©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2022; 10(24): 8662-8666
Published online Aug 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i24.8662
Published online Aug 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i24.8662
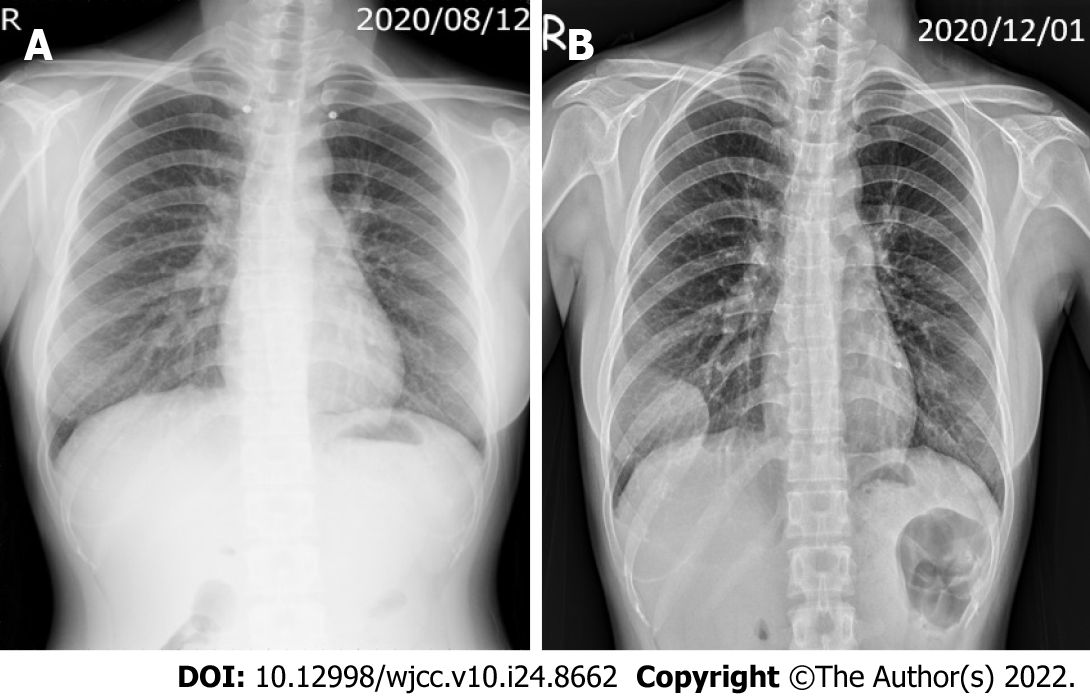
Figure 1 Chest X-ray findings.
A: Initial chest film after the trauma revealed no fracture of the rib or mass lesion; B: Chest film at 3 mo after the trauma revealed a 5.1 cm, partially circumscribed mass-like opacity in the right lower chest wall, with adjacent rib destruction.
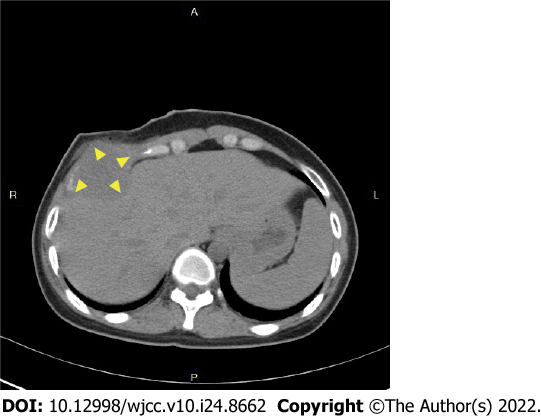
Figure 2
Chest computed tomographic scan showed a 5-cm tumor at the right anterior chest wall, with destruction of the right 6th rib.
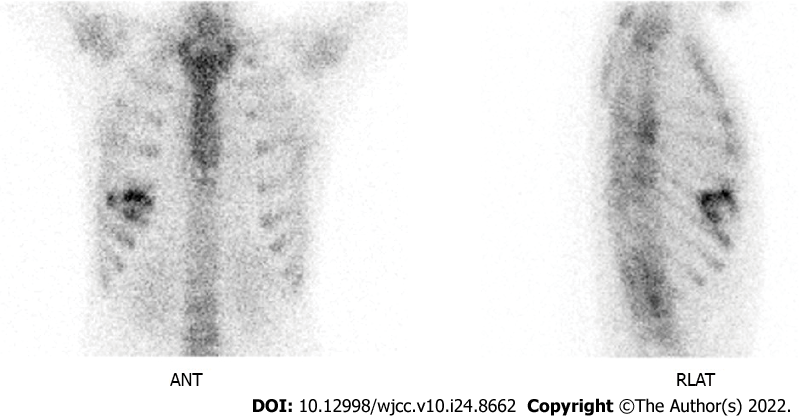
Figure 3
Whole-body bone scan showed increased uptake in the right 5th to 7th ribs.
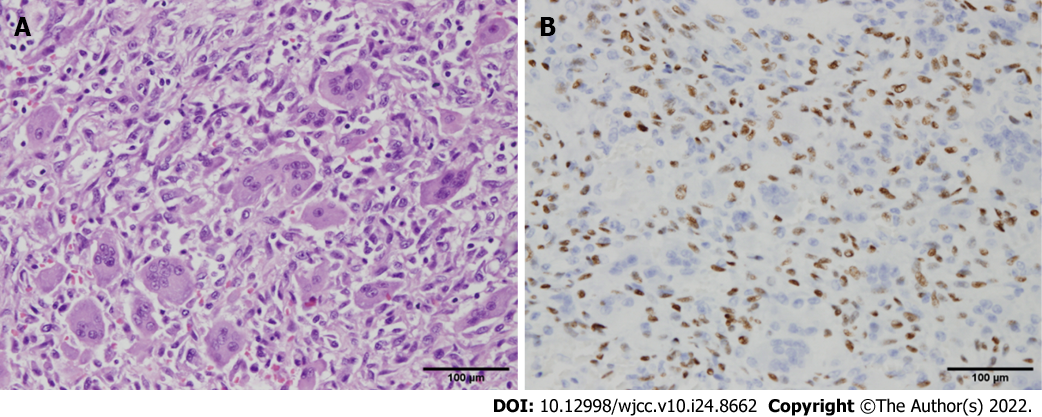
Figure 4 Histopathology findings.
A: Many osteoclast-like giant cells were distributed throughout the tumor, with scattered oval to spindle mononuclear cells in the background (hematoxylin and eosin); B: The mononuclear cells uniformly showed nuclear staining for H3F3A expression (immunohistochemical stain of H3F3A). Original magnification: × 400.
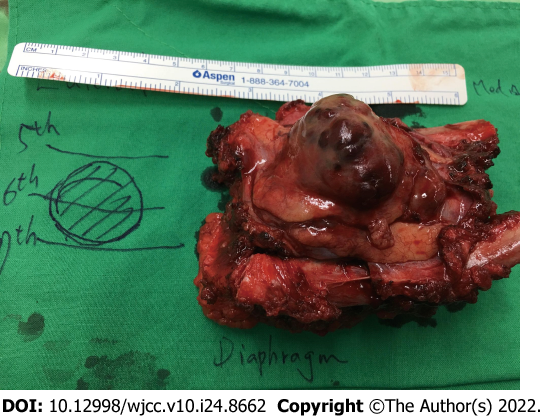
Figure 5
Gross specimen after surgical resection.
- Citation: Chen YS, Kao HW, Huang HY, Huang TW. Traumatic giant cell tumor of rib: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(24): 8662-8666
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i24/8662.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i24.8662