©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 21, 2022; 10(3): 856-869
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.856
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.856
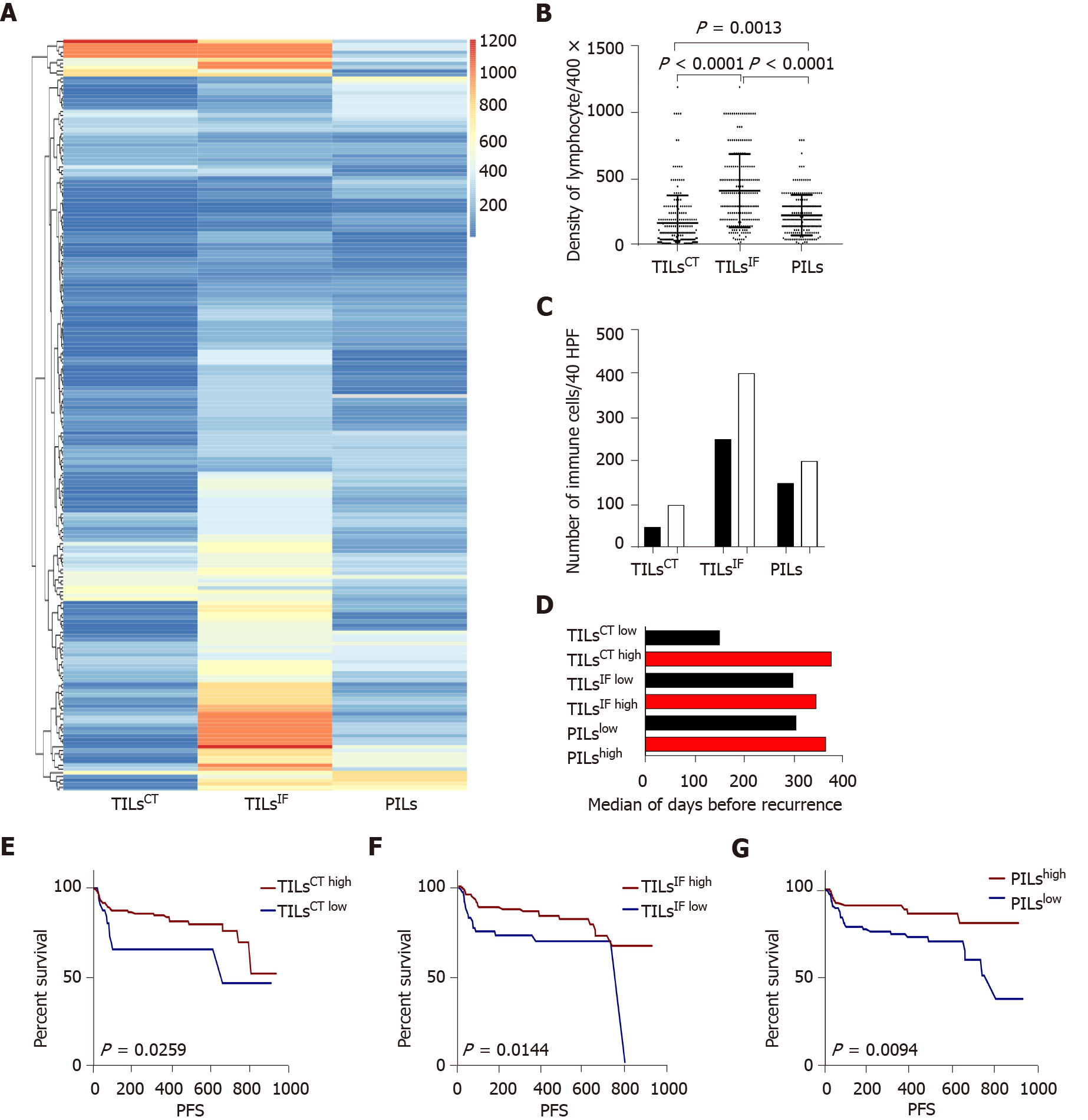
Figure 1 The distribution and recurrence association of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the tumor center, invasive front, and peritumor.
A: The spectrum of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the tumor center (TILsCT), TILs in the invasive front (TILsIF), and TILs in the peritumor (PILs) of 204 cases. TILsCT were lower than TILsIF and PILs. TILsIF was the most flaming part than the other two areas; B: Dot map of TILsCT, TILsIF, and PILs, indicating a heterogeneous distribution of inflammation; C: Comparison of the mean of TILsCT, TILsIF and PILs from patients with tumor recurrence (black bars) or without tumor recurrence (white bars); D: Median survival time for all patients, with high densities (red bars) or low densities (black bars) of TILsCT, TILsIF and PILs; E, F and G: Patients with high TILsCT, TILsIF, and PILs had a lower recurrence rate. TILsCT: Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the tumor center; TILsIF: Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the invasive front 1 mm spacing from the malignant nests; PILs: infiltrating lymphocytes in the peritumor.
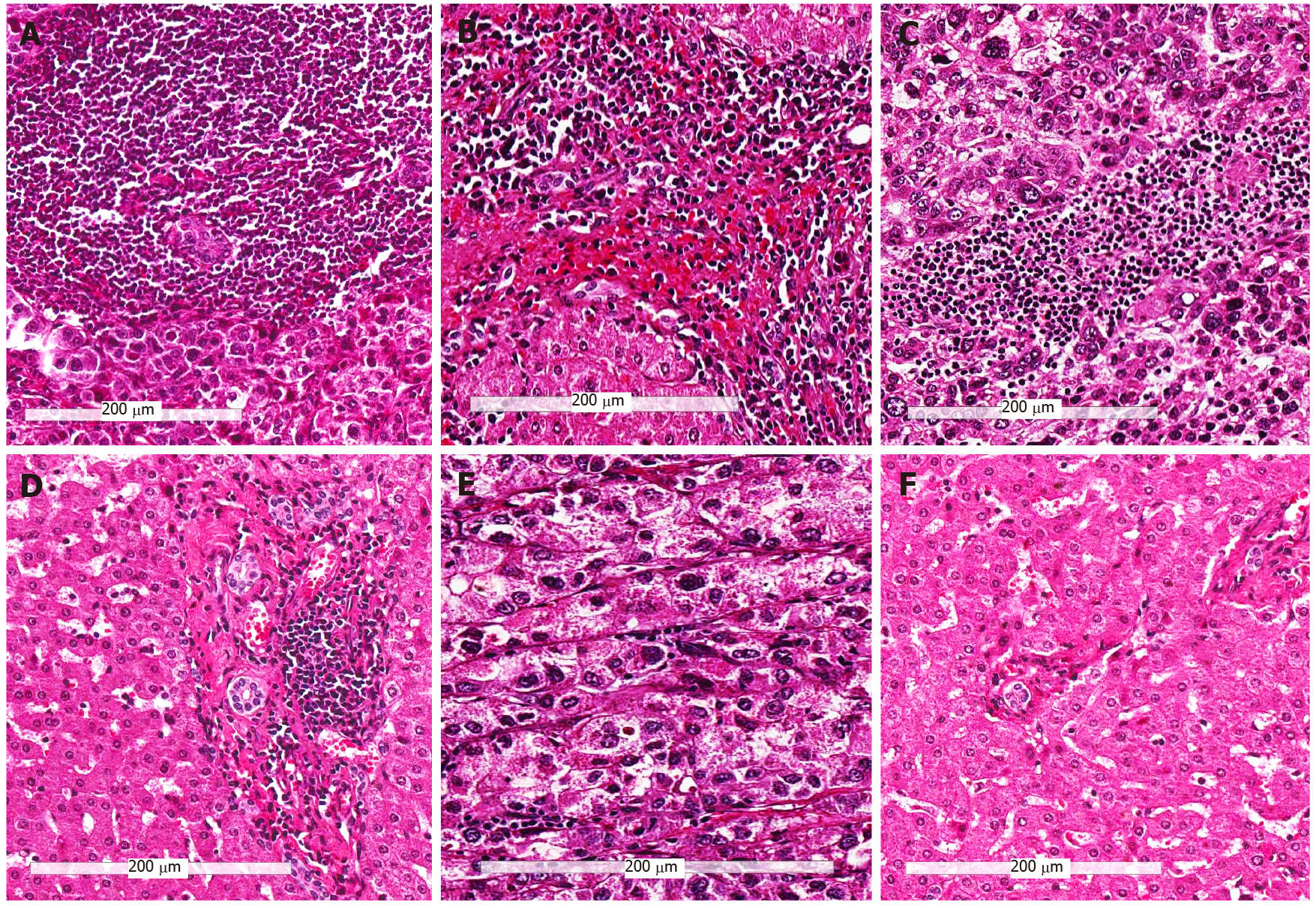
Figure 2 Representative hematoxylin and eosin images of the three immune subtypes (200 ×).
A and B: Tumors with high infiltrating lymphocytes in the tumor center, invasive front and peritumor (Immunehigh) subtype; C and D: Tumors other than immunehigh and immunelow (Immunemod) subtype; E and F: Tumors with low infiltrating lymphocytes in the tumor center, invasive front and peritumor (Immunelow) subtype; A, C, and E: Immune cells in tumor center; B, D, and F: Immune cells in the peritumor region.
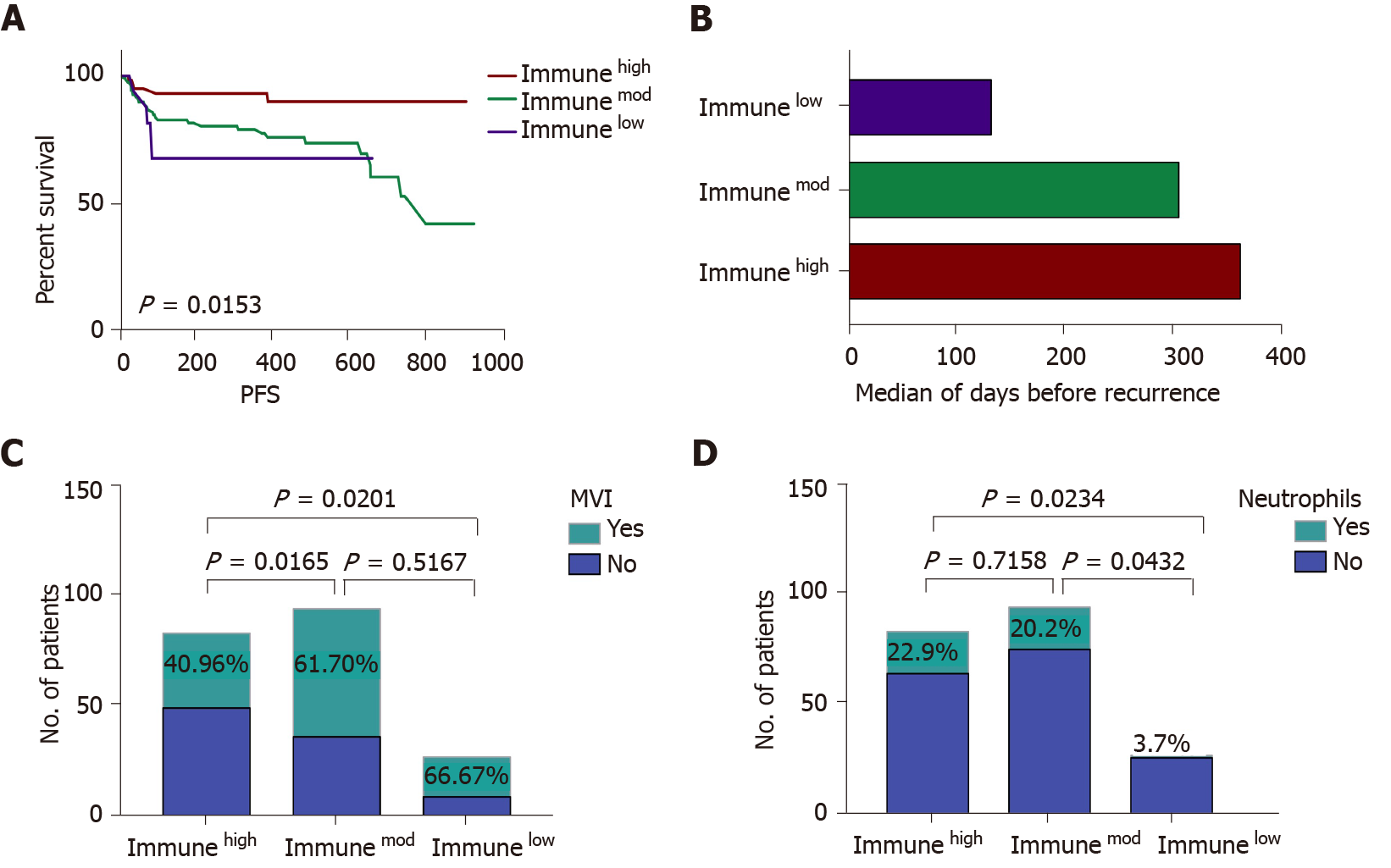
Figure 3 The comparison of immunehigh, immunemod and immunelow subtypes.
A: Immune subtypes can predict patients’ progression-free survival. Immunehigh patients had a low recurrence rate, and immunelow patients experienced a high recurrence rate; B: The median survival time for all patients divided into three categories: Immunehigh (red bars), immunemod (green bars), and immune low (purple bars); C: The incidence rate of microvascular invasion (MVI) in three immune subtypes, immunehigh subtype had a lower rate of MVI compared to immunemod and immunelow subtypes; D: The presence of neutrophils in the three immune subtypes, a high incidence of neutrophils was detected in immunehigh and immunemod subtypes. Immunehigh: Tumors with high infiltrating lymphocytes in the tumor center, invasive front and peritumor; Immunemod: Tumors other than immunehigh and immunelow; Immunelow: Tumors with low infiltrating lymphocytes in the tumor center, invasive front and peritumor; PFS: Progression-free survival; MVI: Microvascular invasion.
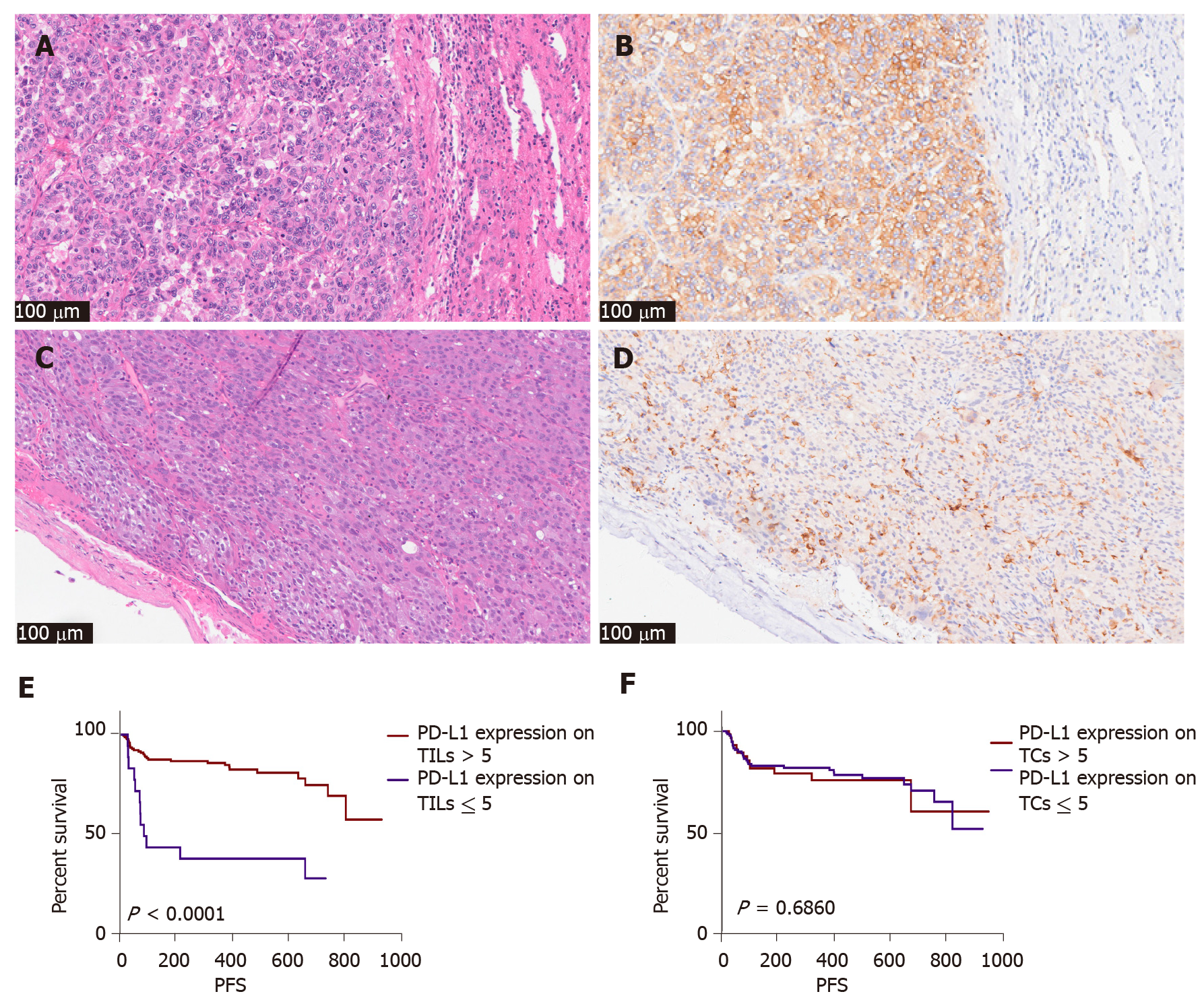
Figure 4 The pathological picture and recurrence association of programmed cell death-ligand 1 SP142 expression in tumor cells and immune cells (200 ×).
A and B: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) picture of programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) SP142 in tumor cells of one case; C and D: H&E and IHC picture of PD-L1 SP142 in immune cells of another case; E: Patients with high expression of PD-L1 (SP142) on tumor infiltrating lymphocytes tend to have less recurrence; F: Expression of PD-L1 (SP142) on tumor cells was not statistically significant. PD-L1: Programmed cell death-ligand 1; IHC: TILs: Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes; TCs: Tumor cells; PFS: Progression-free survival.
- Citation: Du M, Cai YM, Yin YL, Xiao L, Ji Y. Evaluating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma using hematoxylin and eosin-stained tumor sections. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(3): 856-869
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i3/856.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.856