©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2022; 10(34): 12793-12798
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12793
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12793
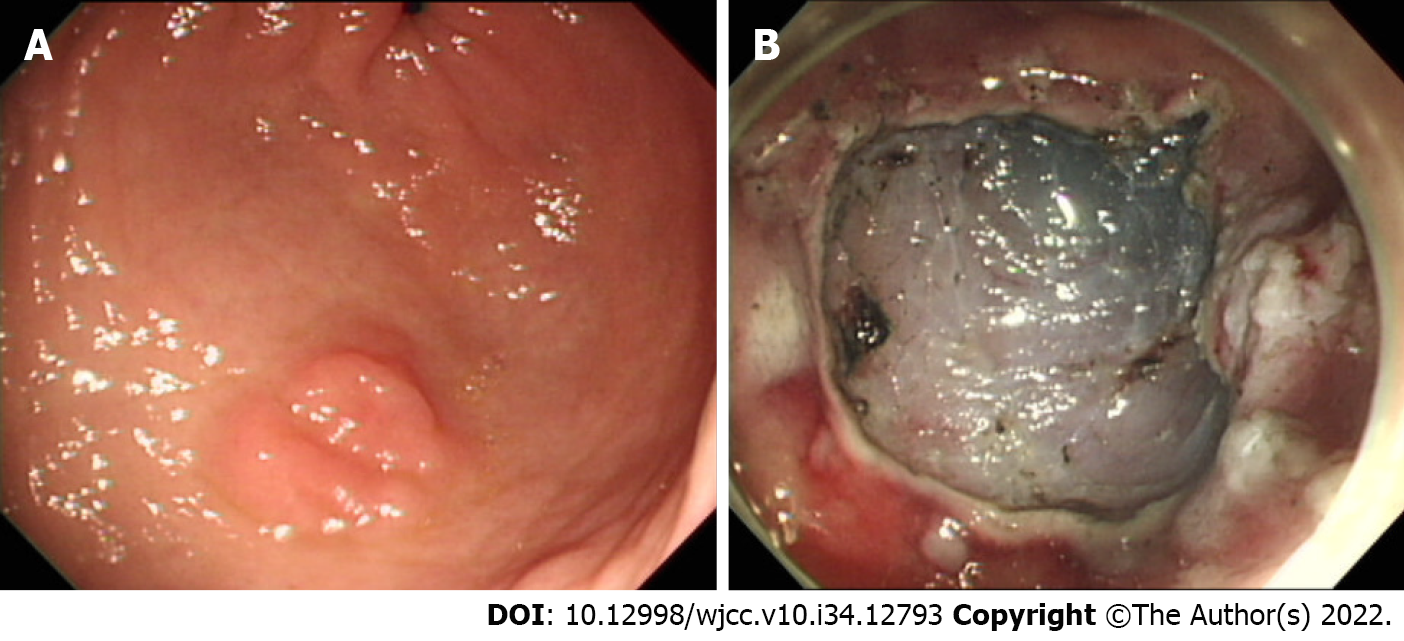
Figure 1 Endoscopic images.
A: A gastric dysplasia at antrum; B: Iatrogenic gastric ulcer after endoscopic submucosal dissection.
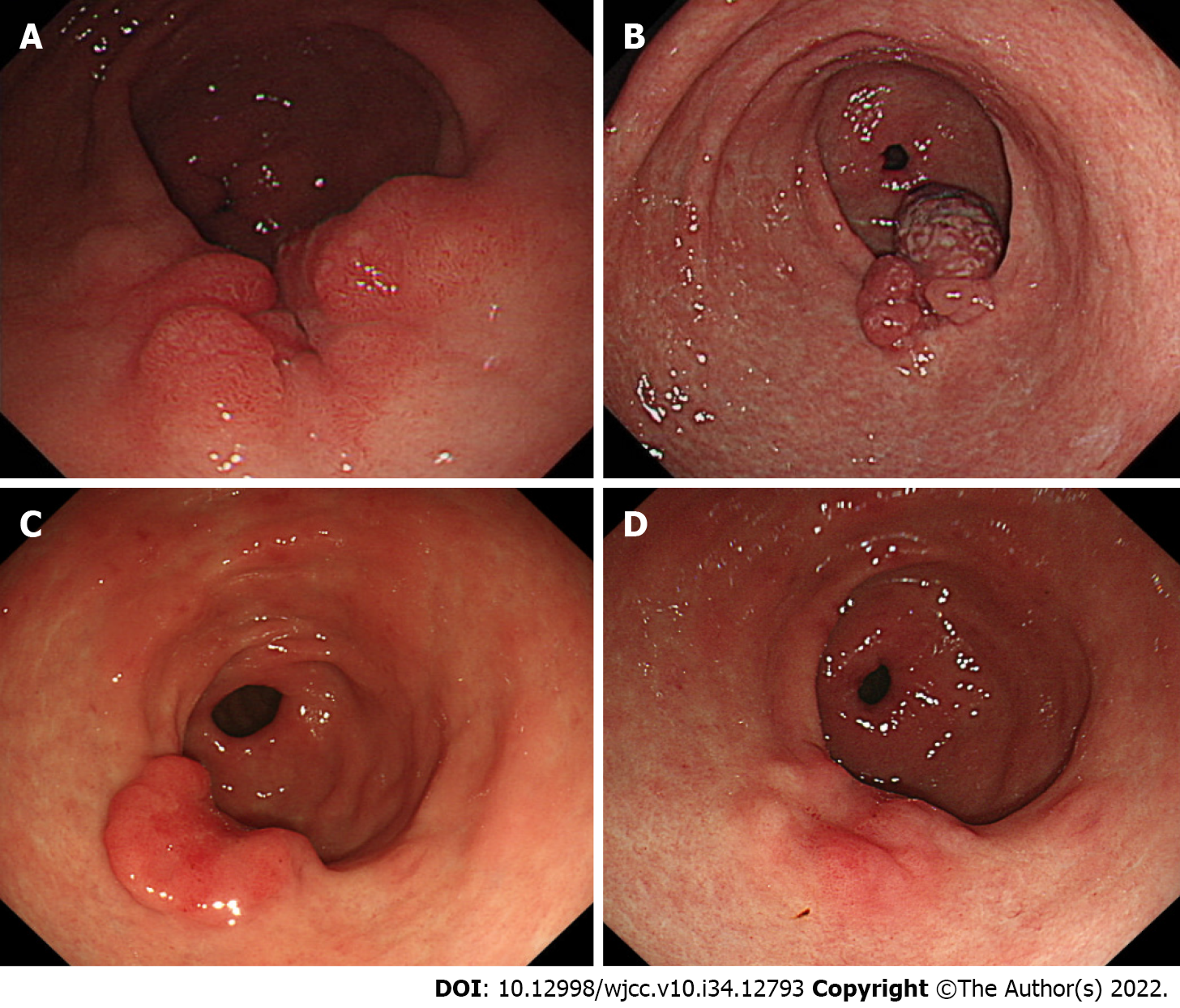
Figure 2 Endoscopy.
A: Polypoid nodular scar at previous endoscopic submucosal dissection site after 3 mo; B: Aggravation of polypoid nodular scar after 1 year; C: Decreased in size of the polypoid nodular scar, 1 year after Helicobacter pylori eradication; D: Regression of polypoid nodular scar, 2 year after Helicobacter pylori eradication.
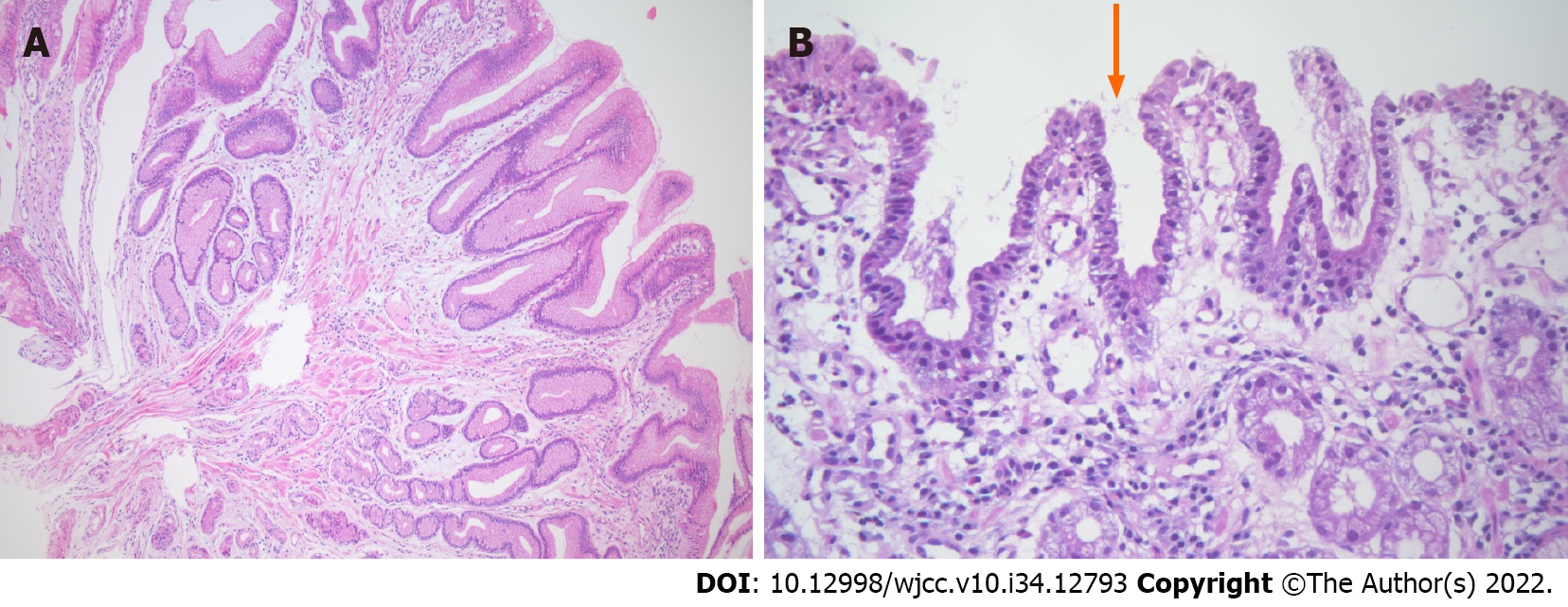
Figure 3 Endoscopic biopsy.
A: Histologic finding of poypoid nodular scar, 3 mo after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastric hyperplastic polyp. This polyp shows tortuous distorted and dilatated glands, abundant lamina propria. There is no evidence of dysplasia (hematoxylin and eosin, ×100); B: Histologic finding of polypoid nodular scar, 1 year after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Helicobacter pylori were identified within foveolar epithelium (arrow) (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400).
- Citation: Jin BC, Ahn AR, Kim SH, Seo SY. Regression of gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection induced polypoid nodular scar after Helicobacter pylori eradication: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(34): 12793-12798
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i34/12793.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12793