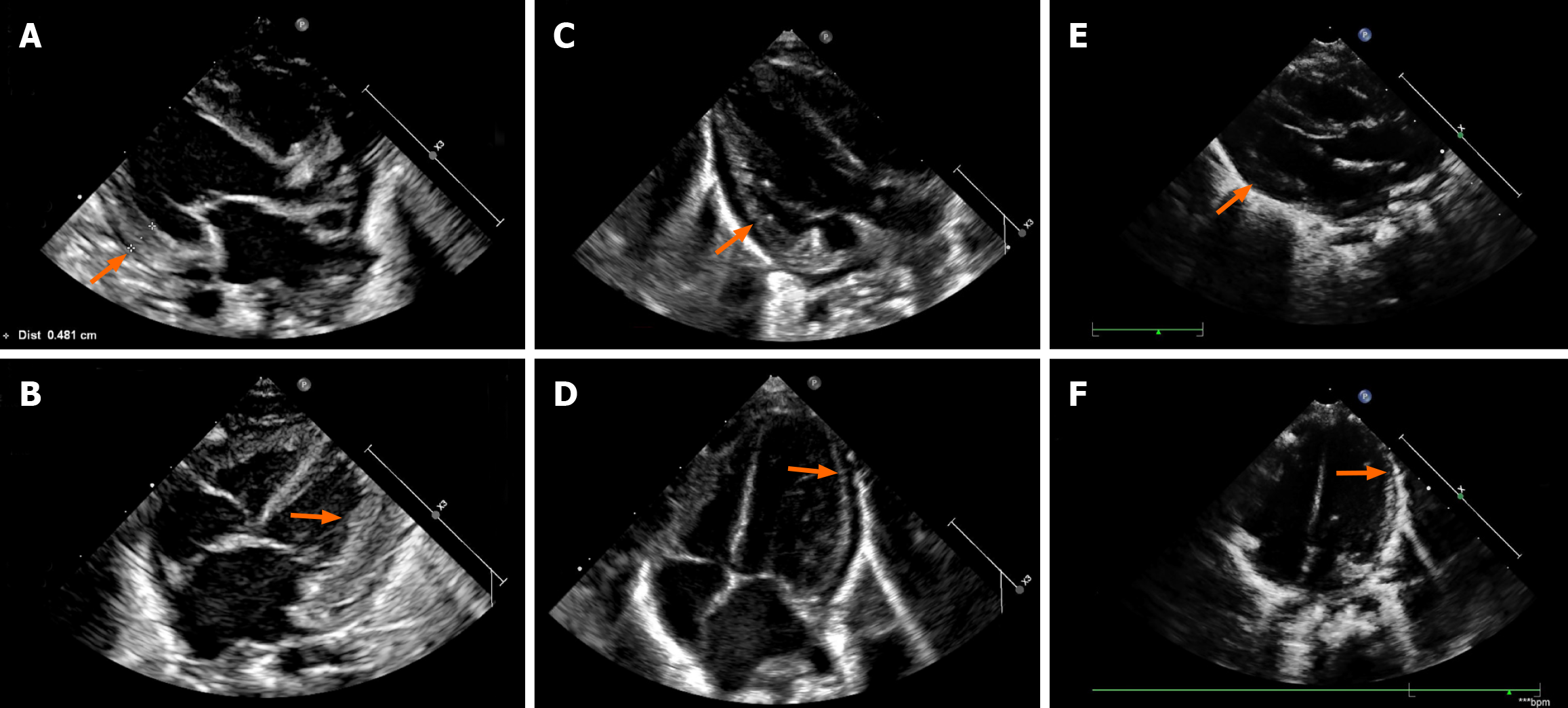
Figure 2 Cardiac color doppler ultrasound changes during levothyroxine treatment.
A and B: Cardiac ultrasound (pre-levothyroxine and 2 days post-levothyroxine) revealed left ventricular hypertrophy and left heart enlargement (orange arrows); C and D: Ultrasound (29 days post-levothyroxine) showed improvement in left heart size and left ventricular hypertrophy (orange arrows); E and F: Ultrasound (92 days post-levothyroxine) showed normalized cardiac structure (orange arrows).
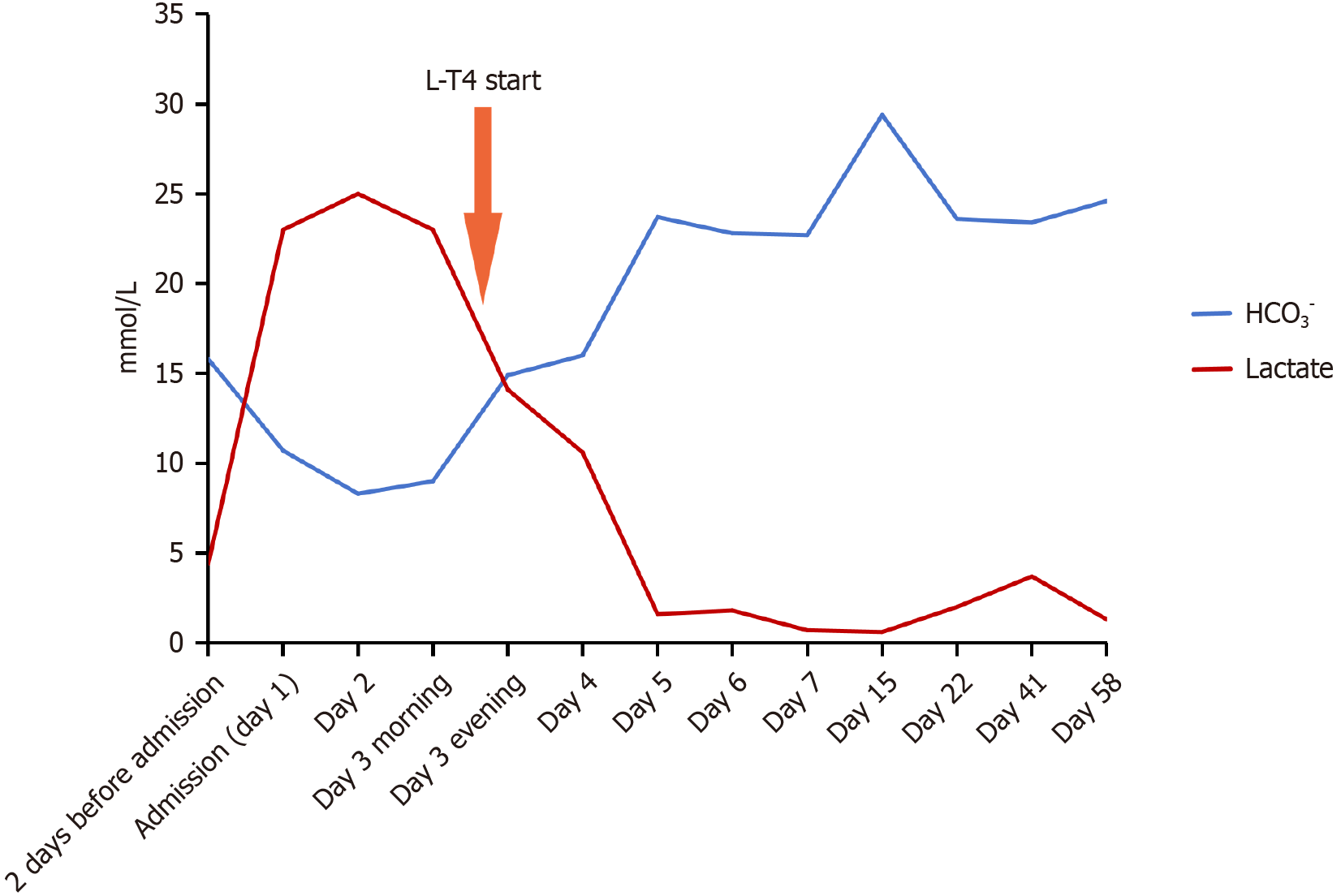
Figure 3 Lactate and bicarbonate levels before and after levothyroxine treatment.
Lactate levels rose progressively post-admission and declined following levothyroxine treatment. Bicarbonate levels trended inversely to lactate. L-T4: Levothyroxine; HCO3-: Bicarbonate.
- Citation: Chen HJ, Li J, Xu XM, Zhang B, Cheng BC, Shi J. Preterm heart failure and refractory lactic acidosis caused by congenital hypothyroidism: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2026; 14(1): 115845
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v14/i1/115845.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v14.i1.115845