©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2023; 11(11): 2496-2501
Published online Apr 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2496
Published online Apr 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2496
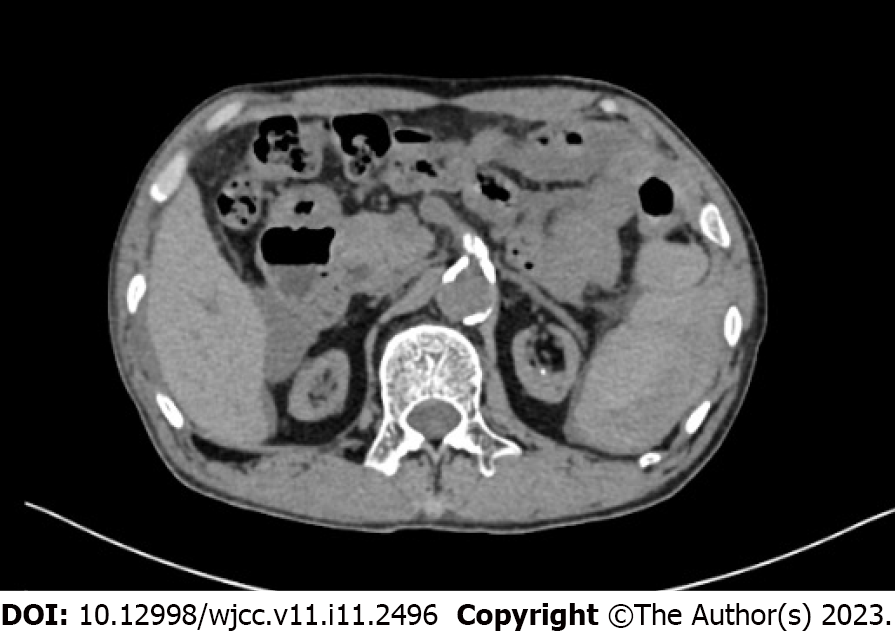
Figure 1 Computed tomography showed perisplenic fluid accumulation.
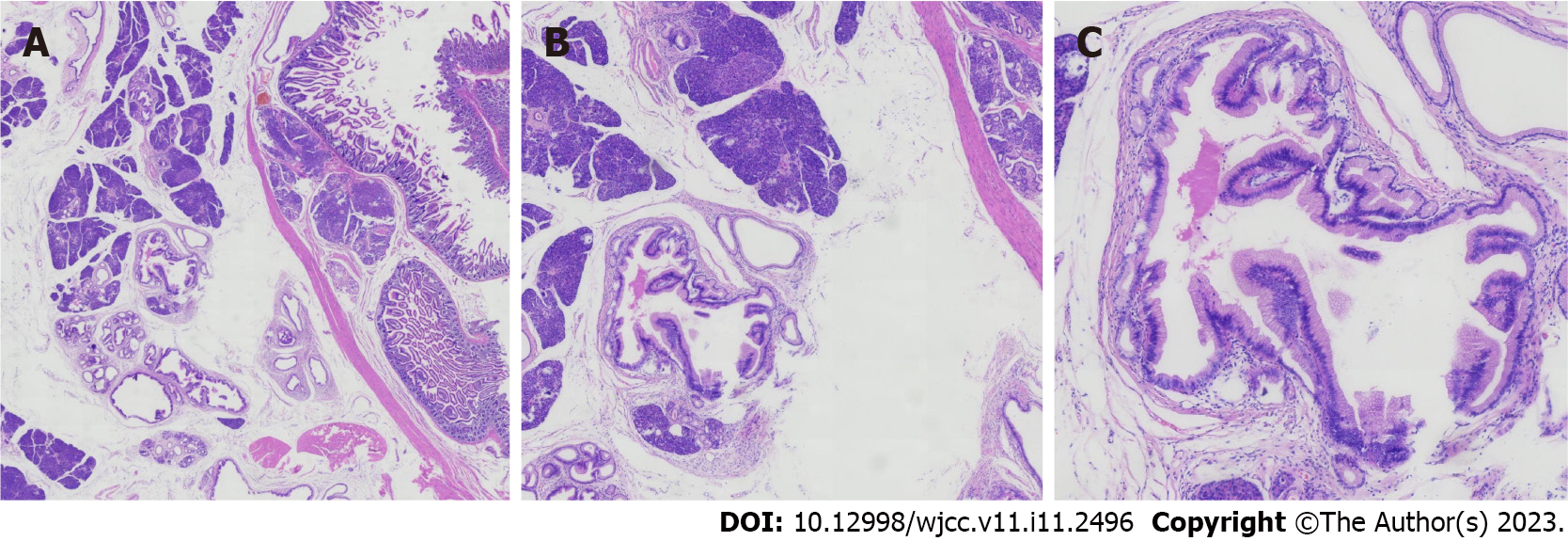
Figure 2 Histopathological analysis of the resected ectopic pancreas.
A: × 15 magnification; B: × 40 magnification; C: × 100 magnification.
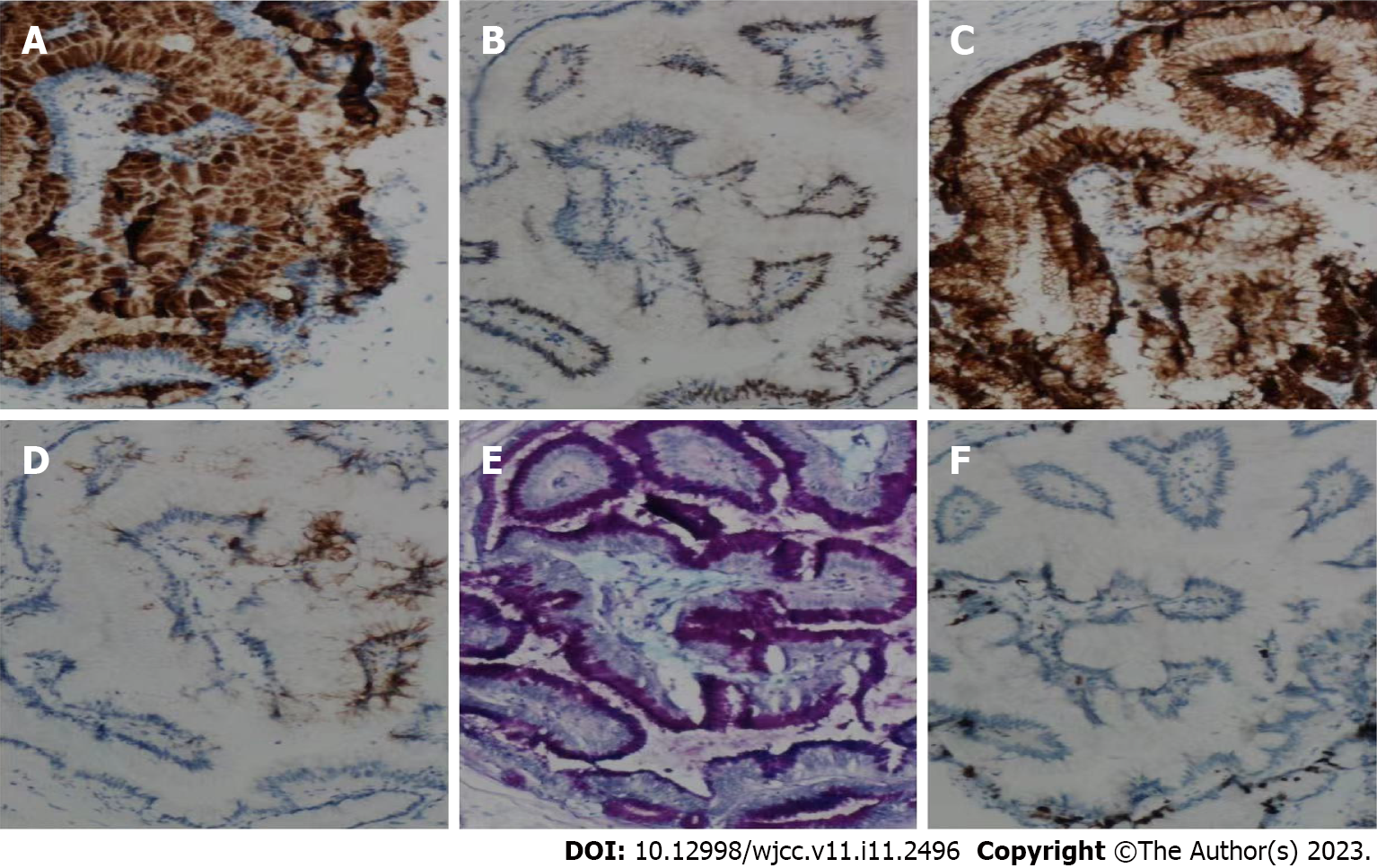
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical examination of the resected ectopic pancreas.
A: MUC5A (× 100 magnification); B: CDX2 (× 100 magnification); C: CK7 (× 100 magnification); D: CK20 (× 100 magnification); E: AB-PAS (× 100 magnification); F: Ki67 (× 100 magnification).
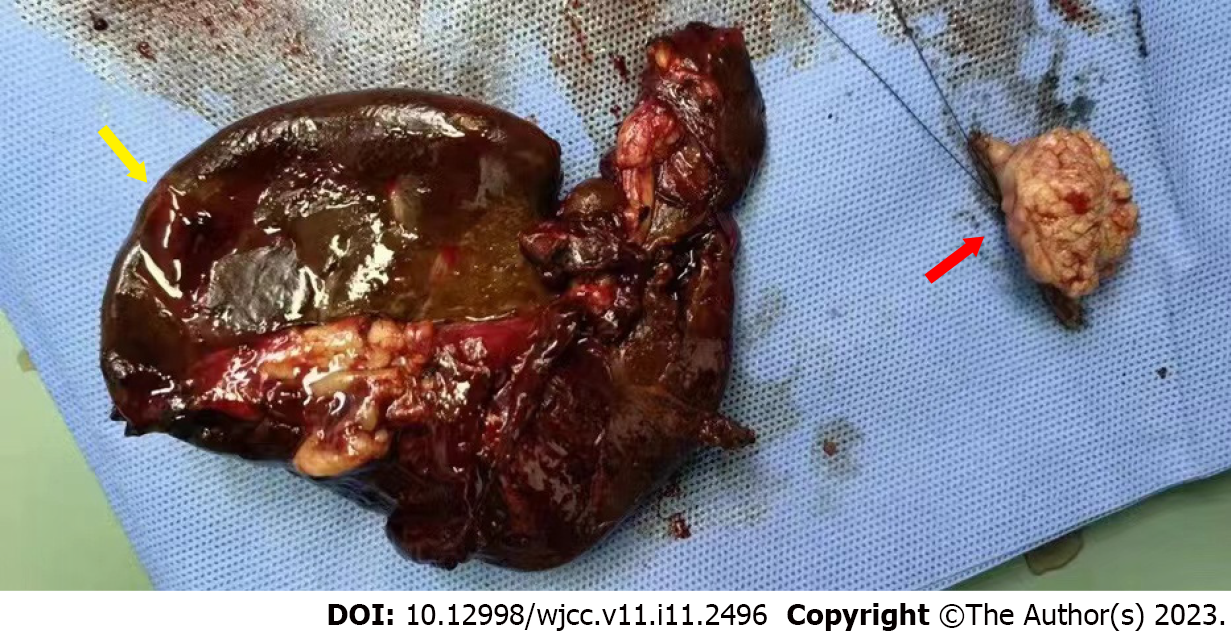
Figure 4 Resected spleen and ectopic pancreas (located in jejunum).
The yellow arrow indicates the resected spleen, and the red arrow indicates the ectopic pancreas.
- Citation: Huang JH, Guo W, Liu Z. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm originating from a jejunal heterotopic pancreas: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(11): 2496-2501
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i11/2496.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2496