©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2025; 13(26): 108052
Published online Sep 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i26.108052
Published online Sep 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i26.108052
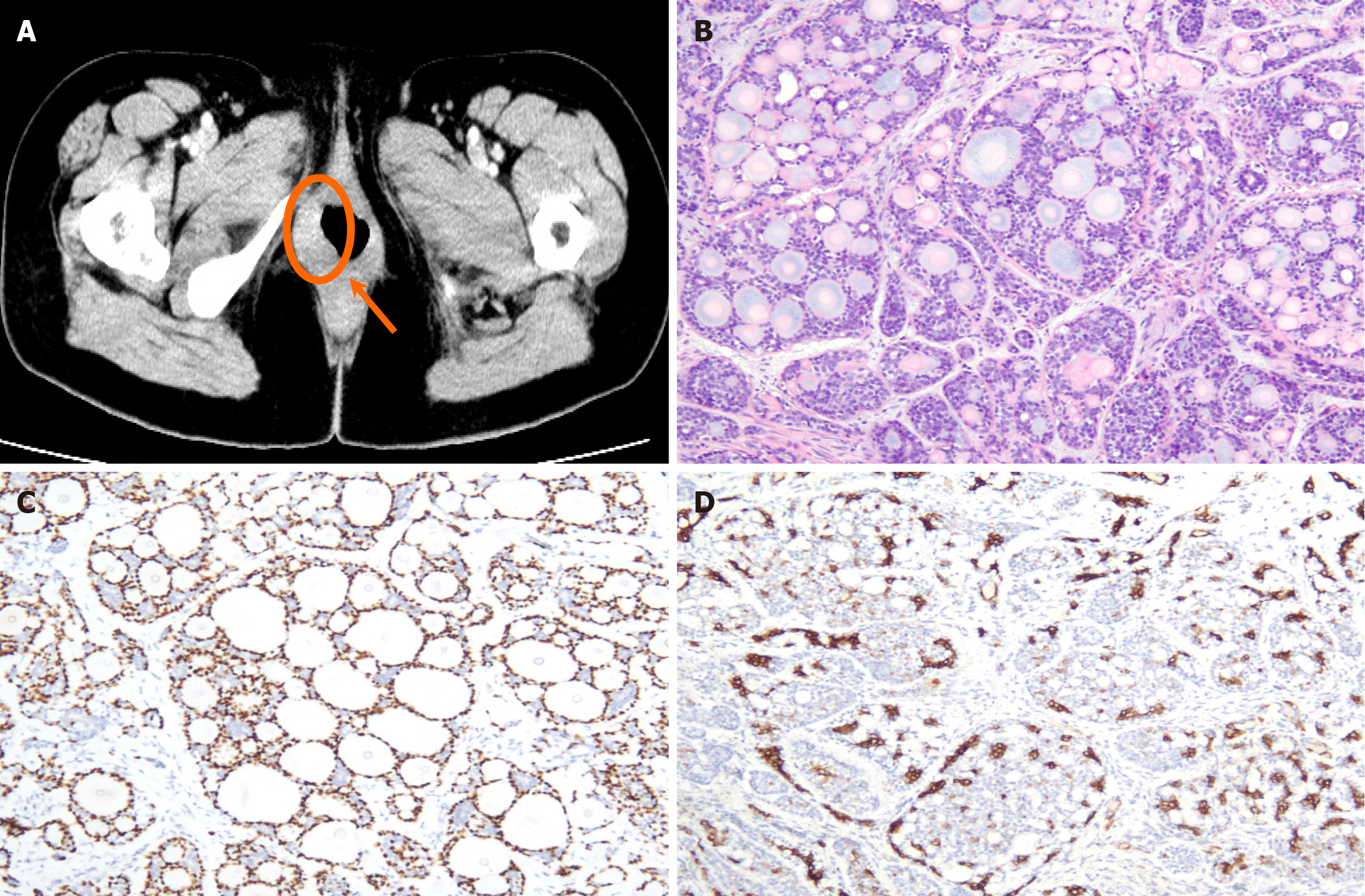
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced pelvic computed tomography imaging and pathological images of case 1.
A: Pelvic Computed tomography with IV contrast revealed right-side asymmetry in the vulvar region, described as a 1.8 cm × 1.5 cm rounded, uneven reinforcement area with blurred margins; B: Pathological images of hematoxylin and eosin-stained samples showing carcinoma with myoepithelial components. Neoplastic cells with mildly enlarged nuclei were noted, and these cells formed irregular papillary or tubular structure (hematoxylin and eosin × 100); C: P63; D: CK7 revealed diffusely positive staining (EnVision × 100).
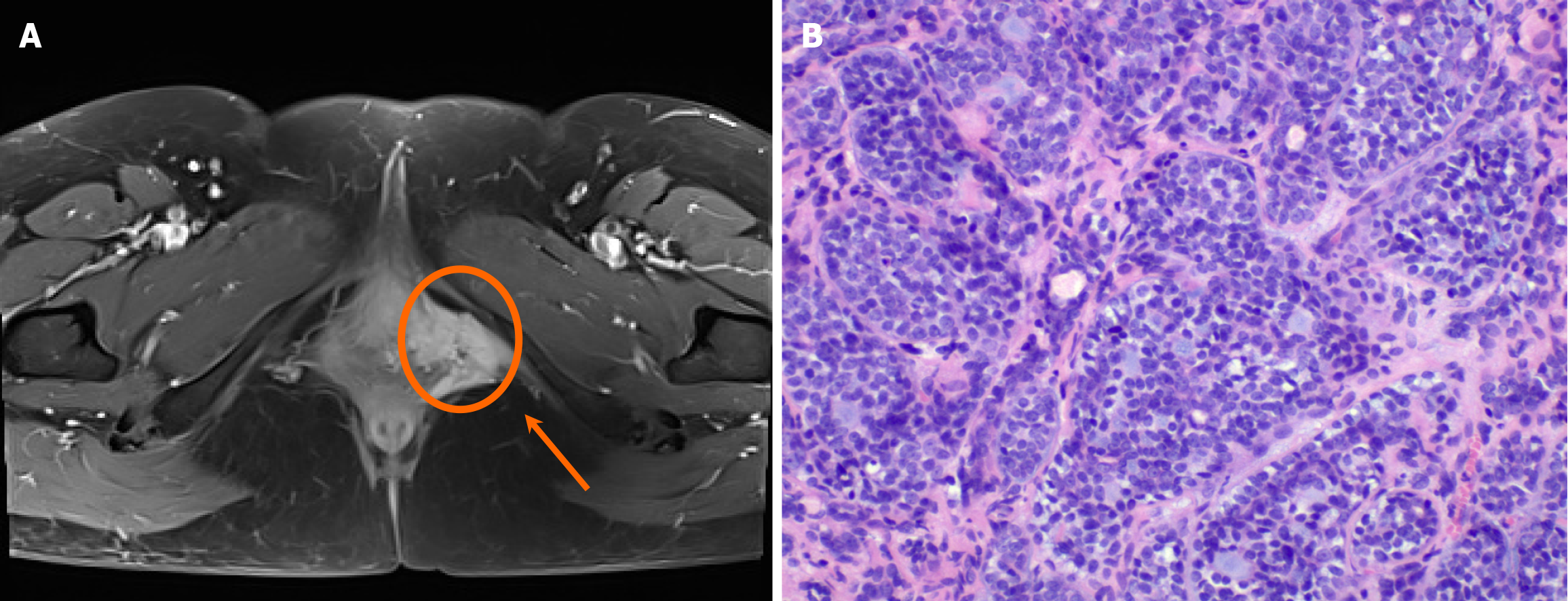
Figure 2 Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging and pathological images of case 2.
A: Enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance revealed left-side asymmetry in the vulvar region, described as a 3 cm × 3 cm unrounded, uneven reinforcement area with blurred margins; B: Pathological images of hematoxylin and eosin-stained samples showing carcinoma with myoepithelial components. Neoplastic cells with mildly enlarged nuclei were noted, and these cells formed irregular papillary or tubular structure (hematoxylin and eosin × 20).
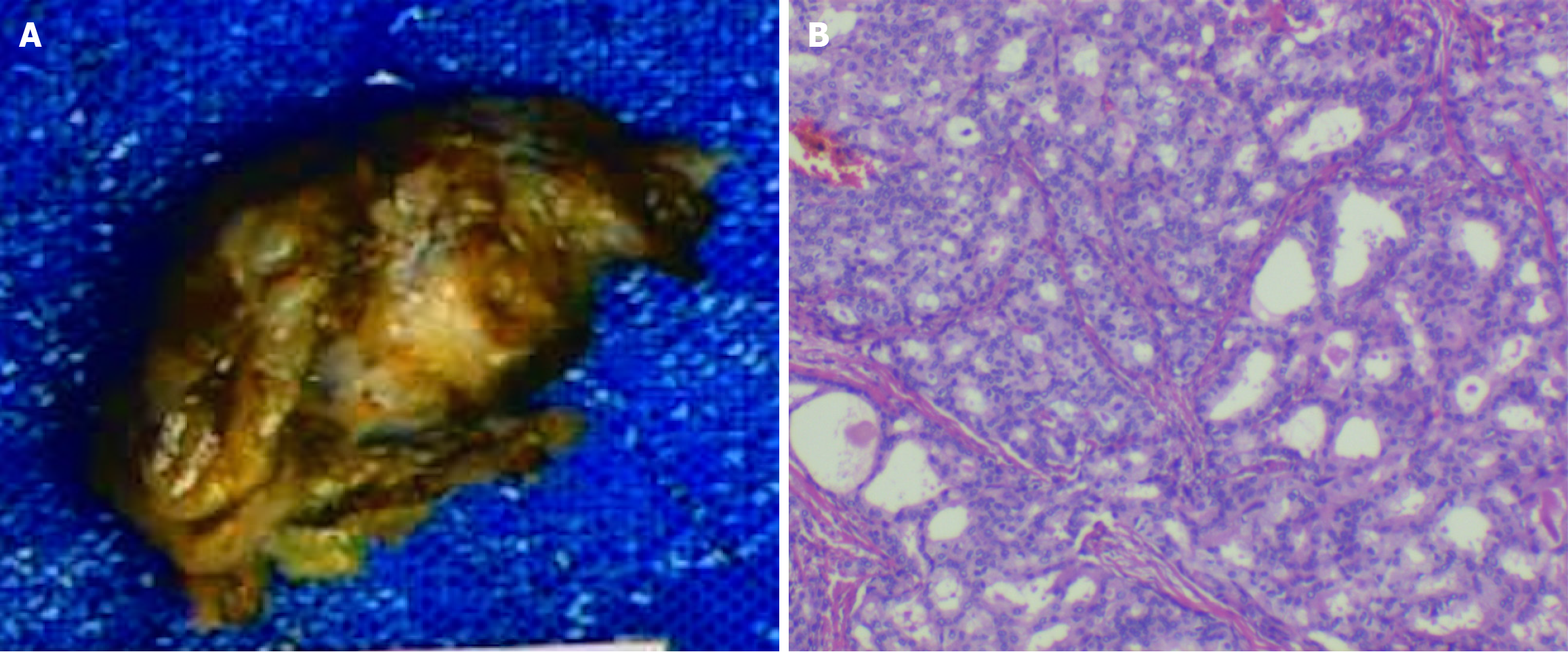
Figure 3 Surgical specimen and pathological images of case 1.
A: Surgical specimen from the vaginal mass; B: Pathological images of hematoxylin and eosin stained samples revealing adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Figure 4 Treatment of case 1 External radiotherapy treatment: The dose was 45 Gy divided into 25 fractions of 1.
8 Gy over the right ingui
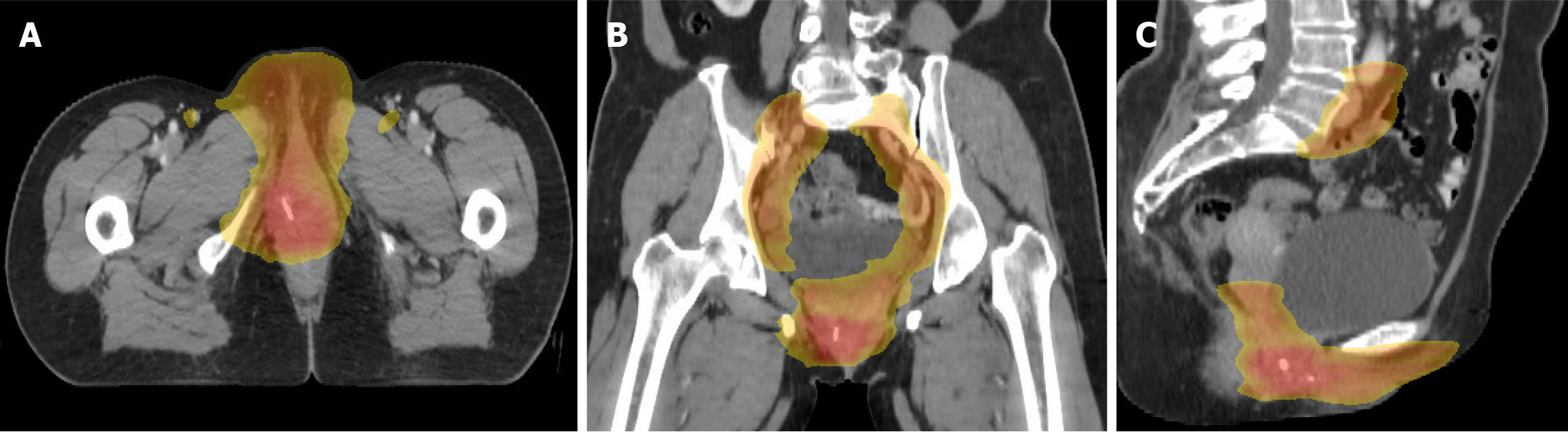
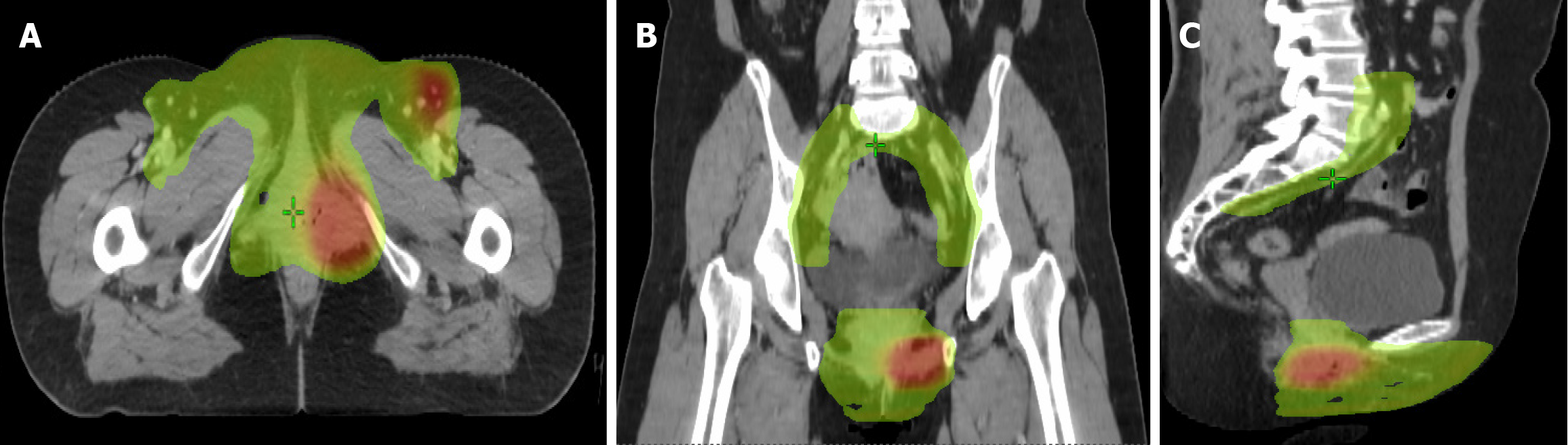
Figure 5 Treatment of case 2 external radiotherapy treatment: The dose was 50.
4 Gy divided into 28 fractions of 1.8 Gy over the inguinal regions and 56 Gy divided into 28 fractions of 2.0 Gy over the tumor bed. A: Transverse image of radiotherapy; B: Coronal image of radiotherapy; C: Sagittal image of radiotherapy.
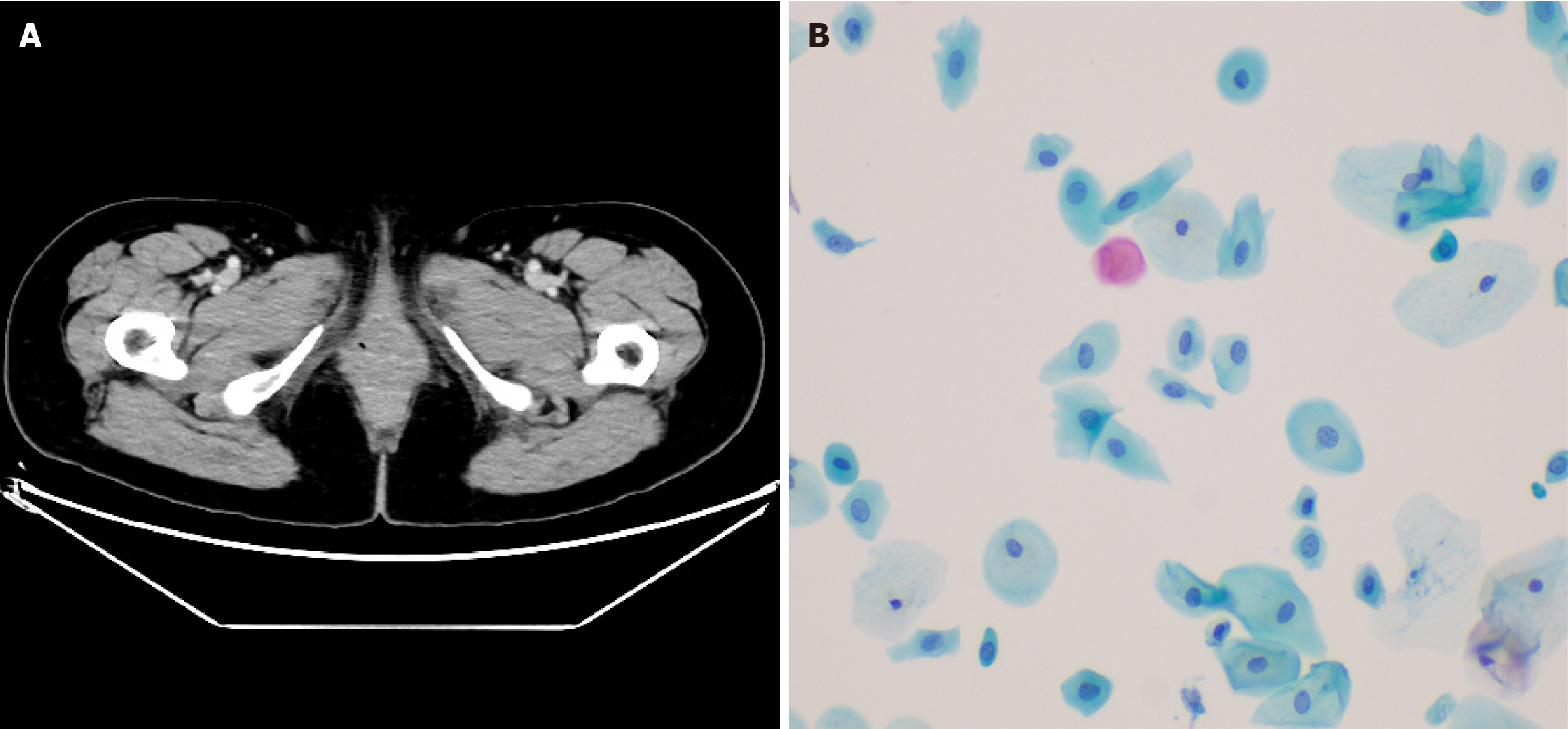
Figure 6 Follow-up of case 1.
A: Images of Pelvic Computed tomography with IV contrast when followed-up 58 months; B: Images of liquid-based cytology testing of the vaginal when followed-up 58 months.
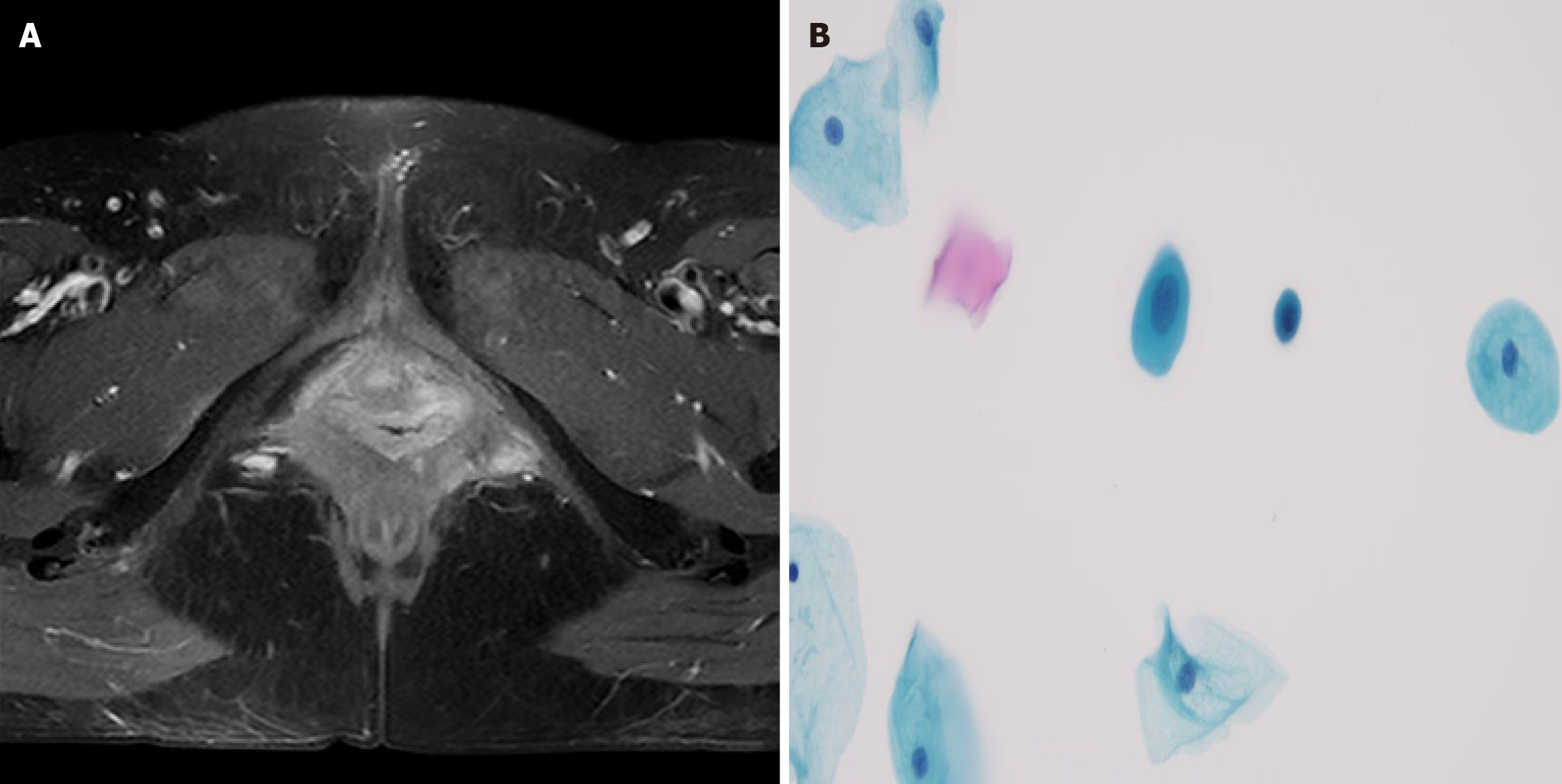
Figure 7 Follow-up of case 2.
A: Image of enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance when followed-up 38 months; B: Images of liquid-based cytology testing of the vaginal when followed-up 38 months.
- Citation: Liu P, Huang HQ, Bian C, Quan Y. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the Bartholin’s gland: Two case reports and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(26): 108052
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i26/108052.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i26.108052