©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2023; 11(31): 7724-7731
Published online Nov 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i31.7724
Published online Nov 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i31.7724
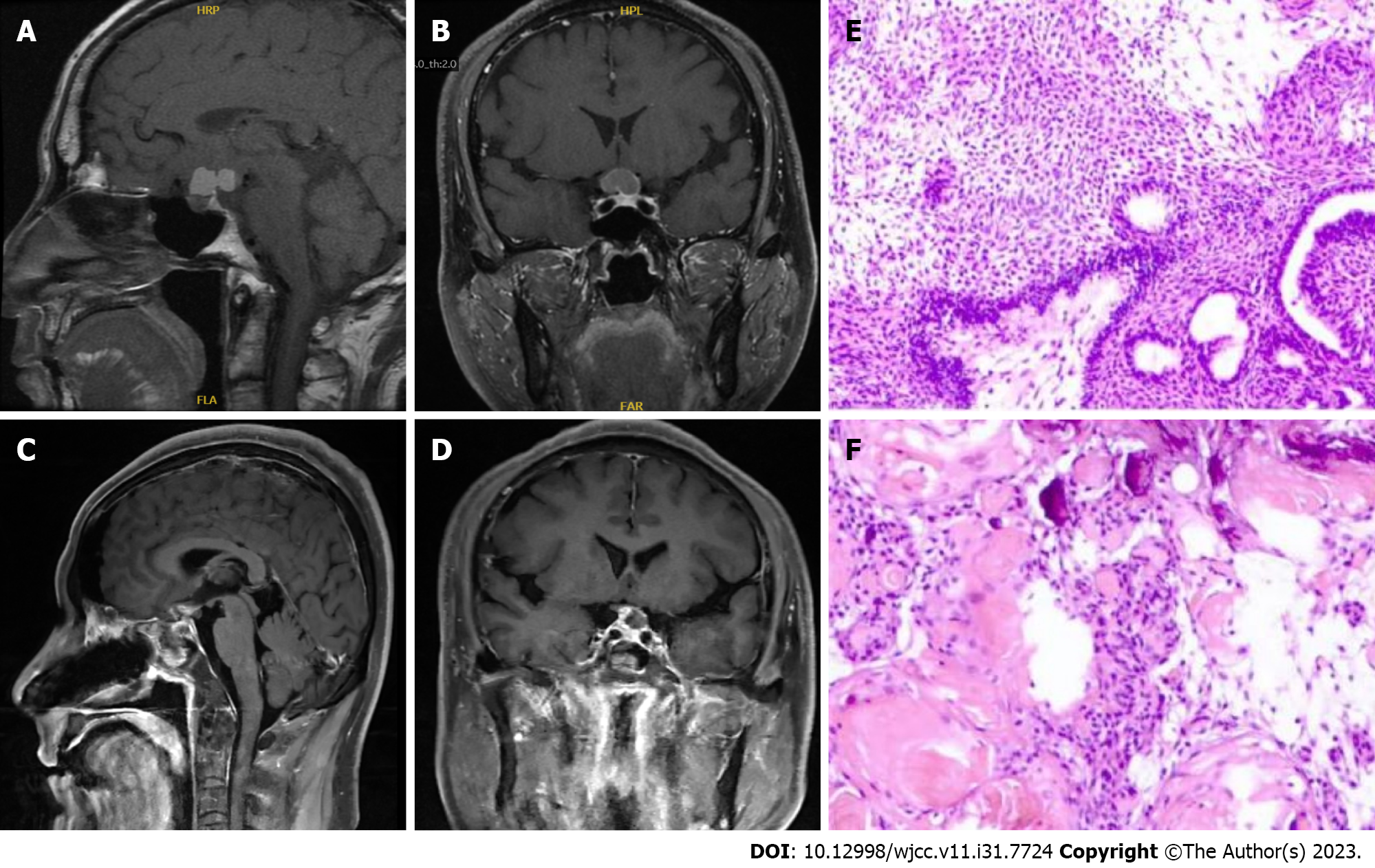
Figure 1 Imaging data and pathological examination images (first operation).
A and B: Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); C and D: Postoperative MRI; E and F: Postoperative pathological findings.
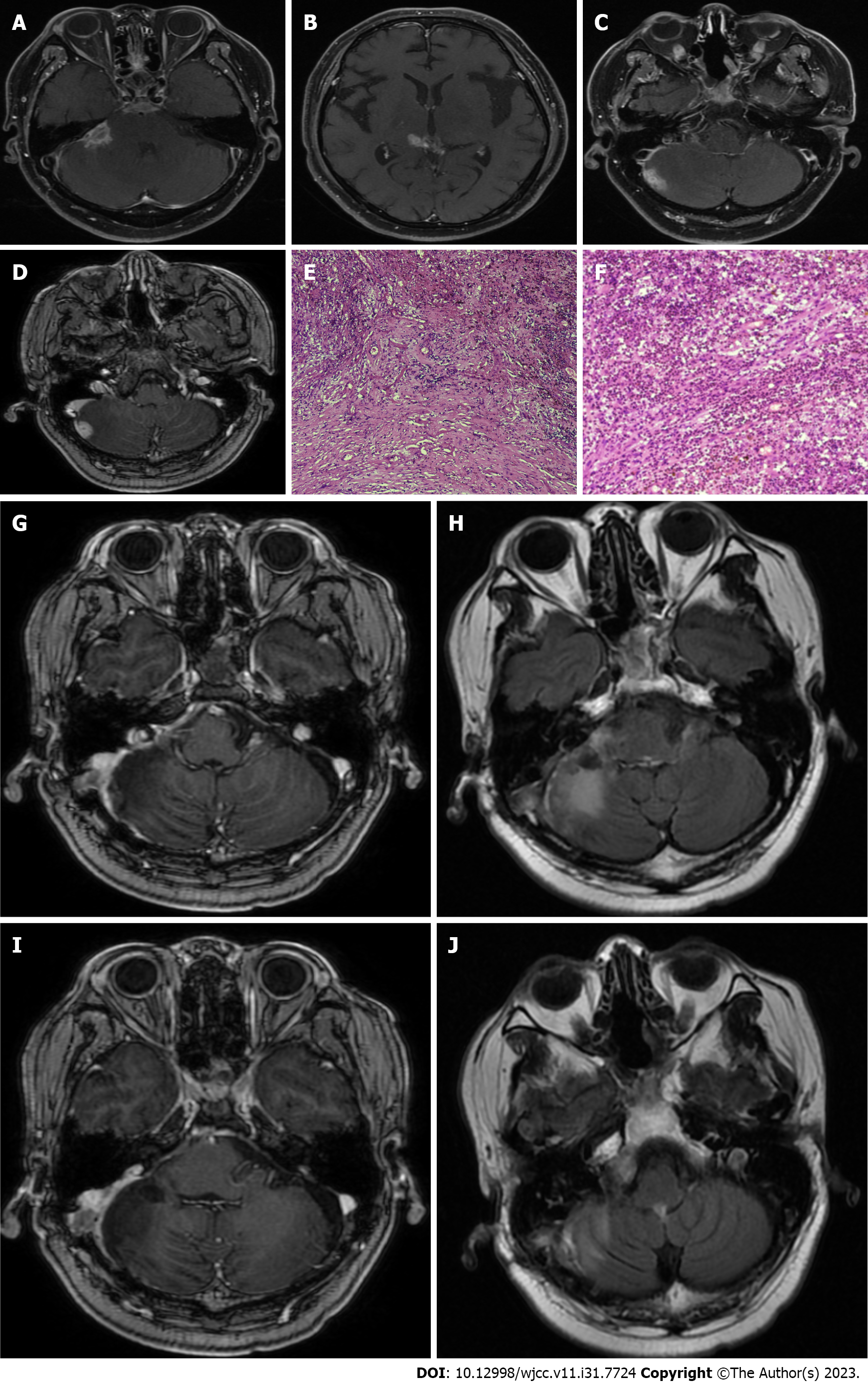
Figure 2 Imaging data and postoperative pathological findings of inflammatory pseudotumor (second operation).
A-D: T1-weighted enhanced magnetic resonance showed that multiple patchy and nodular reinforcing abnormalities around the right pontocerebellar angle, right cerebellum, and tegmental pool were seen, and the right rocky meninges were significantly thickened; E and F: Microscopic finding of fibrocollagenous tissue hyperplasia with infiltration of lymphocytes and other inflammatory cells; G-J: Magnetic resonance imaging showed that the multiple reinforcing nodular shadows around the tegmental pool were significantly smaller than before, and the reinforcing foci in the original right pontocerebellar area and cerebellar area are not shown.
- Citation: Wu H, Ding YW, Yan ZC, Wei M, Wang XD, Zhang HZ. Multiple inflammatory pseudotumor formation after craniopharyngioma resection via an extended nasal endoscopic approach: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(31): 7724-7731
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i31/7724.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i31.7724