©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2024; 12(19): 3956-3960
Published online Jul 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3956
Published online Jul 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3956
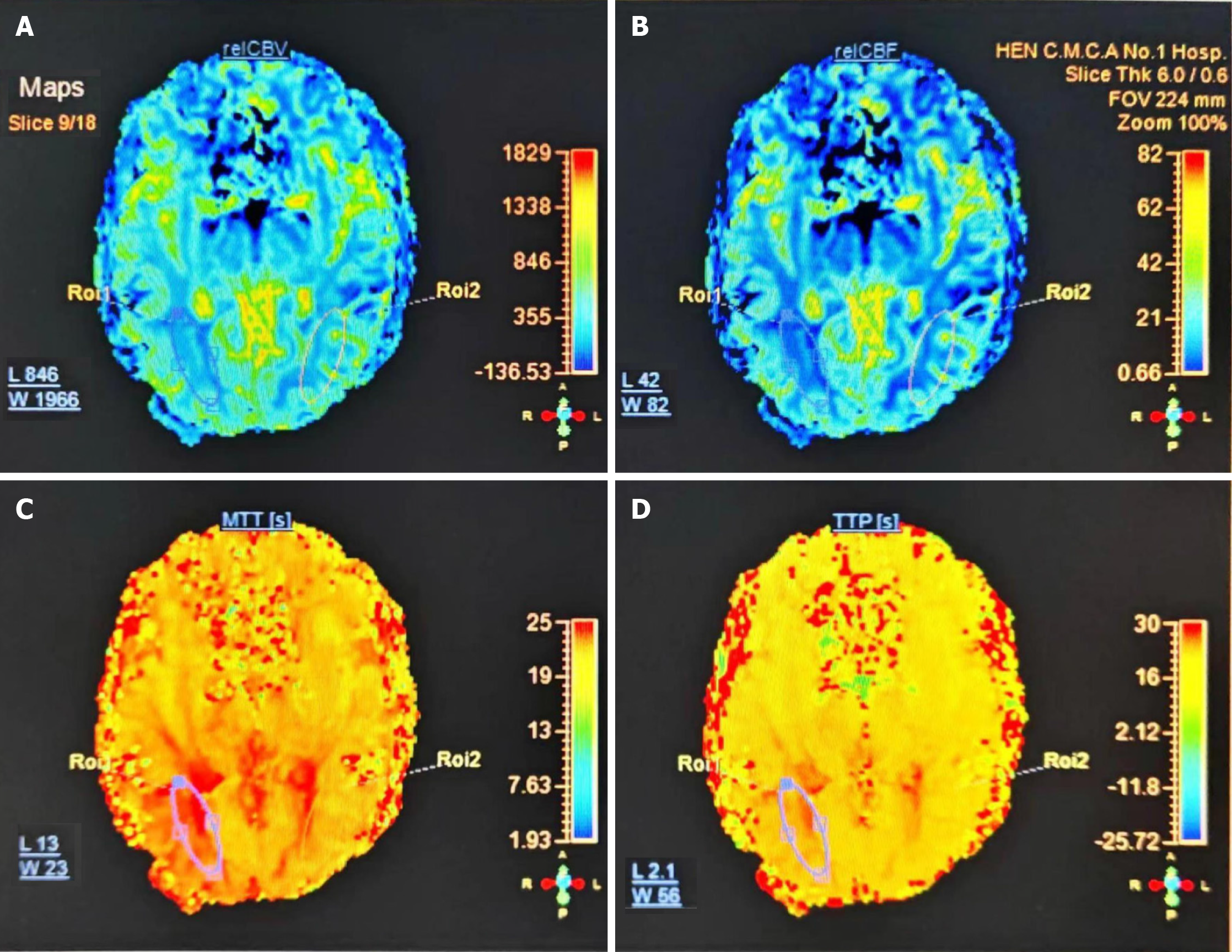
Figure 1 Cerebral Perfusion Imaging 3.
0T. A: Cerebral blood volume; B: Cerebral blood flow; C: Mean transit time; D: time to peak.
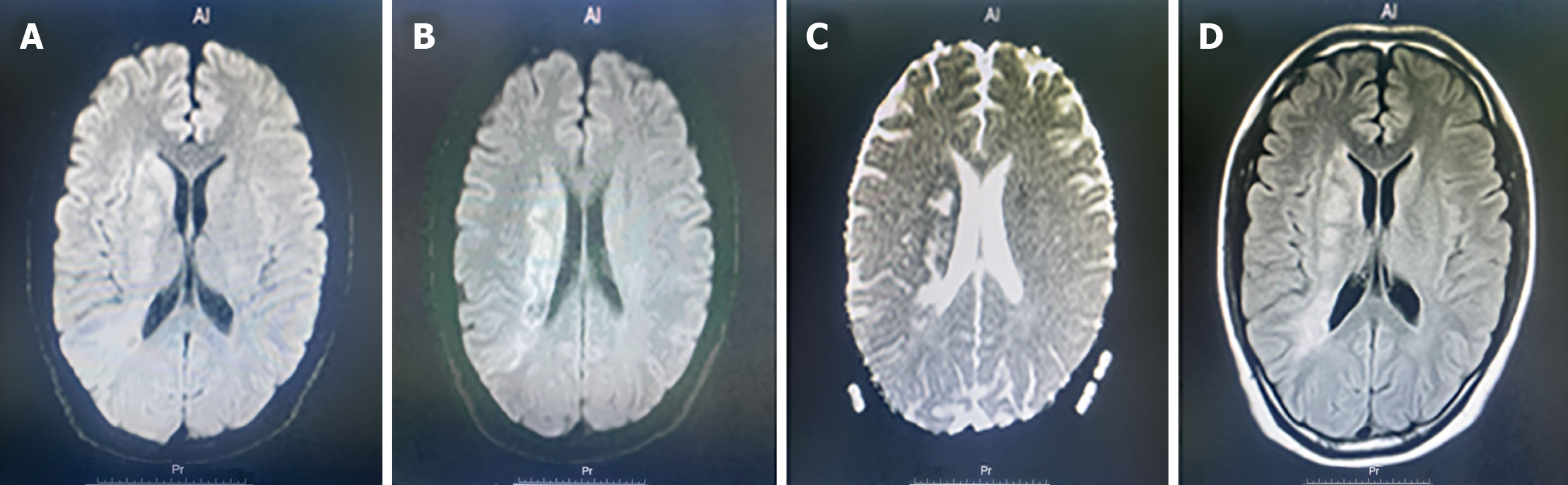
Figure 2 Diffusion-weighted imaging 3.
0T. A: Reg-diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) SENSE; B: sDWI b1000; C: dADC; D: eT2W-FLAIR.
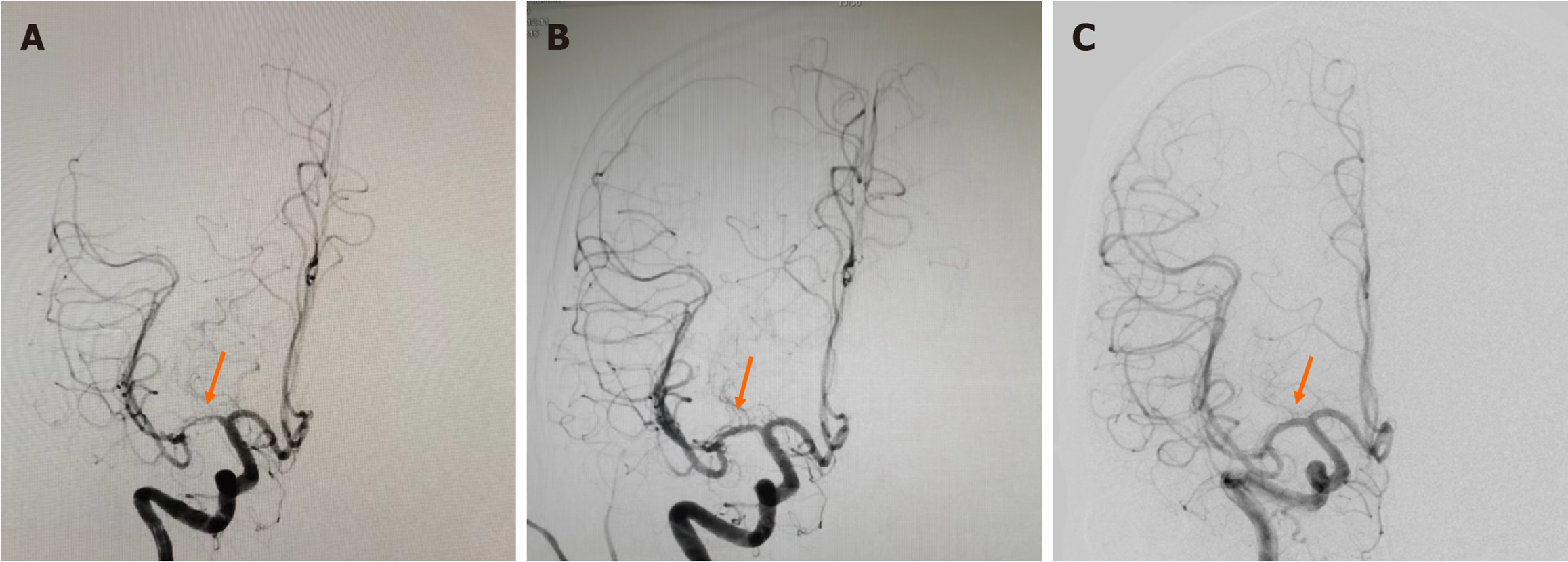
Figure 3 Cerebral digital subtraction angiography.
A: Preoperative digital subtraction angiography (DSA), showing which revealed severe stenosis (approximately 80%) in the M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery (MCA) (arrow); B: Intraoperative DSA Angiography after dilation, showing the vessel wall appeared irregular, the remaining branches showed good opacification (arrow); C: DSA Re-examination 6 months post-surgery, showing no significant stenosis in the right MCA, with a smooth vessel wall (arrow).
- Citation: Zhu PC, Shu LF, Dai QH, Tan HT, Wang JB, Wu T. Drug-coated balloon angioplasty for the treatment of intracranial arterial stenosis in a young stroke patient: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(19): 3956-3960
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i19/3956.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3956