©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 7, 2022; 10(1): 296-303
Published online Jan 7, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.296
Published online Jan 7, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.296
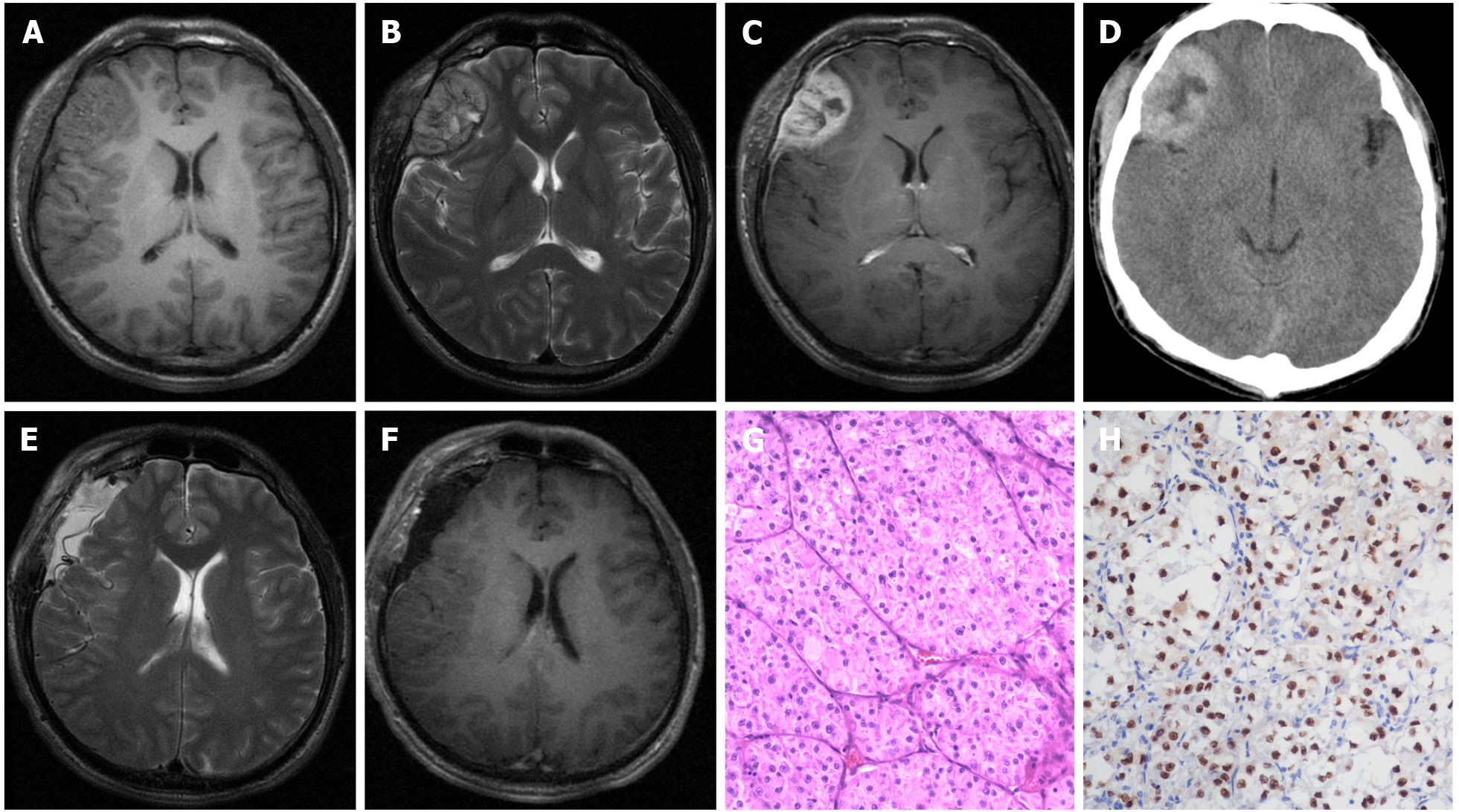
Figure 1 Radiological and histopathological findings.
A-D: Pre-operative magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography revealed a right frontal lesion with an isointense signal on T1 images (axial), hyperintense signal on T2 images (axial), and heterogeneous enhancement after the administration of gadolinium (axial) with a heterogeneously high-density appearance (axial). The presence of a "dural tail sign" was highly suggestive of meningioma; E and F: Postoperative magnetic resonance imaging proved that this lesion had completely resolved; G: Pathological morphology informed the diagnosis of intracranial alveolar soft-part sarcoma (hematoxylin-eosin, × 200); H: Showing that the tumor stained positively for TEF-3, immunohistochemical examination (× 200) further confirmed the diagnosis.
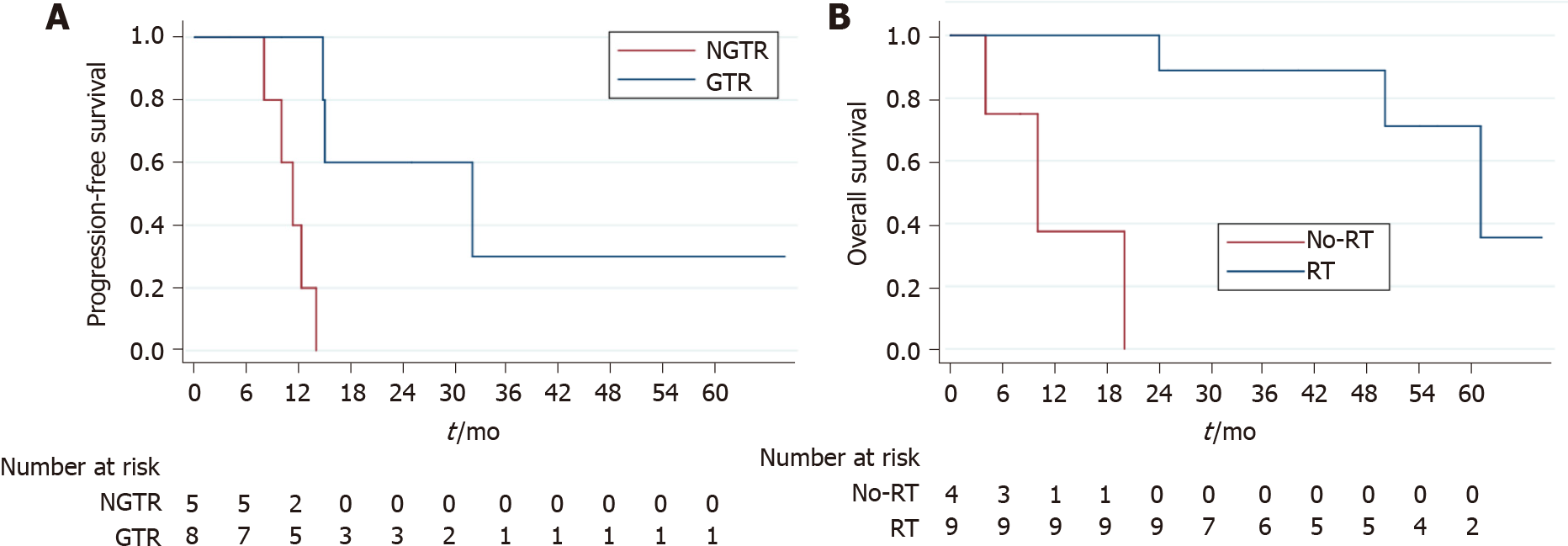
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
A: Gross total resection can prolong progression-free survival (PFS); B: Radiotherapy can improve overall survival (OS). ASPS: Alveolar soft part sarcoma; IASPS: Intracranial alveolar soft part sarcoma.
- Citation: Chen JY, Cen B, Hu F, Qiu Y, Xiao GM, Zhou JG, Zhang FC. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of primary intracranial alveolar soft-part sarcoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(1): 296-303
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i1/296.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.296