©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2023; 11(33): 7972-7979
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.7972
Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.7972
Figure 1 Neurological function.
A: The observation group had statistically higher posttreatment sensory function scores than the control group; B: The observation group had significantly higher posttreatment motor function scores than the control group. aP < 0.01 vs before treatment; bP < 0.05 vs control group.
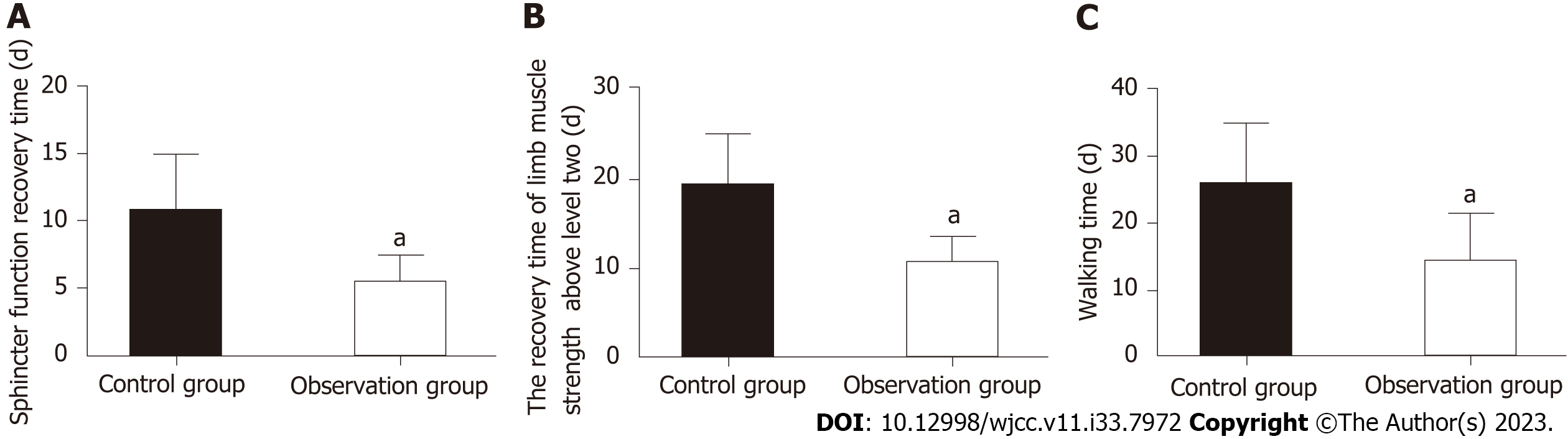
Figure 2 Recovery.
A: The observation group had an obviously shorter sphincter function recovery time than the control group; B: The observation group had an obviously shorter limb muscle strength recovery time than the control group; C: The observation group had obviously earlier ambulation than the control group. aP < 0.01 vs control group.
Figure 3 Inflammatory factors.
A: The observation group had evidently lower posttreatment interleukin-6 than the control group; B: The observation group had evidently lower posttreatment C-reactive protein than the control group; C: The observation group had evidently lower posttreatment tumor necrosis factor-α than the control group. aP < 0.01 vs before treatment; bP < 0.05 vs control group. IL-6: Interleukin-6; CRP: C-reactive protein; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Sun YF, Liu LL, Jiang SS, Zhang XJ, Liu FJ, Zhang WM. Influence of ganglioside combined with methylprednisolone sodium succinate on efficacy and neurological function in patients with acute myelitis. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(33): 7972-7979
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i33/7972.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.7972