©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2023; 11(33): 8071-8077
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8071
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8071
Figure 1 Head magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Head T1 image; B-D: Bilateral stenosis at the beginning of the middle cerebral artery, thickening and tortuosity of adjacent meningeal vessels, and multiple thickening and tortuosity of the surrounding vascular network.
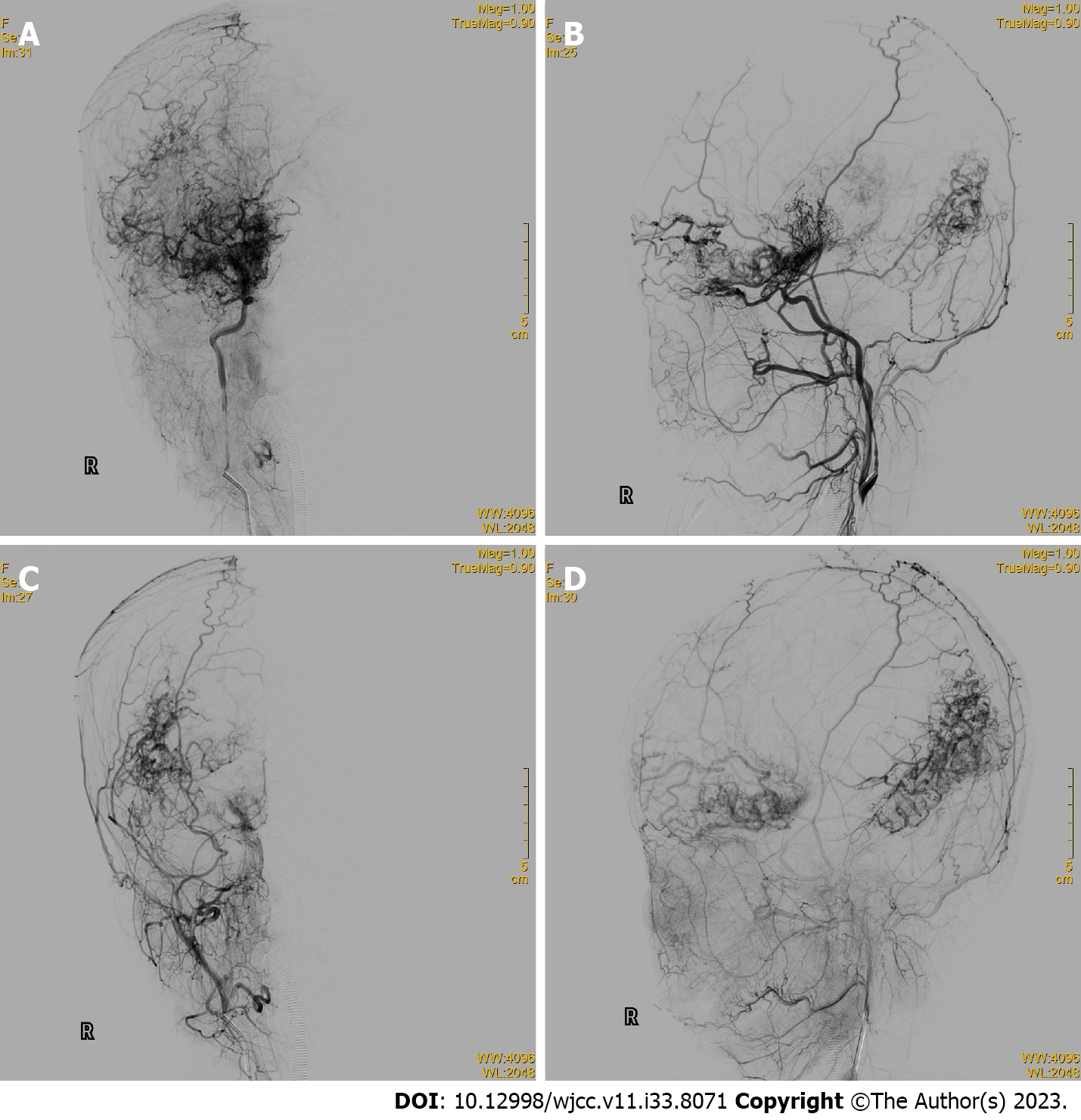
Figure 2 Brain digital subtraction angiography.
A: Anteroposterior view of a right internal carotid artery (ICA) angiogram; B: Lateral view of a right ICA angiogram; C: Anteroposterior view of a right external carotid artery (ECA) angiogram; D: Lateral view of a right ECA angiogram. Diffuse vascular malformations and transmural blood supply can be observed.
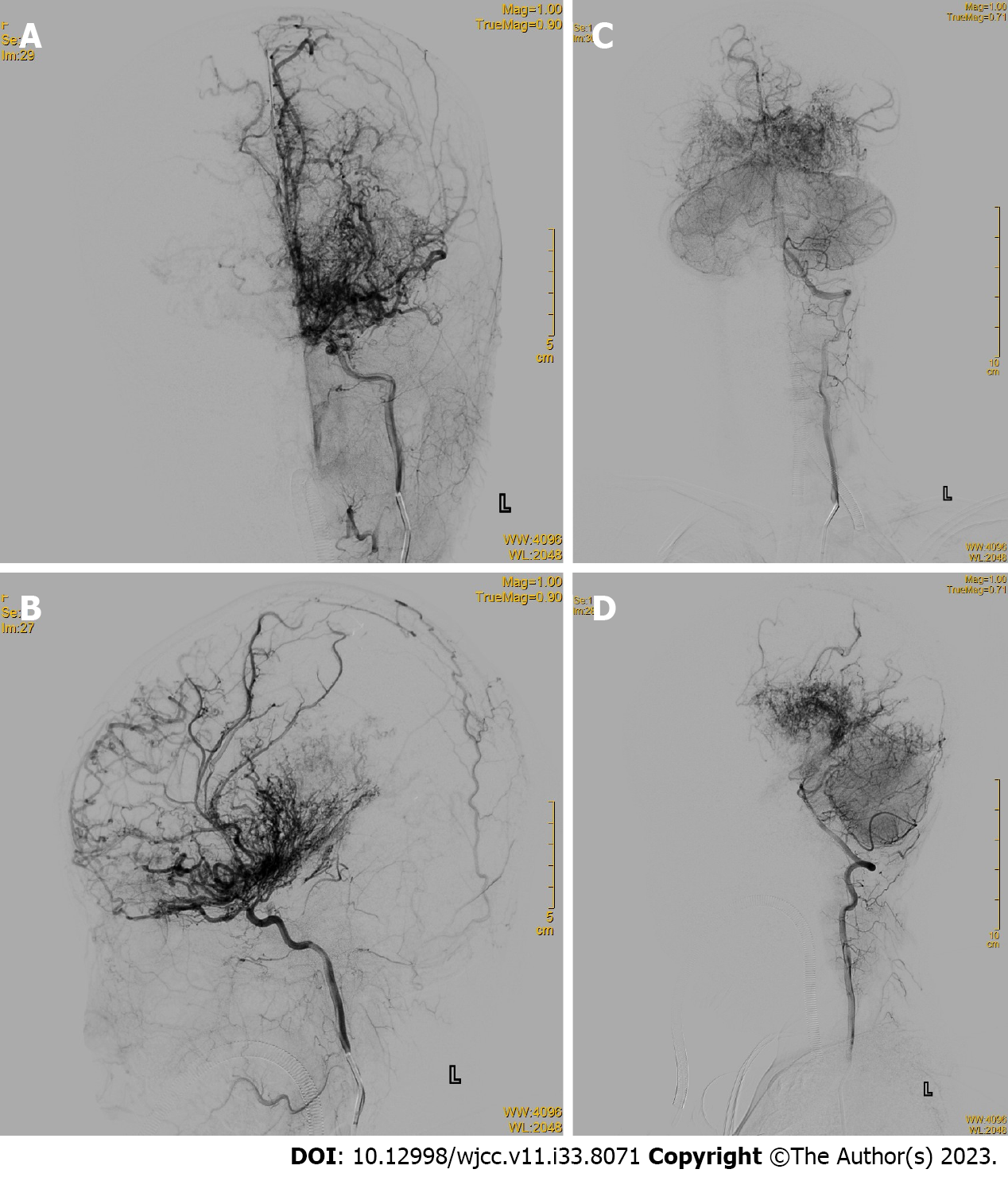
Figure 3 Brain digital subtraction angiography.
A: Anteroposterior view of a left internal carotid artery (ICA) angiogram; B: Lateral view of a left ICA angiogram; C: Anteroposterior view of a right vertebral artery (VA) angiogram; D: Lateral view of VA angiogram.
- Citation: Luo FR, Zhou Y, Wang Z, Liu QY. Cerebral proliferative angiopathy in pediatric age presenting as neurological disorders: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(33): 8071-8077
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i33/8071.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8071