©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2023; 11(33): 8058-8064
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8058
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8058
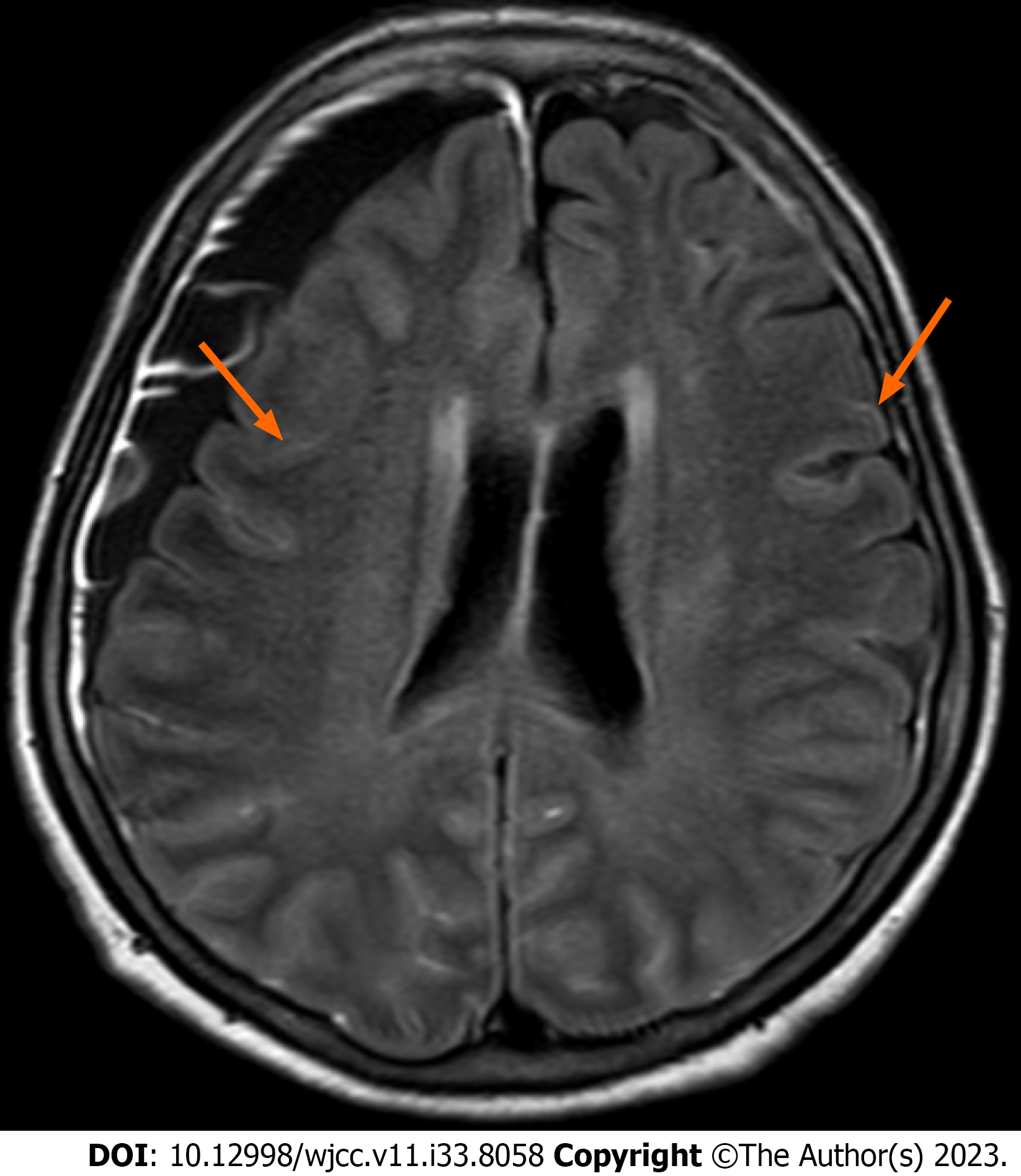
Figure 1 Axial T2-FLAIR brain magnetic resonance imaging reveals pachymeningeal enhancement in both frontoparietal convexities.
Figure 2 An 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography with computed tomography scan shows high FDG uptake in the right ethmoid sinus, liver, and both adrenal glands.
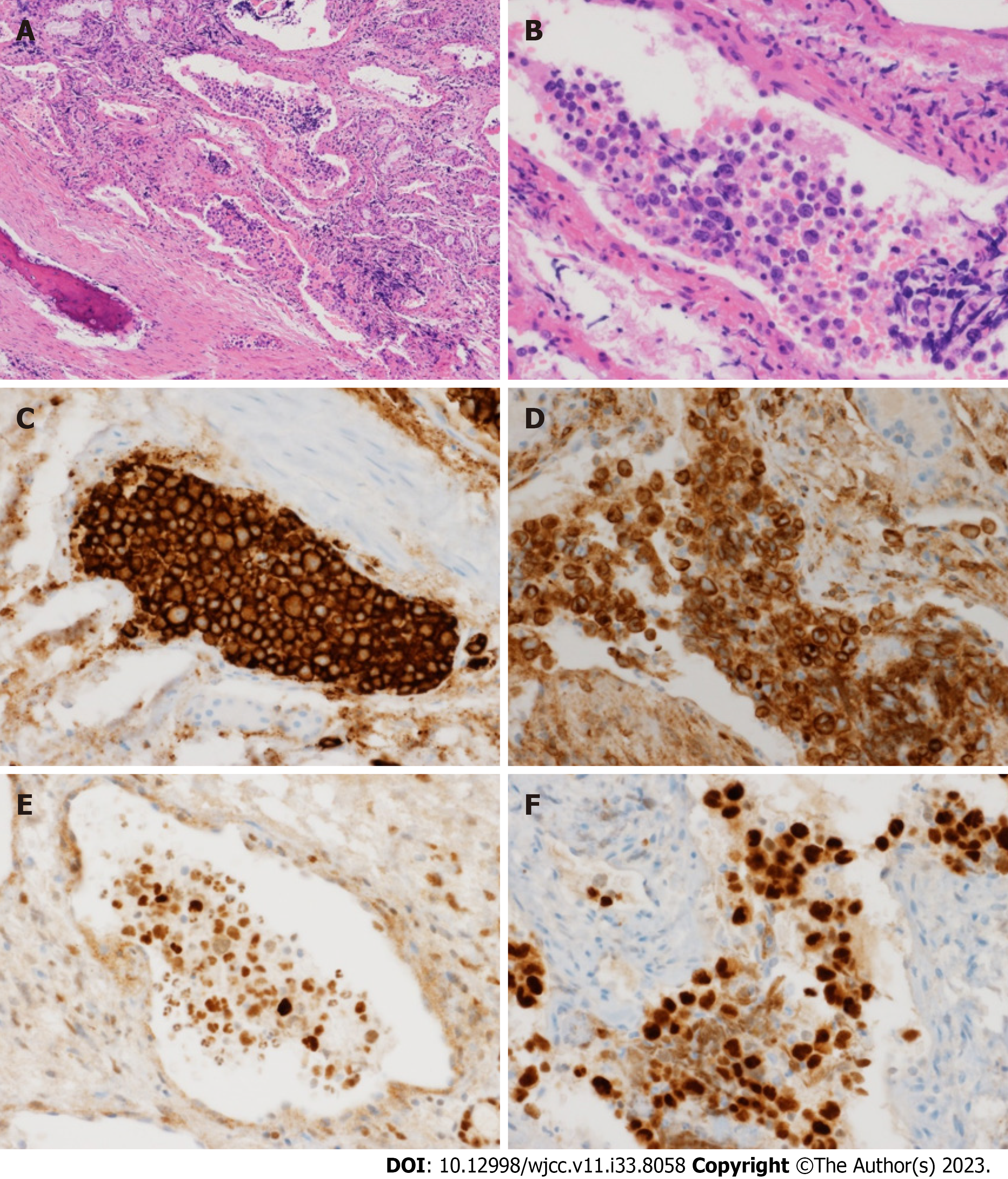
Figure 3 Haematoxylin and eosin stained section of the biopsy specimen demonstrates atypical large lymphoid cells with prominent nucleoli in the blood vessel.
A: Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (×100); B: H&E (×400); C: Immunohistochemical staining: CD20 (×400); D: BCL2 (×400); E: BCL6 (×400); F: IRF4/MUM1 (×400).
- Citation: Lee YP, Son SM, Kwon J. Asian variant intravascular large B-cell lymphoma with highly suspected central nervous system involvement: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(33): 8058-8064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i33/8058.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8058