©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2022; 10(21): 7545-7552
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7545
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7545
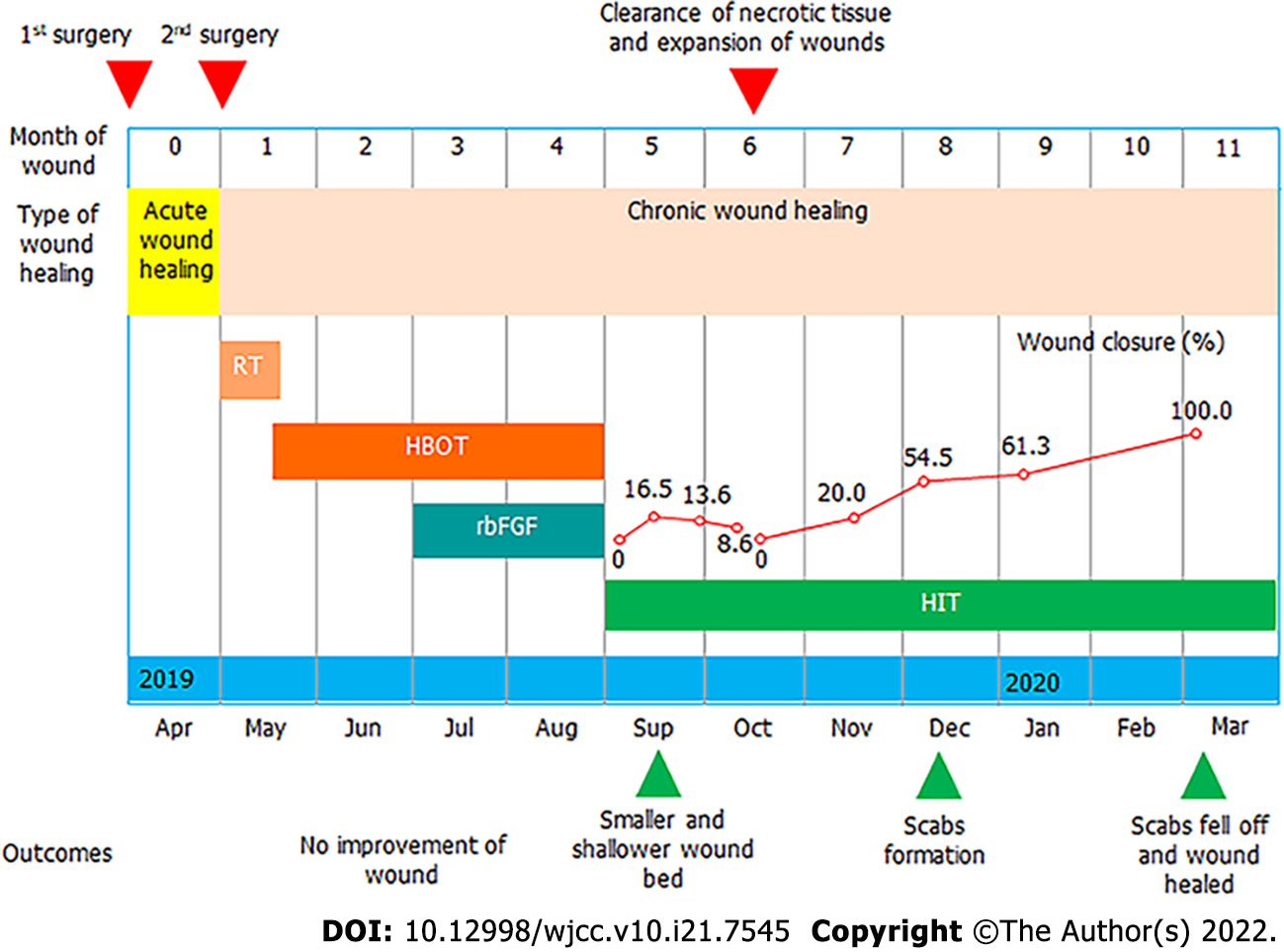
Figure 1 Clinical course, treatments, and outcomes of the case.
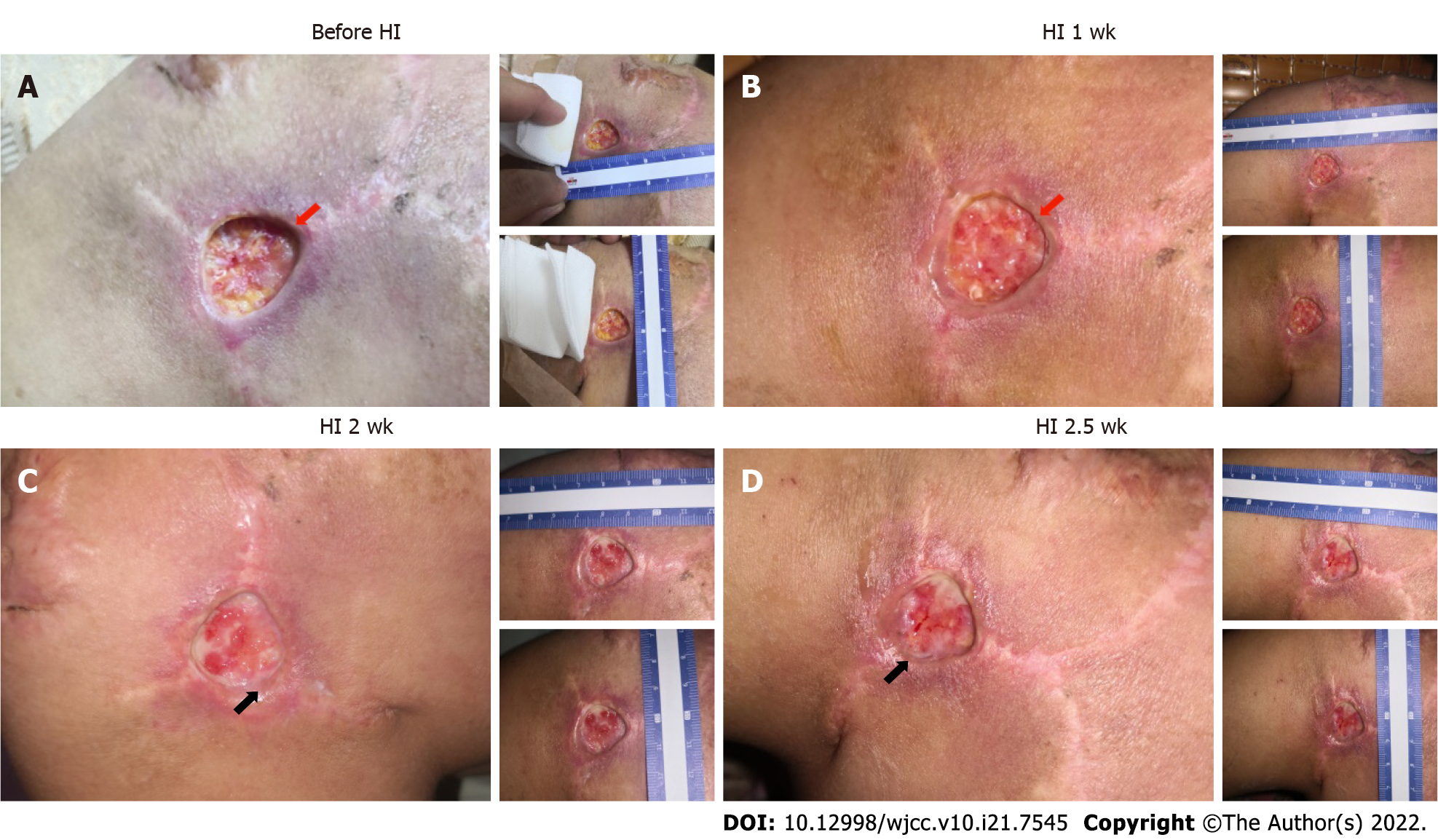
Figure 2 Outcomes of the patient after hydrogen inhalation therapy in the first 3 wk.
A: Deep wound (red arrow) before hydrogen inhalation therapy, with the skin separated from the subcutaneous tissue; B: The wound grew shallower (red arrow), and the skin adhered better to the subcutaneous tissue; C: Wound edge migration was initiated (black arrow), and more blood vessels were visible in the wound bed; D: More migration around the wound edge (black arrow).
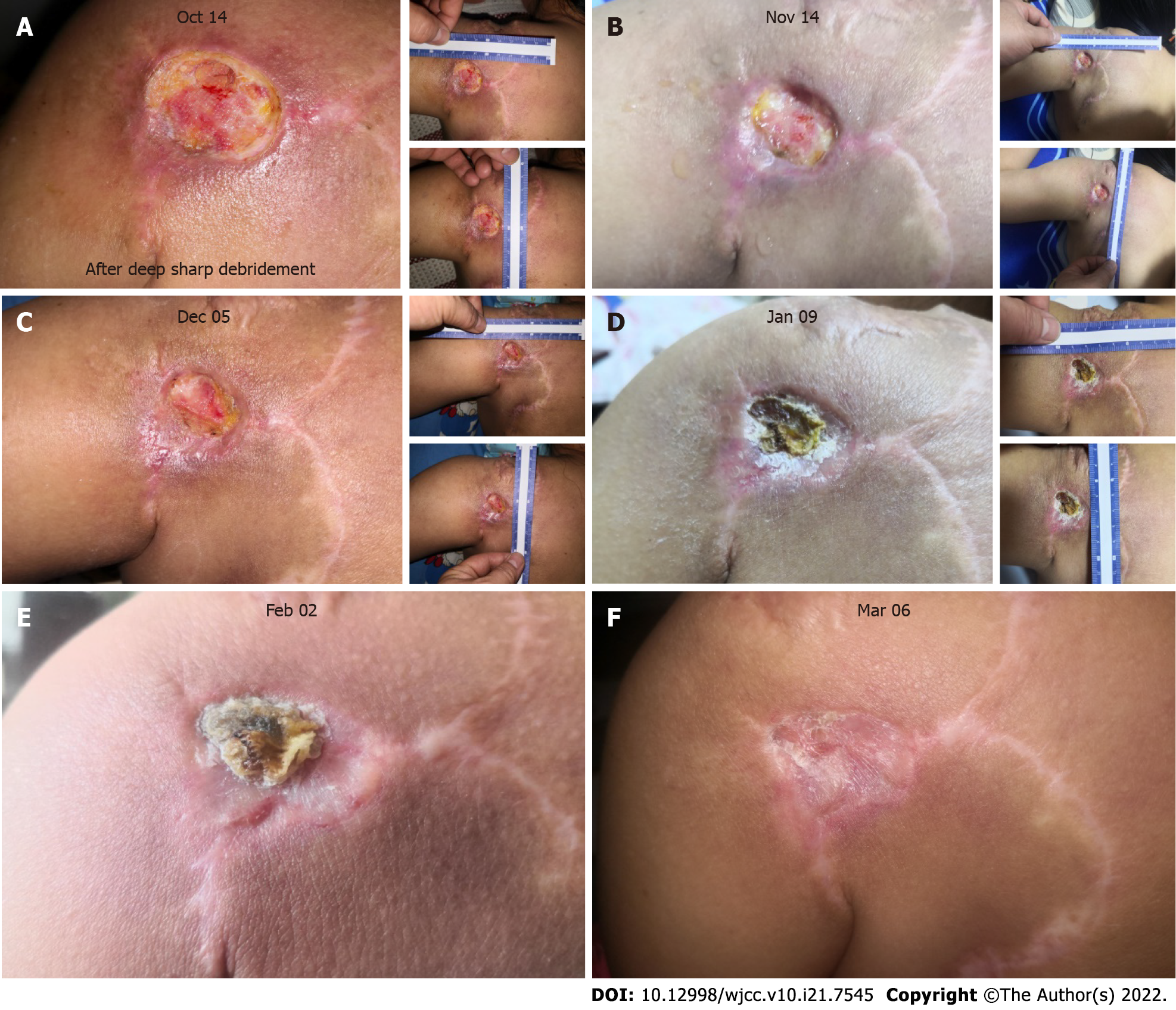
Figure 3 Healing process of the patient’s chronic wound in the 5 mo following hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
A: On the first day after deep, sharp debridement (October 14, 2019), the wound was enlarged to 2.5 cm × 2.3 cm; B: One month later (November 14, 2019), rapid reepithelialization had occurred, and wound edge migration was observed; C: The wound closed further (December 5, 2019), and a small amount of exudate was secreted around the wound edge; D: A scab formed on top of the wound bed (January 9, 2020); E: Tissue beneath the wound was further remodeled and repaired, with a scab covering the wound bed (February 2, 2020); F: The scab fell off and the wound was healed.
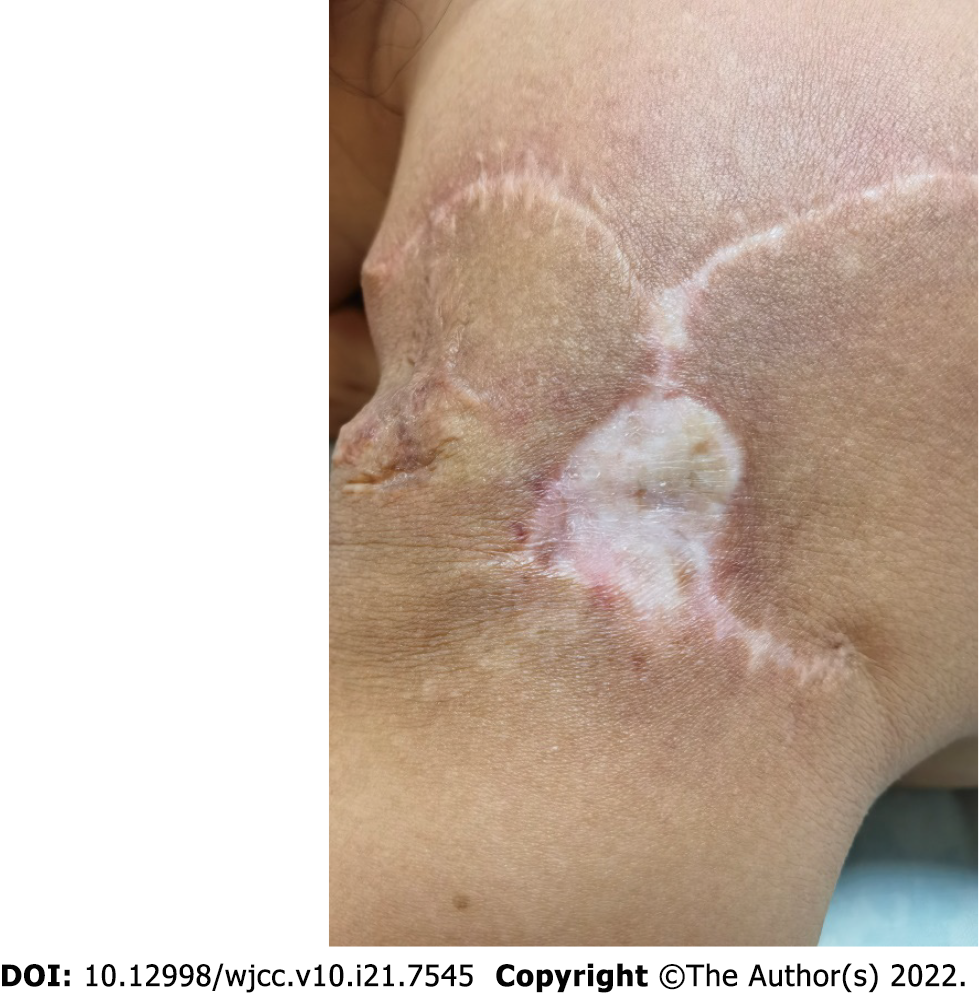
Figure 4 The patient’s facial appearance at the 1-yr follow-up after surgery.
- Citation: Zhao PX, Luo RL, Dang Z, Wang YB, Zhang XJ, Liu ZY, Wen XH, Liu MY, Zhang MZ, Adzavon YM, Ma XM. Effect of hydrogen intervention on refractory wounds after radiotherapy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(21): 7545-7552
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i21/7545.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7545