©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 16, 2022; 10(32): 11853-11860
Published online Nov 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.11853
Published online Nov 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.11853
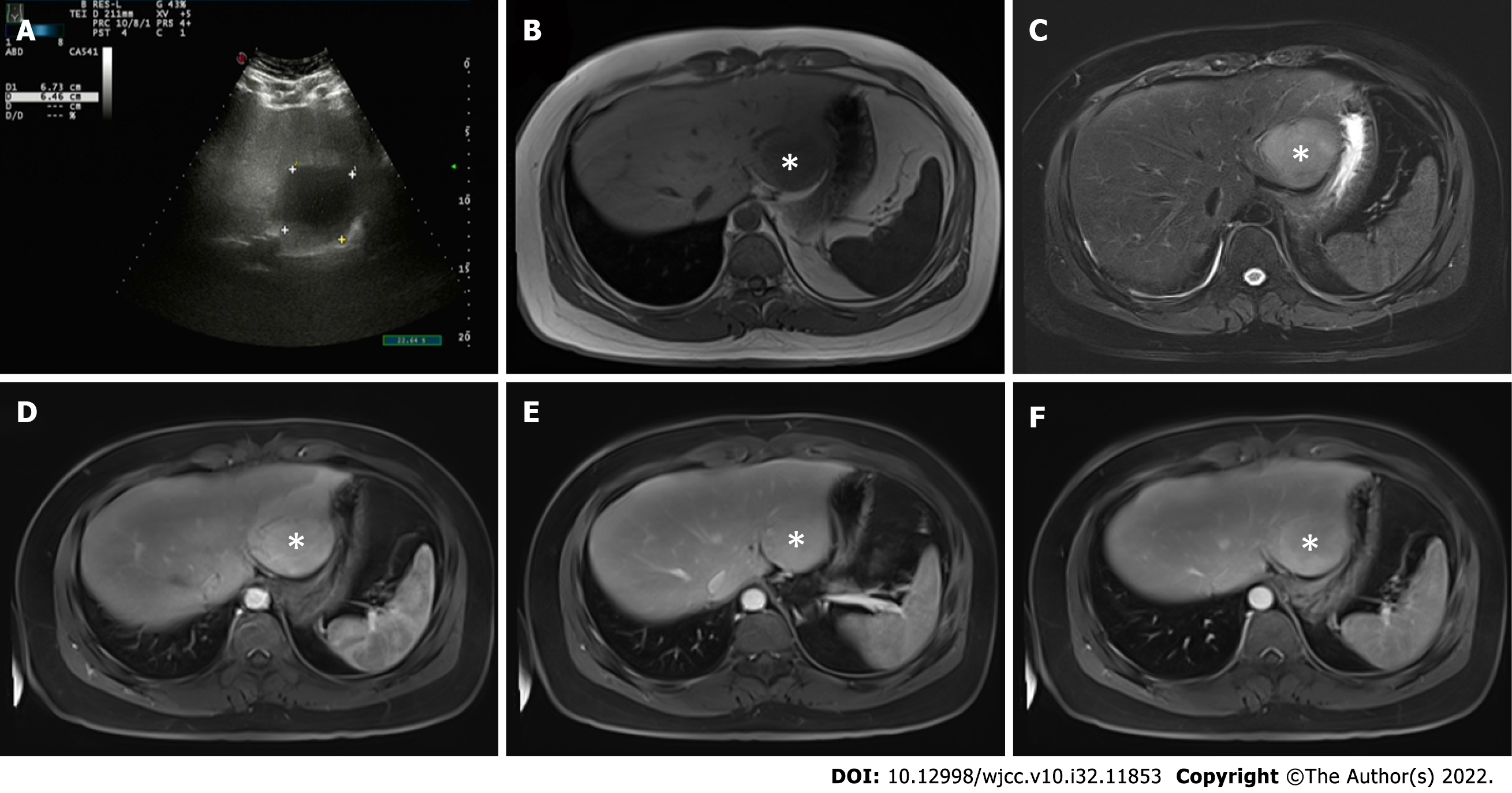
Figure 1 Abdominal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging findings (tumors were marked by the asterisk).
A: Abdominal ultrasound showed that the liver capsule was intact, and a low-echo area of 67 mm × 64 mm could be seen in segments II and III of the liver; B and C: Plain and enhanced upper abdominal magnetic resonance imaging showed that the T1-weighted imaging (B) of liver segments II and III (48 mm × 53 mm) was low, and T2-weighted imaging (C) revealed medium and high signal shadows; D: There was obvious patchy enhancement in the liver at the edge of the lesions in the arterial phase; E and F: Some signals in the lesions in the venous phase (E) were reduced, and in the balanced phase (F), the enhanced signal decreased slightly.
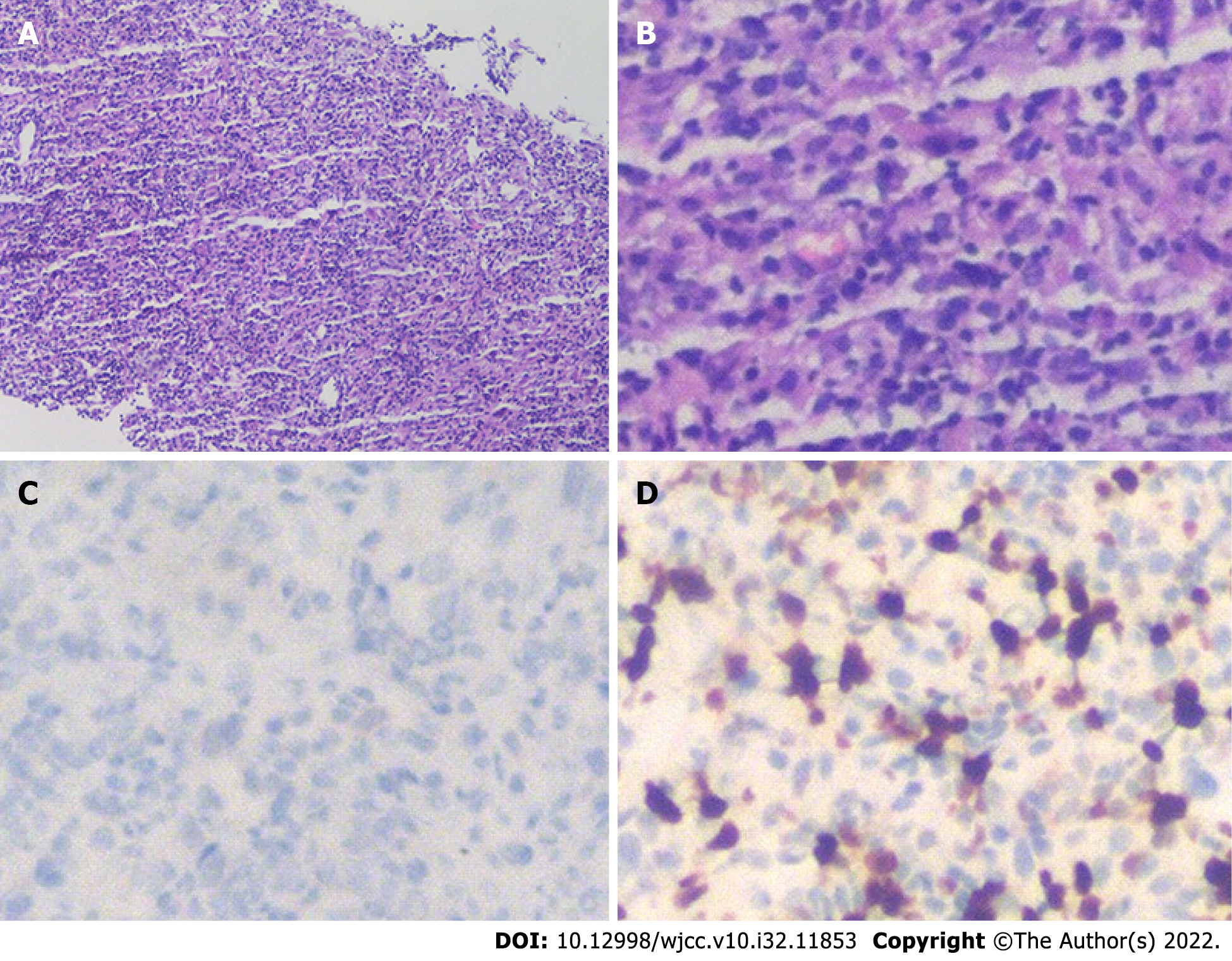
Figure 2 Microscopic examination results of liver biopsy under ultrasound guidance.
A: Routine HE staining showed that there was no obvious monoclonal proliferation of cells (100×), and immunohistochemistry showed that the mass was composed of lymphocytes, myofibroblasts, spindle cells and plasma cells; B: At higher magnification (400×), HE staining was more obvious; C and D: ALK-D5F3 (C) and Ki-67 (D) immunohistochemistry of spindle cells was positive (400×). HE: Hematoxylin and eosin.
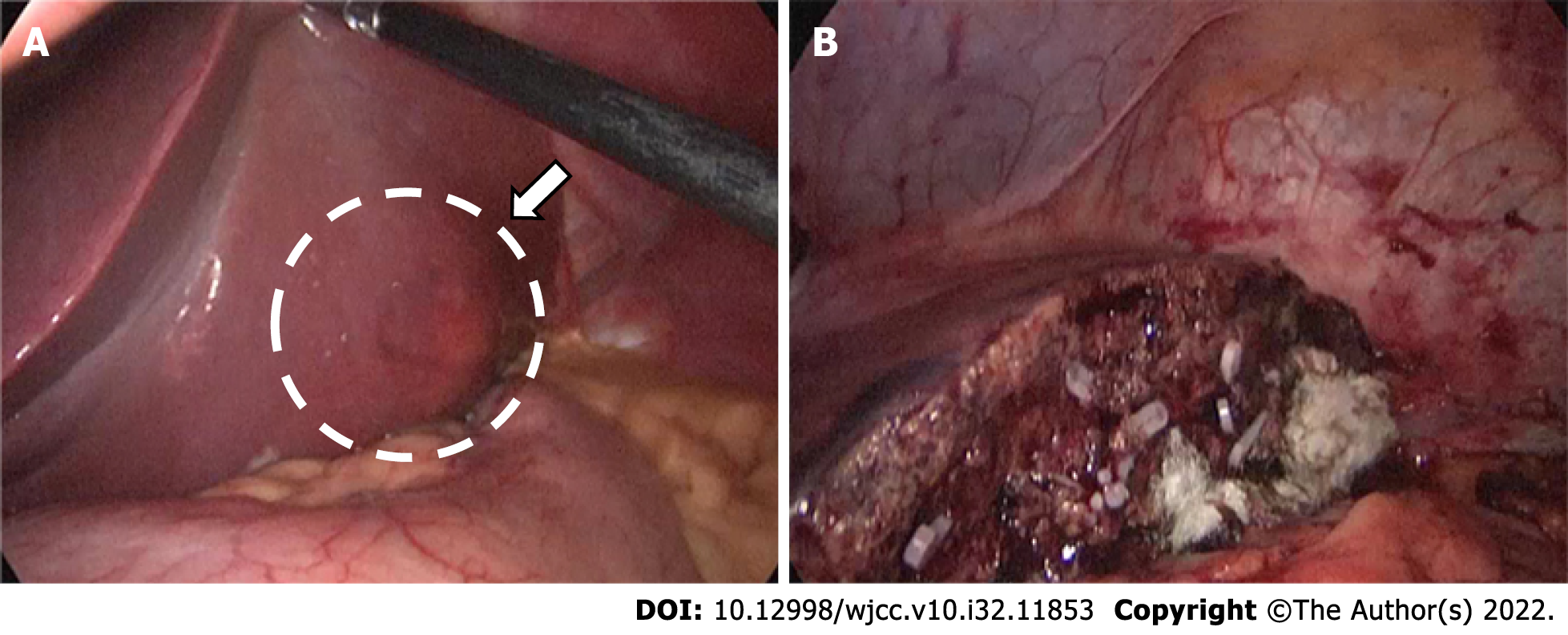
Figure 3 Intraoperative photographs.
A: A nodular bulge with a diameter of about 5 cm (arrow) was seen on the visceral surface of liver segments II and III; B: The tumor was completely removed after partial hepatectomy.
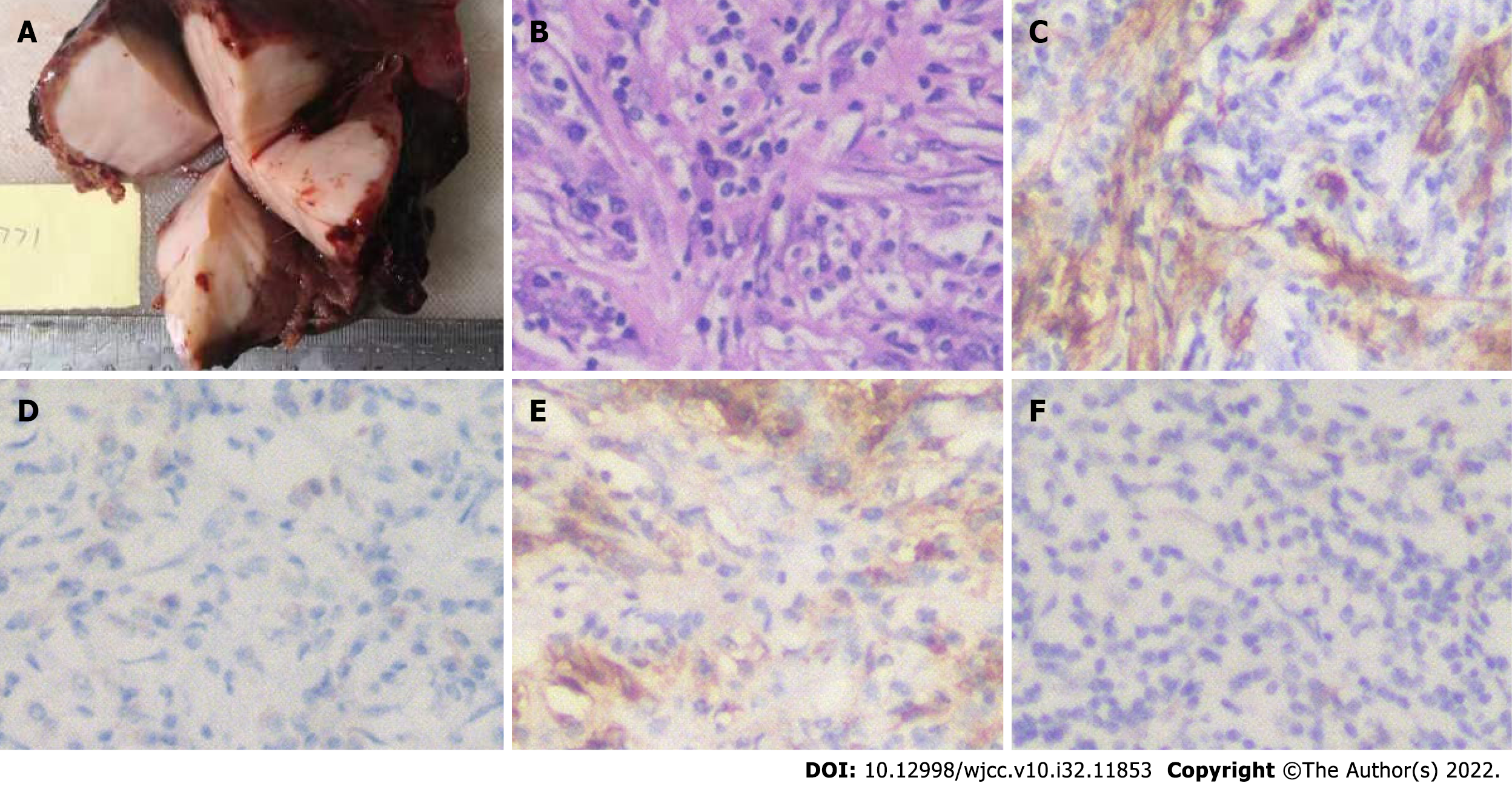
Figure 4 Imaging and immunohistochemistry of the surgical specimens.
A: The maximum diameter of the inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in the liver nodule was 6.5 cm. Yellow–white granulation-like tissue was seen in the sections, and the parenchyma was hard; B: Hematoxylin and eosin staining after surgery showed fibroblast proliferation and abundant plasma cell and lymphocyte infiltration in the stroma; C: Immunohistochemistry (400×) was positive for smooth muscle actin; D and E: Spindle cells (400×) were also positive for CD38 (D) and CD138 (E); F: Tumor cells showed a positive cytoplasmic reaction with ALK (400×).
- Citation: Li YY, Zang JF, Zhang C. Laparoscopic treatment of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in liver: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(32): 11853-11860
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i32/11853.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i32.11853