©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2022; 10(9): 2961-2968
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2961
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2961
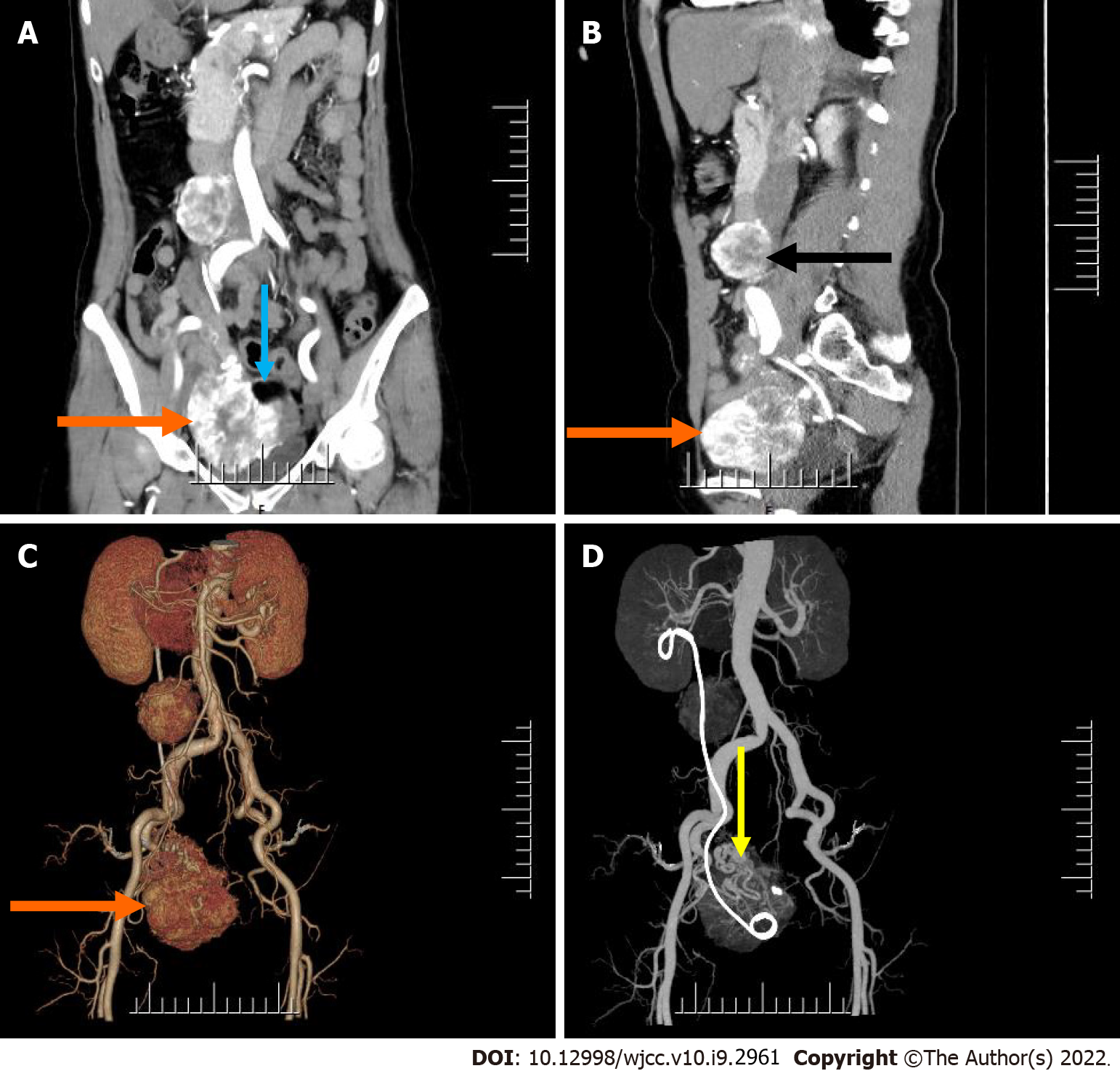
Figure 1 Pre-operative abdomen computed tomography contrast-enhanced scan.
A and B: Computed tomography (CT) images showed an irregular mass in the right adnexal region (orange arrow) and a round mass in the right retroperitoneum (black arrow) (A: Cornal; B: Sagittal); C and D: Post-processed CT images showed 3D reconstruction of both lesions (orange and yellow arrow).
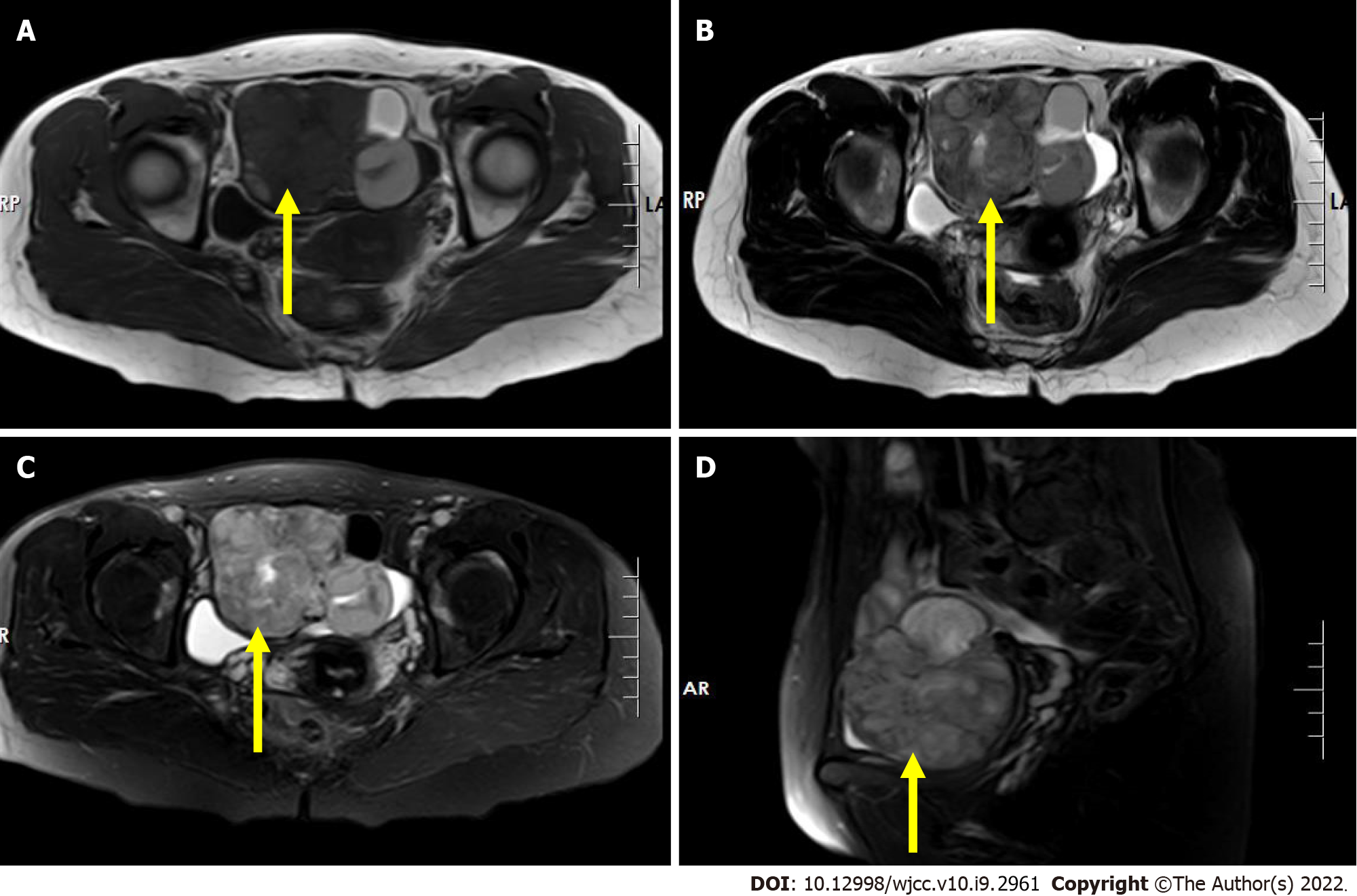
Figure 2 Pre-operative pelvis magnetic resonance imaging scan.
A: T1-weighted image shows an irregular mass with mixed signal in the right adnexal region with iso/hypo-signal intensity (axial, yellow arrow); B: T2-weighted image shows an irregular mass with a heterogeneous slightly high signal intensity in the right adnexal region (axial, yellow arrow); C and D: Short time of inversion recovery image shows an irregular mass with a heterogeneous slightly high signal intensity in the right adnexal region (yellow arrow) (C: Cornal; D: Sagittal).
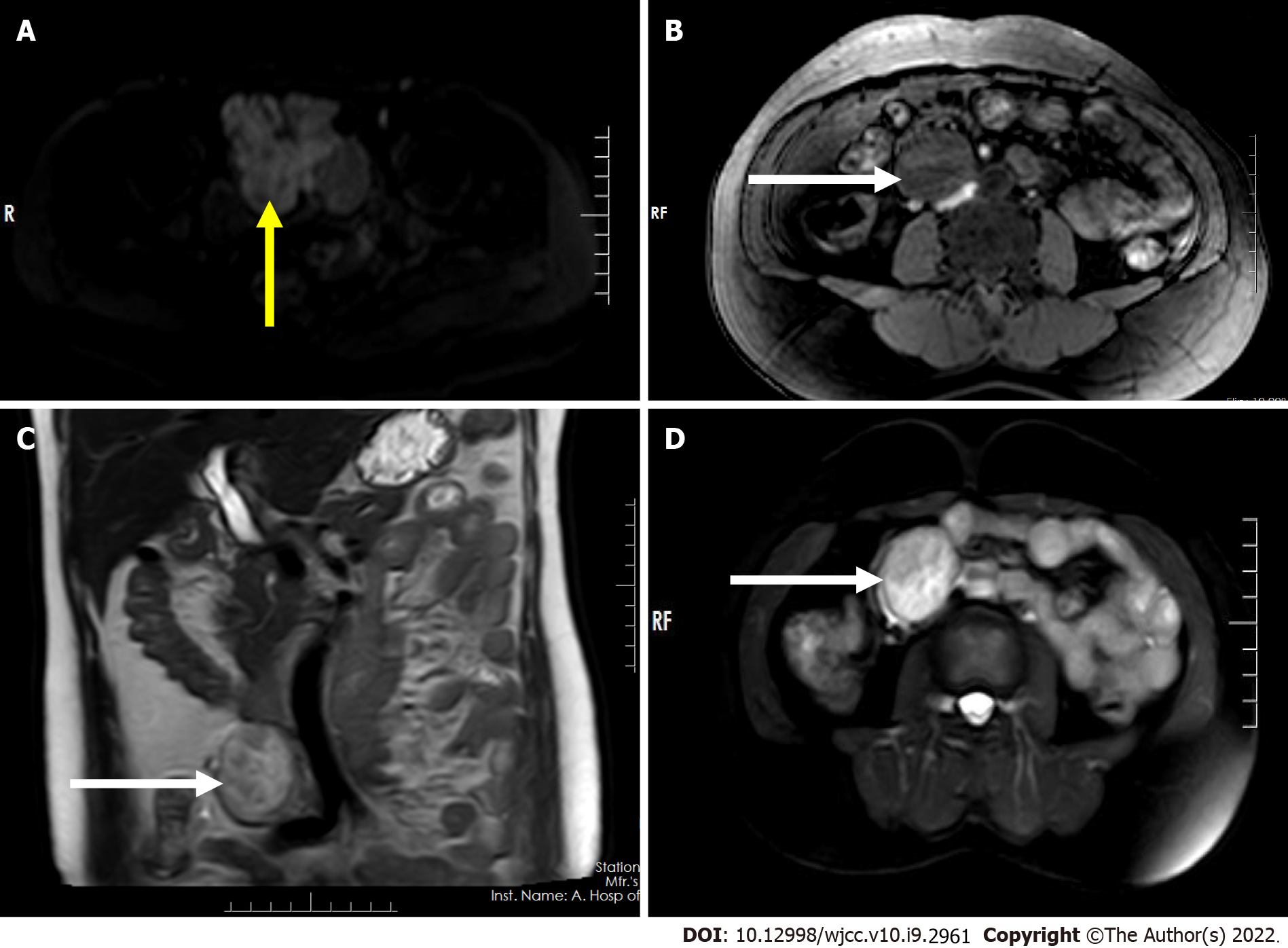
Figure 3 Pre-operative abdomen and pelvis magnetic resonance imaging scan.
A: Axial diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) image shows hypersignal intensity of the lesion in the right adnexal region (axial, yellow arrow); B: T1-weighted image shows a regular mass with low signal intensity in the right retroperitoneum (axial, white arrow); C: T2-weighted image shows a regular mass with inhomogeneous slightly-high/high signal intensity in the right retroperitoneum (coronal, white arrow); D: STIR image shows a regular mass with inhomogeneous high signal intensity in the right retroperitoneum (axial, white arrow).
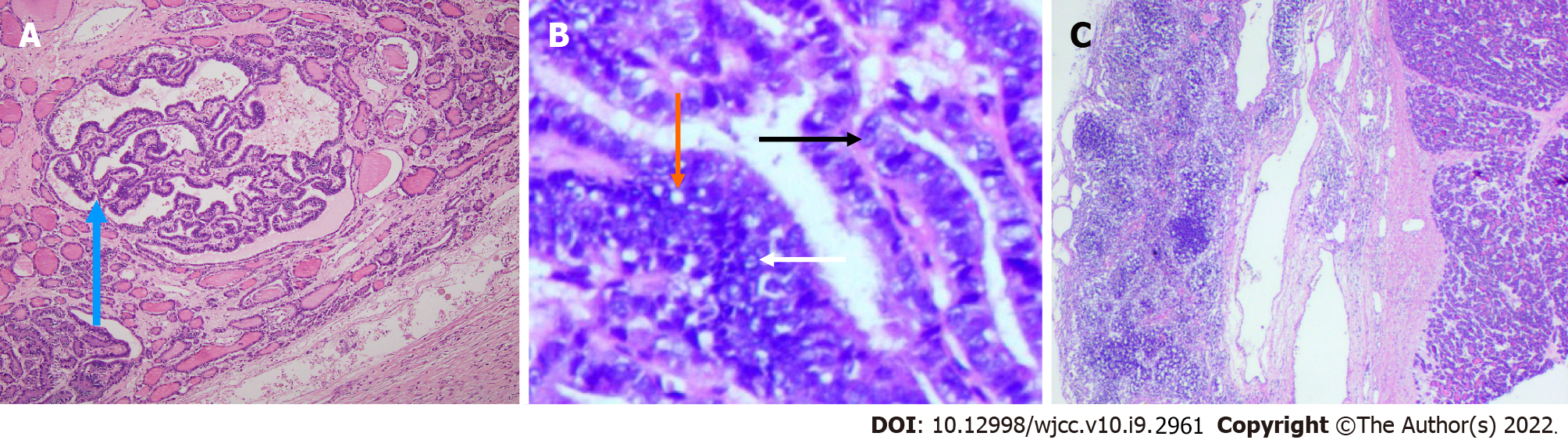
Figure 4 Surgically resected specimen of case.
A: At low magnification, there are scattered follicular structures of different sizes and papillary structures (blue arrow) in some areas (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 100); B: At high magnification, ovoid or round cells are seen to be poleally disordered, with enlarged and overlapping nuclei, which are transparent or ground glass like (black arrow) and irregular in shape, including nuclear sulcus (white arrow) and pseudoinclusion bodies (orange arrow) (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 200); C: There is metastasis to the right retroperitoneum lymph node.
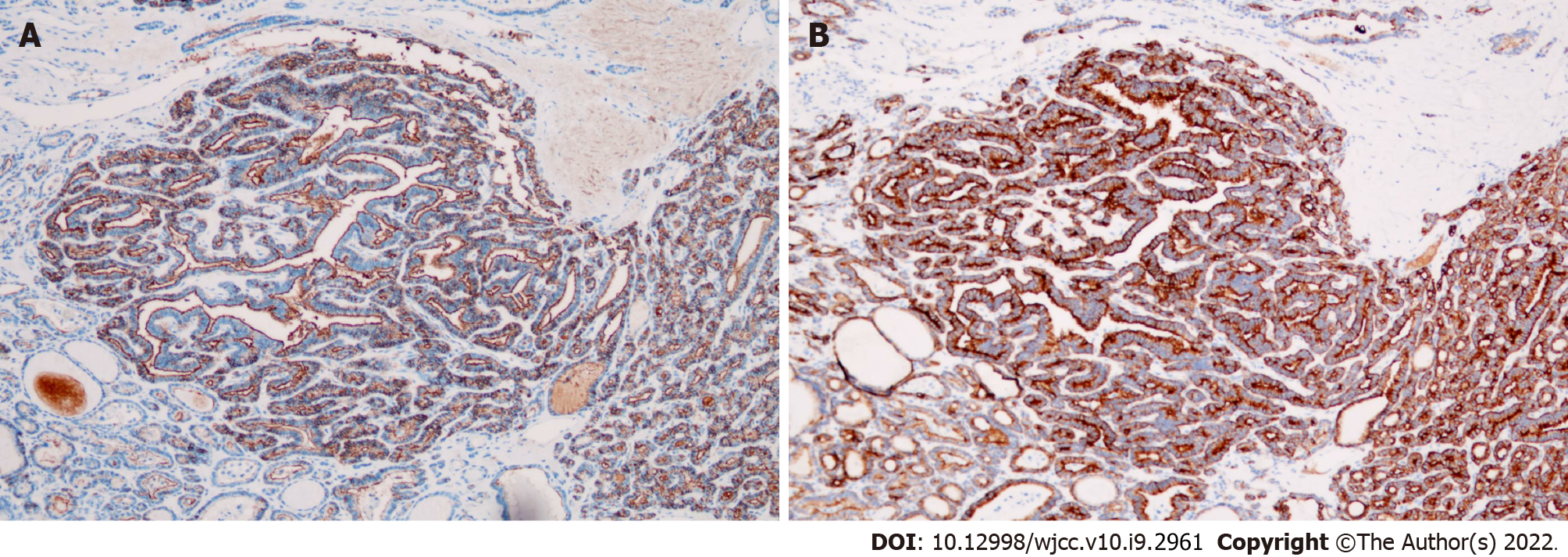
Figure 5 Surgically resected specimen of case.
A: Immunoreactivity for HBME-1 (× 100 magnification); B: Immunoreactivity for CK19 (× 100 magnification).
- Citation: Xiao W, Zhou JR, Chen D. Malignant struma ovarii with papillary carcinoma combined with retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(9): 2961-2968
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i9/2961.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2961