©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2023; 11(18): 4326-4333
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4326
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4326
Figure 1 The results of chest computed tomography.
A: A small amount of patchy high-density shadow in the middle lobe of the right lung, clearly demarcated from the surrounding tissue, and the size of high-density shadow is about 0.5 cm × 0.5 cm × 0.5 cm; B: A few patchy high-density shadows on the lateral surface of the right lung, clearly demarcated from the surrounding tissue, and the size of high-density shadows is about 0.5 cm × 0.5 cm × 0.5 cm.
Figure 2 Macroscopic findings.
A: The size of lung tissue in the right middle lobe was 9.0 cm × 5.0 cm × 1.0 cm; B: The section was grey red and soft. A hemorrhagic area (1.5 cm × 0.8 cm × 0.5 cm) was seen locally (the yellow arrow).
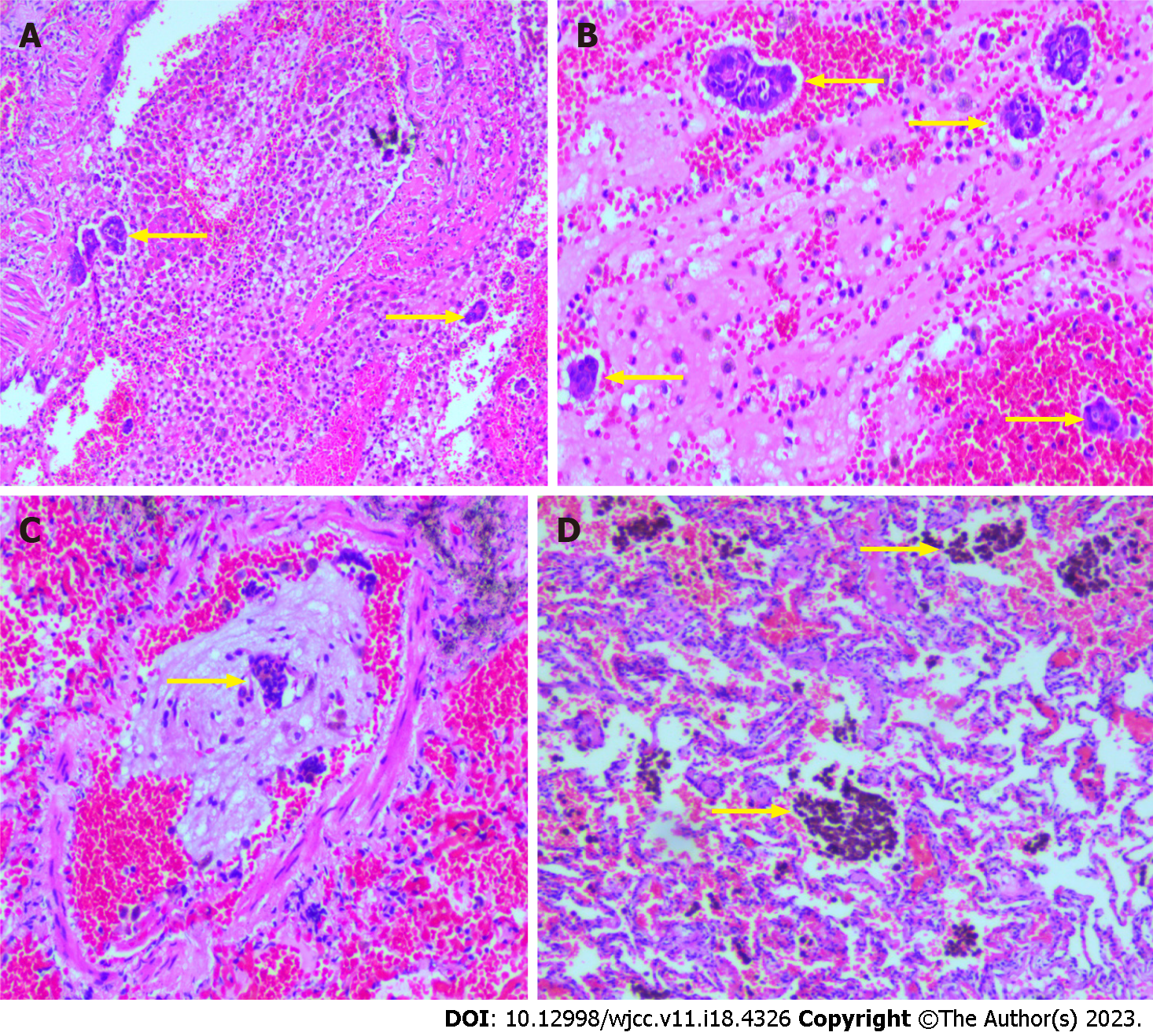
Figure 3 The image of hematoxylin and eosin.
A: Showed hemorrhage foci were seen in the alveolar cavity, scattered glandular epithelial cells were found in the bleeding foci (100 ×, the yellow arrow); B: Scattered glandular epithelial cells and inflammatory cells are seen in the hemorrhage (200 ×, the yellow arrow); C: Glandular epithelial cells were seen in the vascular cavity of some lung tissues (100 ×, the yellow arrow); D: Hemosiderin deposits were seen in some alveolar cavity (100 ×, the yellow arrow).
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical and Special staining.
A: The immunohistochemical staining was cytokeratin positive (100 ×, the yellow arrow); B: Special staining showed a Prussian blue staining positive for hemosiderin in the alveolar cavity (100 ×, the yellow arrow).
- Citation: Yao J, Zheng H, Nie H, Li CF, Zhang W, Wang JJ. Endometriosis of the lung: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(18): 4326-4333
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i18/4326.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4326