©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2025; 13(10): 101647
Published online Apr 6, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i10.101647
Published online Apr 6, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i10.101647
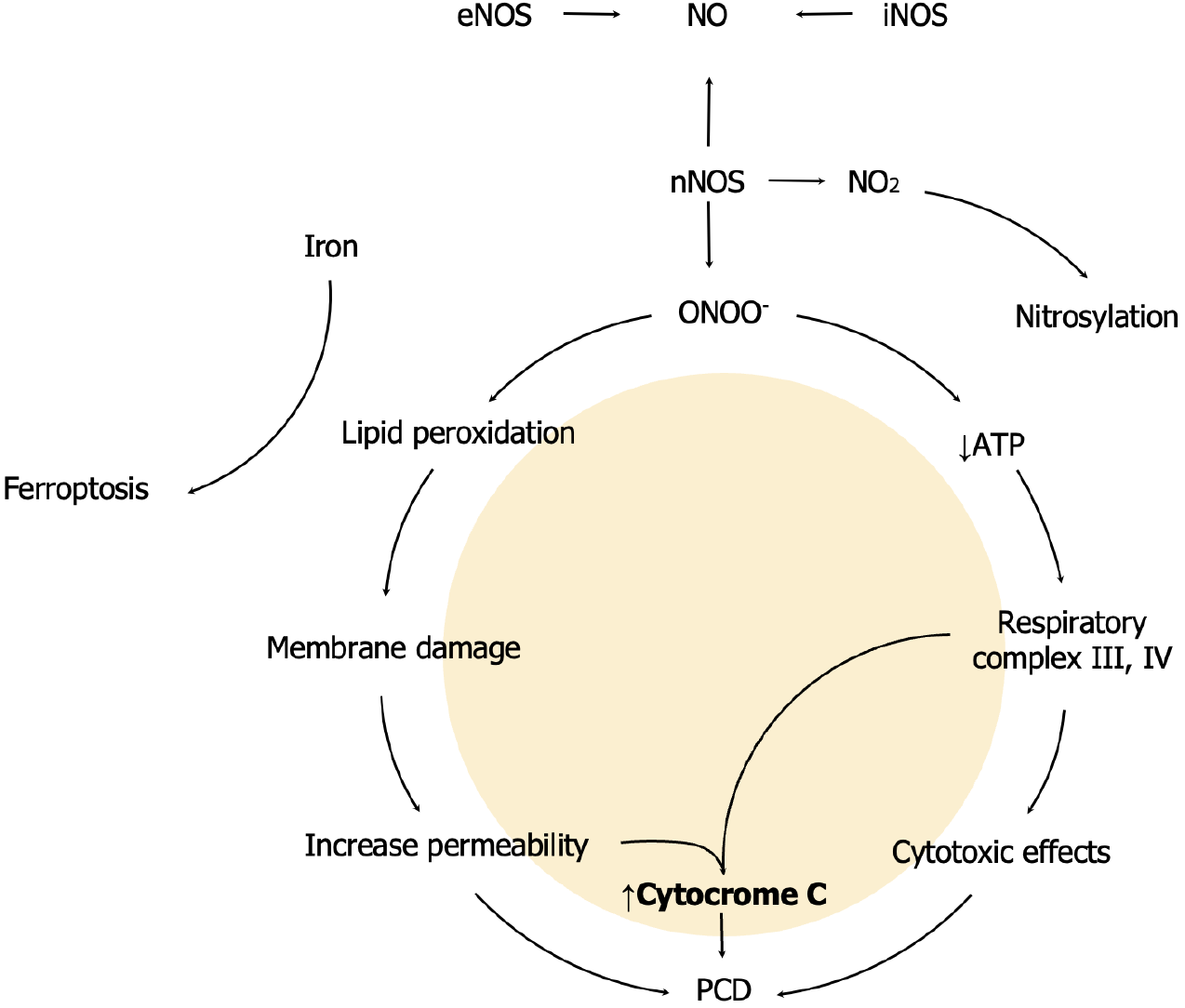
Figure 1 The biomolecular pathways of nitric oxide in brain damage after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase or type 3; nNOS: Neuronal nitric oxide synthase or type 1; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase or type 2); NO: Nitric oxide; NO2: Nitrogen dioxide; ONOO-: Peroxynitrite; PCD: Programmed cell death.
- Citation: Anaya-Prado R, Canseco-Villegas AI, Anaya-Fernández R, Anaya-Fernandez MM, Guerrero-Palomera MA, Guerrero-Palomera C, Garcia-Ramirez IF, Gonzalez-Martinez D, Azcona-Ramírez CC, Garcia-Perez C, Lizarraga-Valencia AL, Hernandez-Zepeda A, Palomares-Covarrubias JF, Blackaller-Medina JH, Soto-Hintze J, Velarde-Castillo MC, Cruz-Melendrez DA. Role of nitric oxide in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: A biomolecular overview. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(10): 101647
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i10/101647.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i10.101647