©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2022; 10(5): 1716-1722
Published online Feb 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1716
Published online Feb 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1716
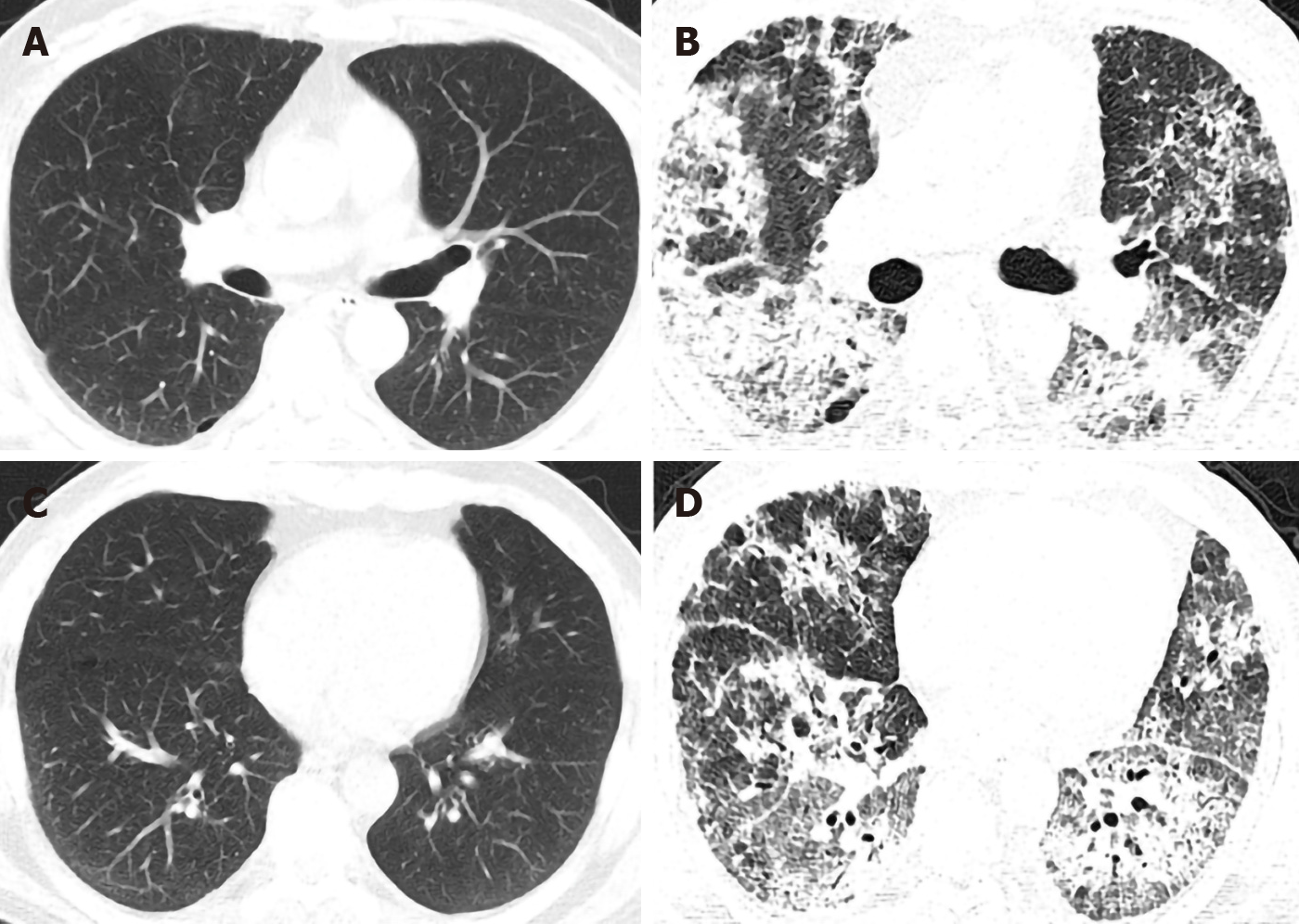
Figure 1 High-resolution computed tomography of the patient before and after vedolizumab administration.
A and B: The lung window of the patient in the high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) before vedolizumab administration was basically normal except for some scattered miliary nodules and localized emphysema; C and D: the lung window of the patient in the HRCT after two doses of vedolizumab administration showed the new-onset severe diffuse infiltrates, interlobular thickening and fibrosis.
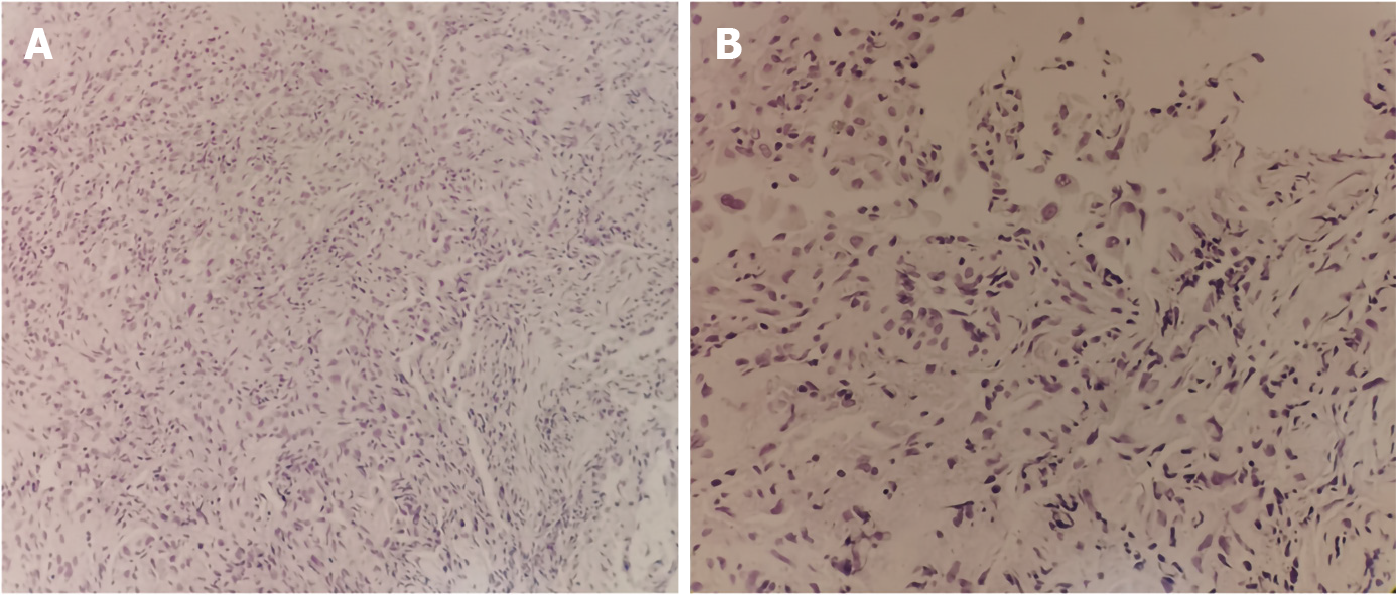
Figure 2 Pathology of transbronchial lung biopsy.
A: Irregular glandular structures in the hyperplastic fibrous tissue and infiltrated lymphocytes scattered throughout the interstitium were noted (H&E, x200); B: The glandular cavity was covered with single or stratified epithelium, the epithelial cells were cubic or polygonal, some of the cells had large nuclei and slightly dense chromatin. Intranuclear vacuoles, nuclear fragmentation and binuclear cells were noted. The focal gland cavity contains histiocytes, and the interstitium was infiltrated with scattered lymphocytes. No tumor cells were noted (H&E, x400).
- Citation: Zhang J, Liu MH, Gao X, Dong C, Li YX. Vedolizumab-associated diffuse interstitial lung disease in patients with ulcerative colitis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(5): 1716-1722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i5/1716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1716