©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. May 16, 2022; 10(14): 4519-4527
Published online May 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4519
Published online May 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4519
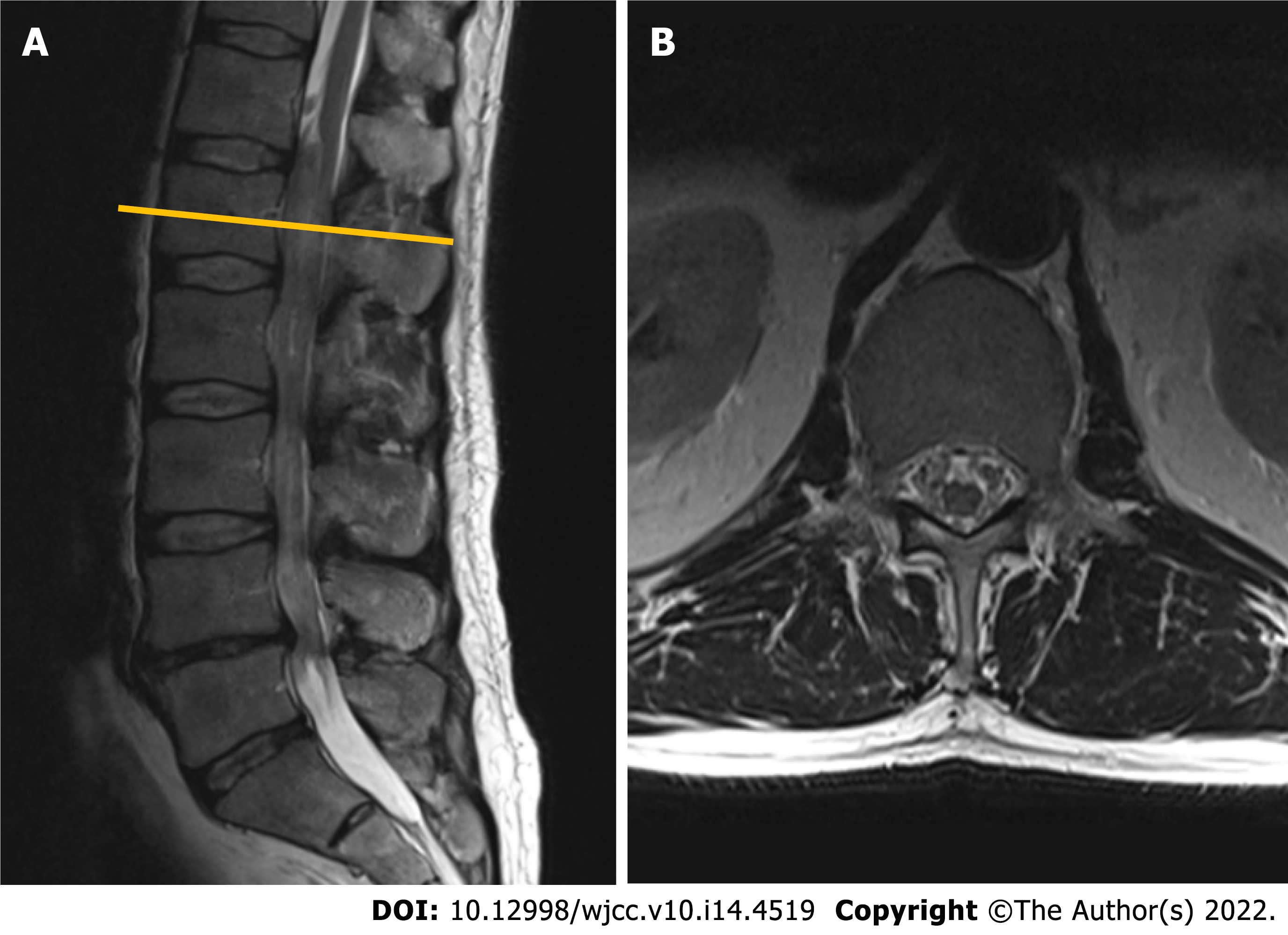
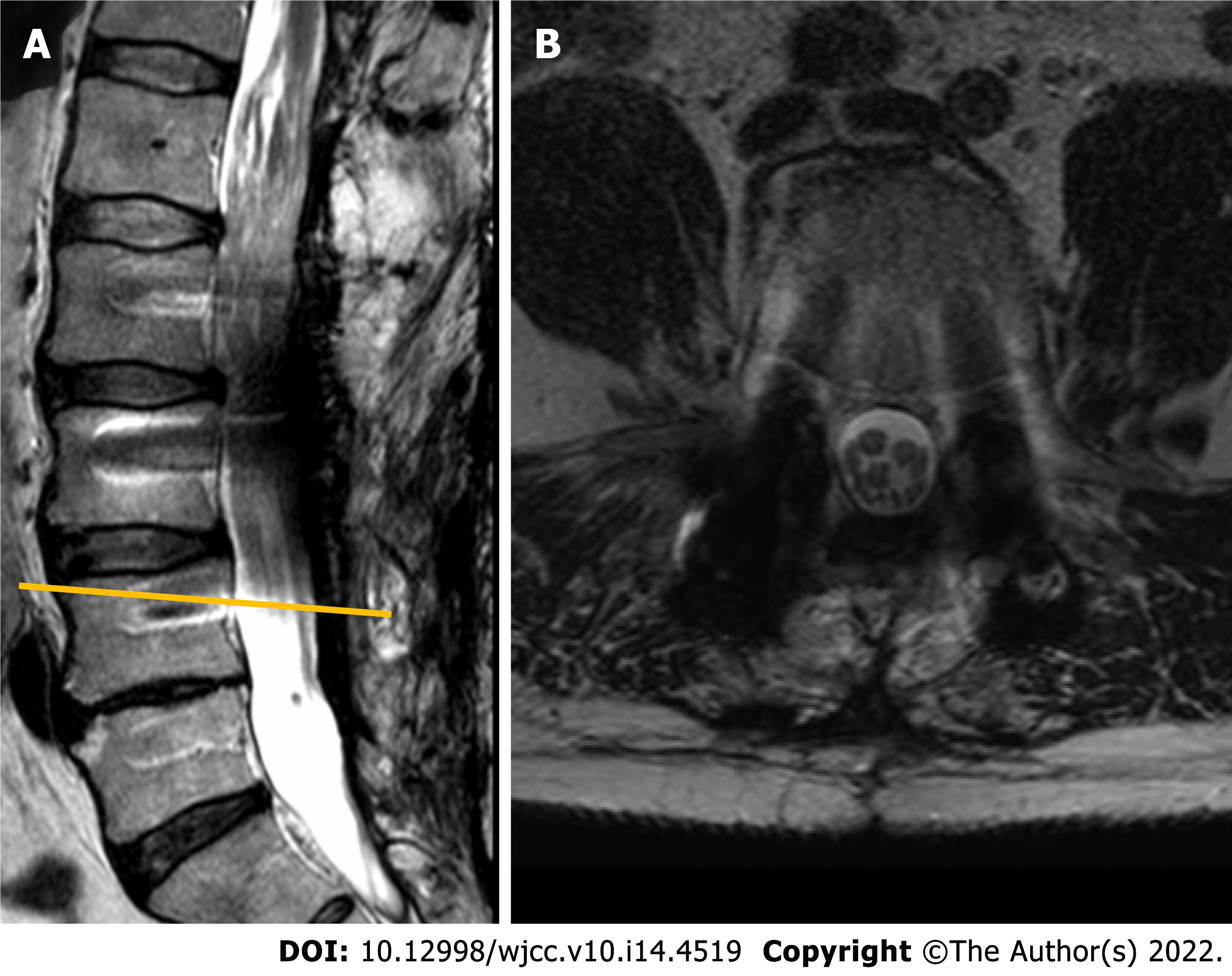
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (T2-weighted imaging sequence) performed in 2010 revealed a non-enhancing intradural tumor extending throughout the Th12-L4 vertebral levels.
A: Sagittal plane: a non-enhancing intradural tumor extending throughout the Th12-L4 vertebral levels; B: Axial plane. Tumor at the level of L1 vertebral body. Note few enlarged lumbar nerve roots engulfing conus medullaris.
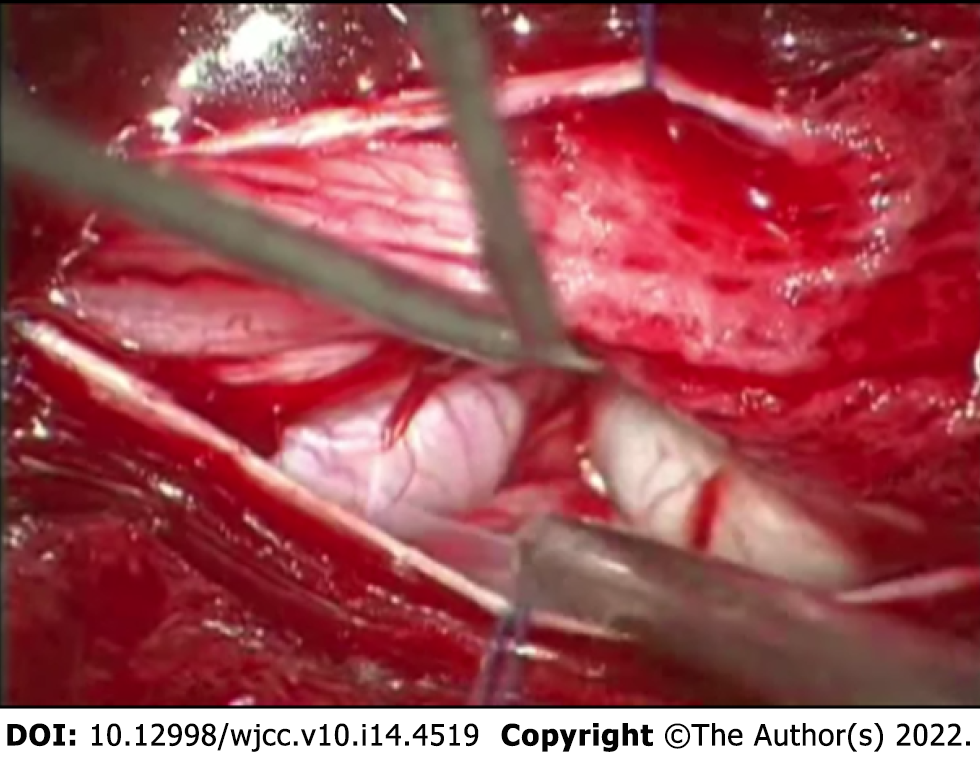
Figure 2 Intraoperative photograph demonstrating the enlarged nerve root which emerged immediately following the duratomy.
Figure 3 The histological appearance of the pathological specimen, final diagnosis was consistent with plexiform neurofibroma.
A: 10 ×-magnified hematoxylin-eosin staining (H&E) micrograph: note the preserved gross architecture of the nerve and coagulated resection margin; B: 40 ×-magnified H&E micrograph. Appearance of hypocellular tumor consisting of Schwann cells with wavy contours and elongated nuclei with fine dense chromatin, fibroblasts, and mast cells. No signs of atypia were observed.
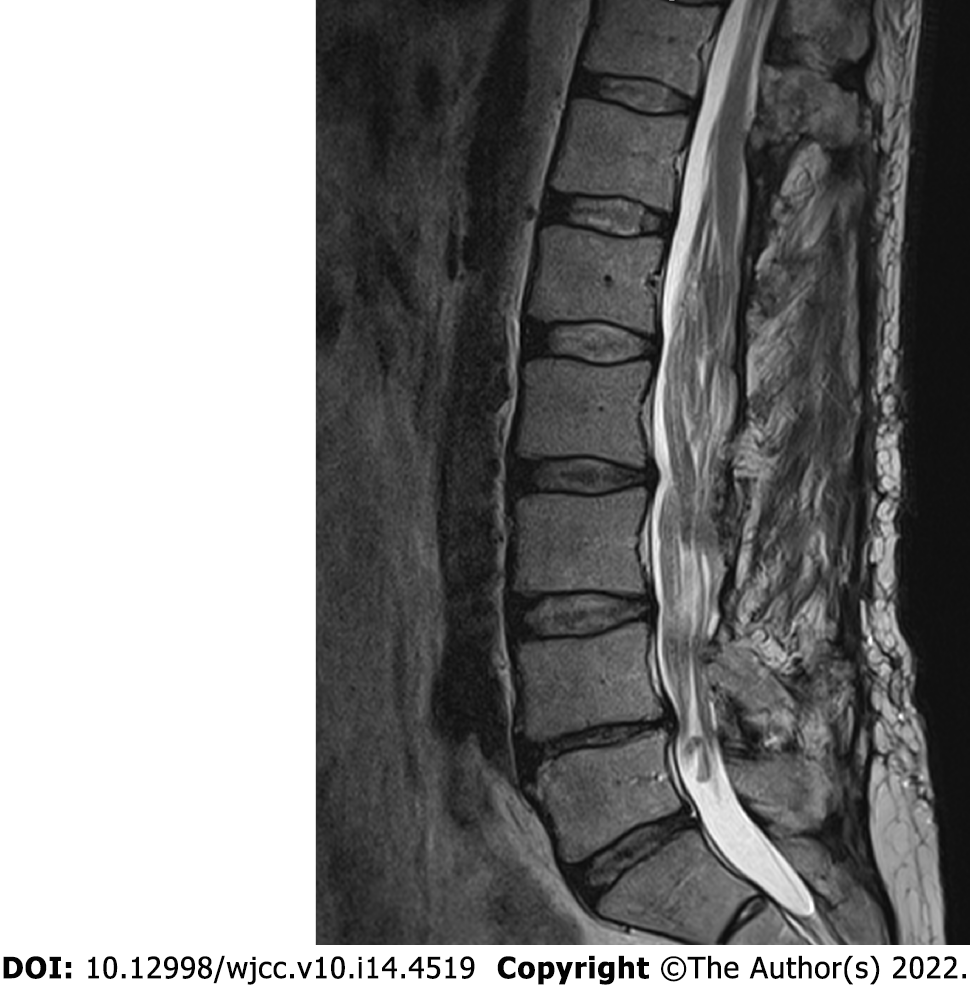
Figure 4 Subsequent magnetic resonance imaging (T2-weighted imaging sequence) control performed in 2015, midsagittal plane.
Note the slight increase in tumor mass over the 5 years following the initial surgery. Neoplastic expansion is accommodated by bony decompression and duraplasty.
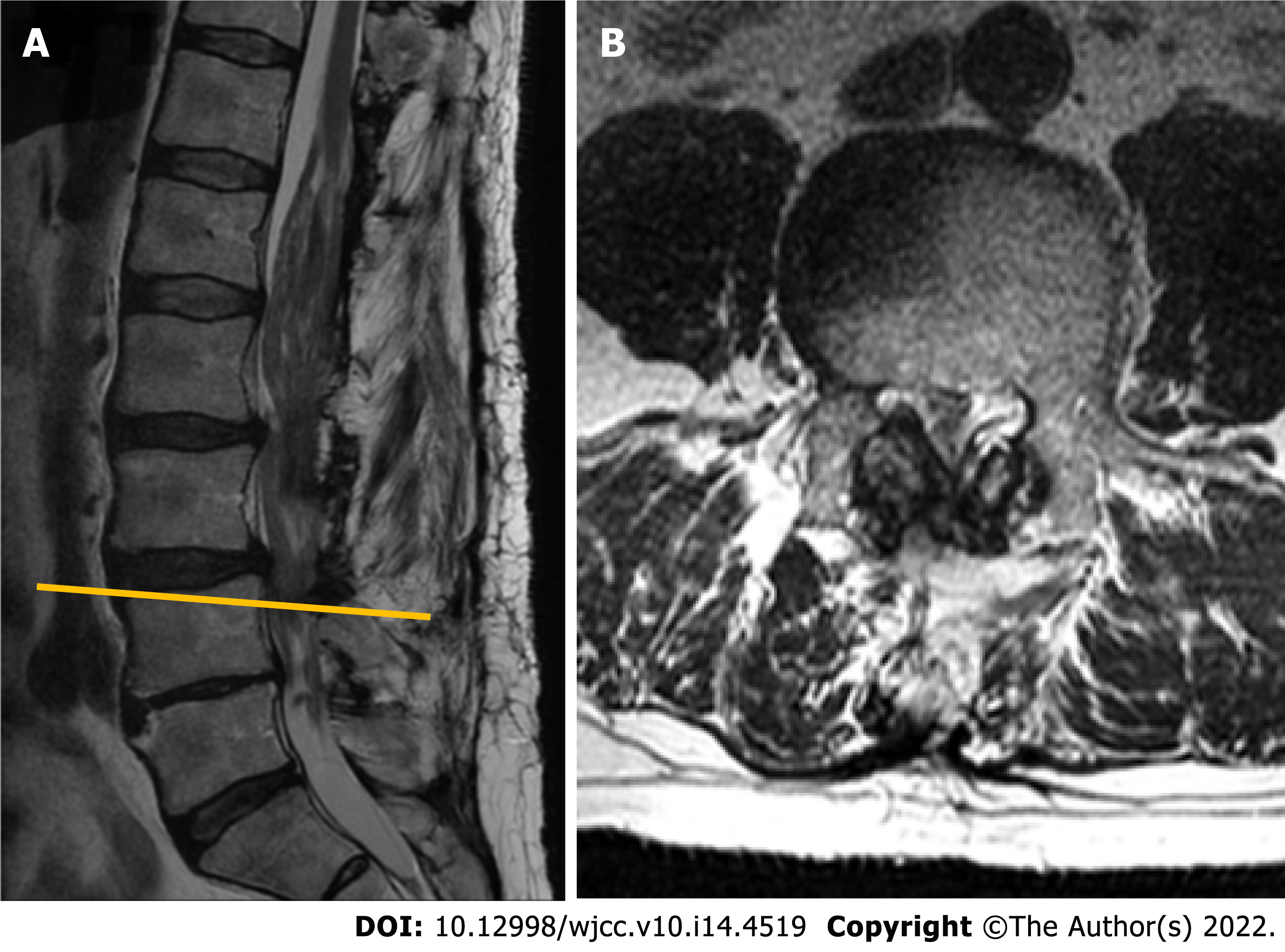
Figure 5 Magnetic resonance imaging (T2-weighted imaging sequence) performed in 2018.
A: Sagittal plane. Note markedly enlarged tumorous masses occupying the majority of the spinal canal, with a most significant stenosis at L3-L4 segment; B: Axial plane at L4 vertebral body level. Instability-induced ligamenta flava and facet joints (not seen in the section) hypertrophy, resulting in lumbar spinal stenosis at L3-L4 Level.
Figure 6 The magnetic resonance imaging (T2-weighted imaging sequence) performed in 2020 following the second surgery involving L4-L5 Laminectomy and L2-L5 transpedicular fixation.
A: Sagittal plane. Position of titanium screws following the transpedicular fixation. Titanium-induced artefacts prevent from reliable evaluation of the spinal canal and its contents; B: Axial plane at L3-L4 segment level. Note the additional space available in the central canal following the extended decompression.
- Citation: Chomanskis Z, Juskys R, Cepkus S, Dulko J, Hendrixson V, Ruksenas O, Rocka S. Plexiform neurofibroma of the cauda equina with follow-up of 10 years: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(14): 4519-4527
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i14/4519.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4519