©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2023; 11(26): 6194-6199
Published online Sep 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i26.6194
Published online Sep 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i26.6194
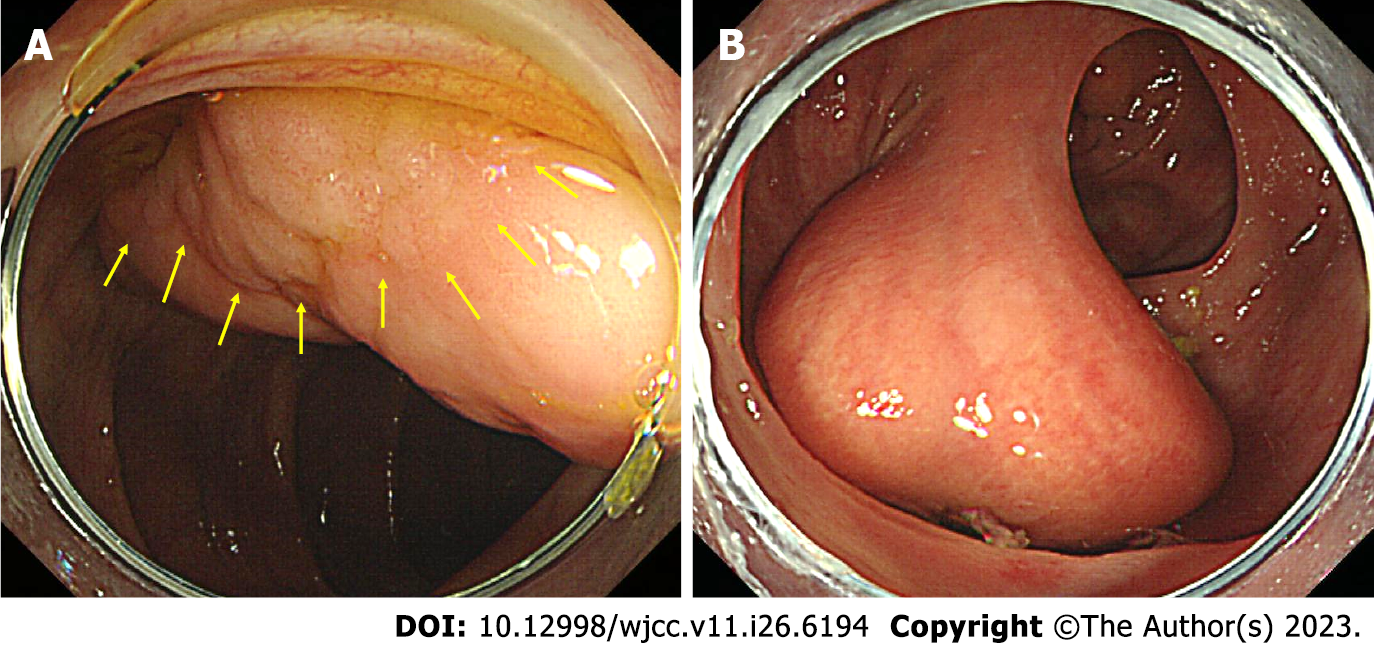
Figure 1 Colonoscopic images.
A: Colonic lipoma with a laterally spreading tumor (LST) of granular type. The margin of the LST was observed along the yellow arrow. It was difficult to observe the overall margin of the LST because the LST was pressed against the lipoma; B: When the patient’s posture was changed to the supine position, LST invasion was not observed in the neck of the lipoma.
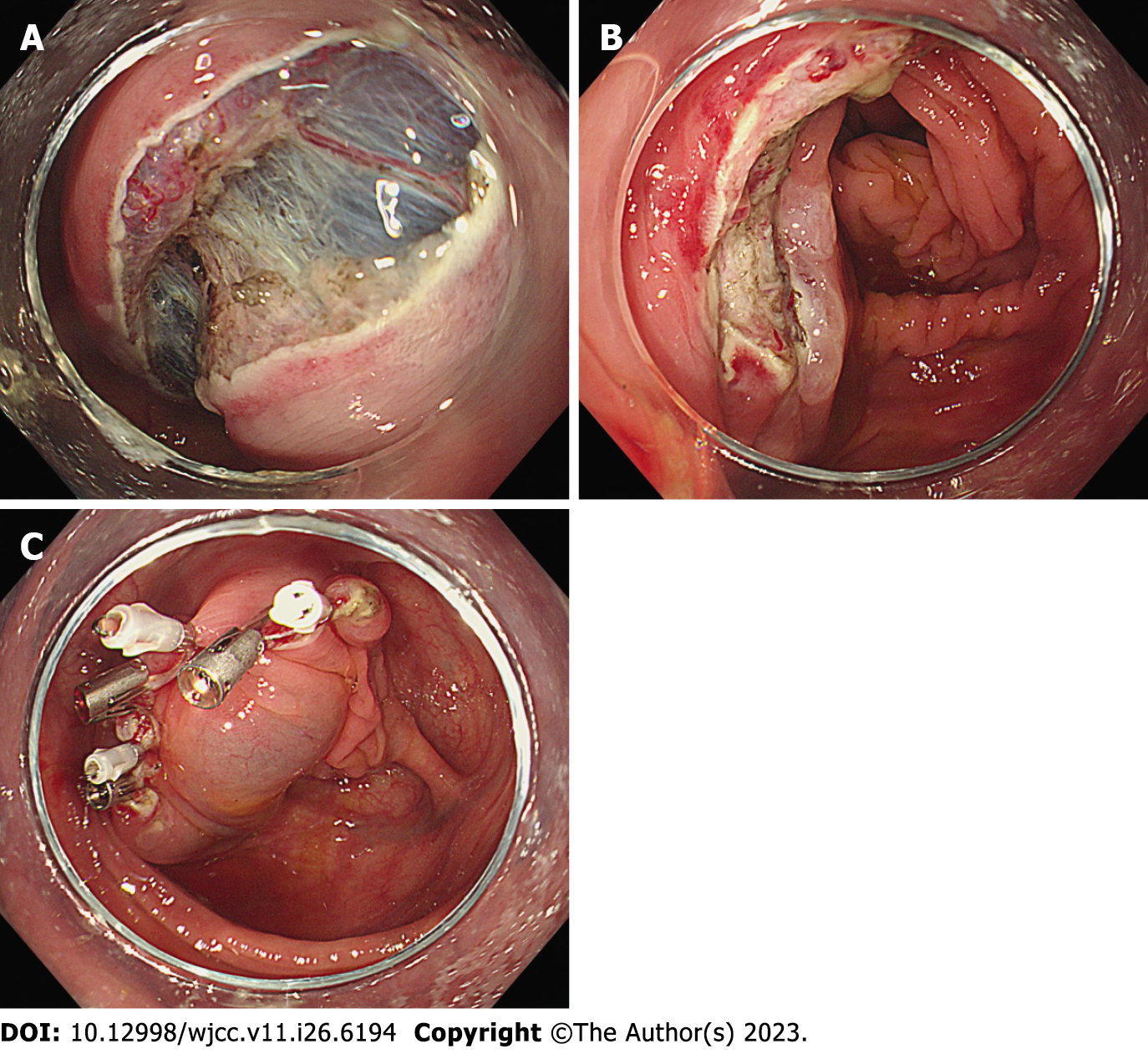
Figure 2 Endoscopic submucosal dissection.
A: Dissection was attempted through the submucosa rather than through the lipoma; B: No remaining lipoma was observed on the endoscopic submucosal dissection bed; C: Complete closure with hemoclips.
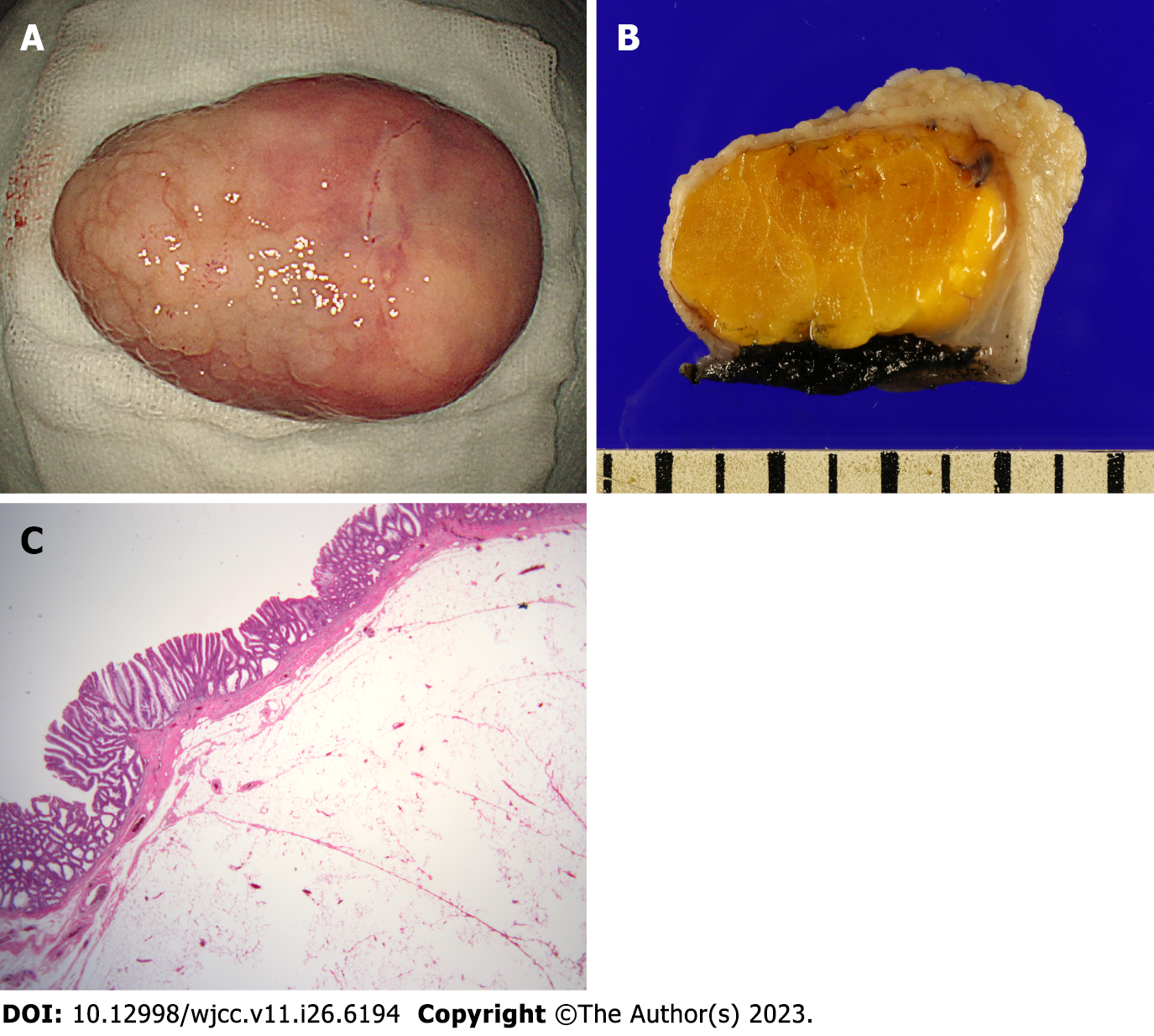
Figure 3 Pathologic findings.
A: Macroscopically, a yellow lipoma was observed in the submucosa and a laterally spreading tumor was observed on the mucosal surface; B: The black color at the bottom of the lipoma was not a burnt area due to electrical thermal injury, but a stain indicated the border of the bottom for pathological evaluation; C: Microscopically, the mucosal lesion on the surface of the lipoma showed tubulovillous adenoma with low-grade dysplasia (H&E staining, magnification × 12.5).
- Citation: Bae JY, Kim HK, Kim YJ, Kim SW, Lee Y, Ryu CB, Lee MS. Large colonic lipoma with a laterally spreading tumor treated by endoscopic submucosal dissection: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(26): 6194-6199
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i26/6194.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i26.6194