©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 7, 2022; 10(1): 205-216
Published online Jan 7, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.205
Published online Jan 7, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.205
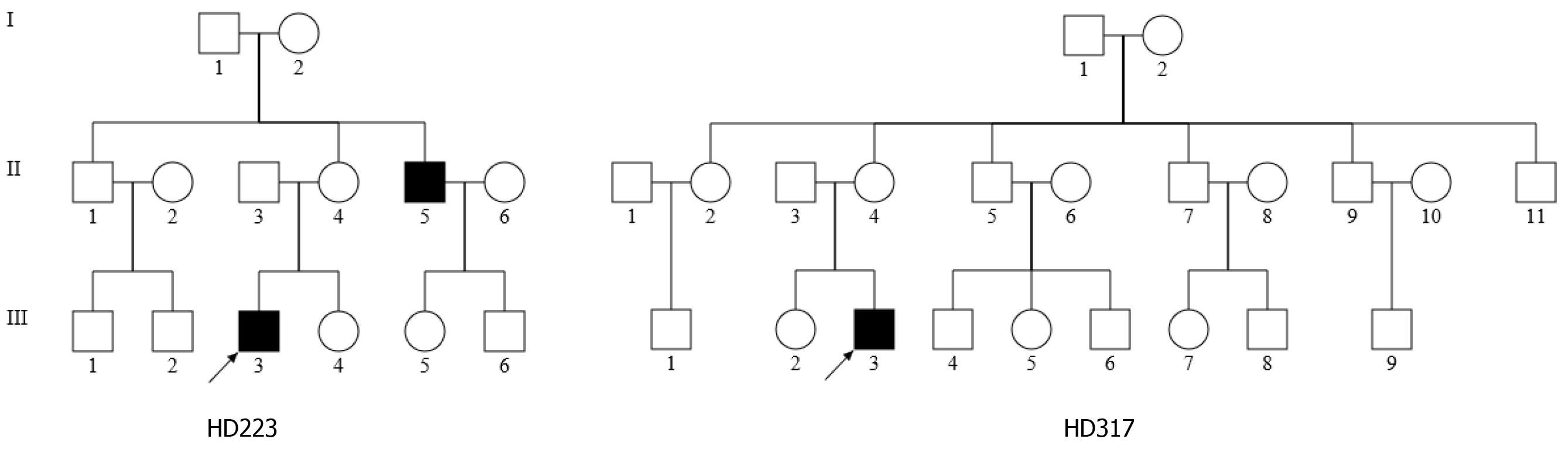
Figure 1 Two Chinese families with hearing loss.
An arrow denotes the proband.
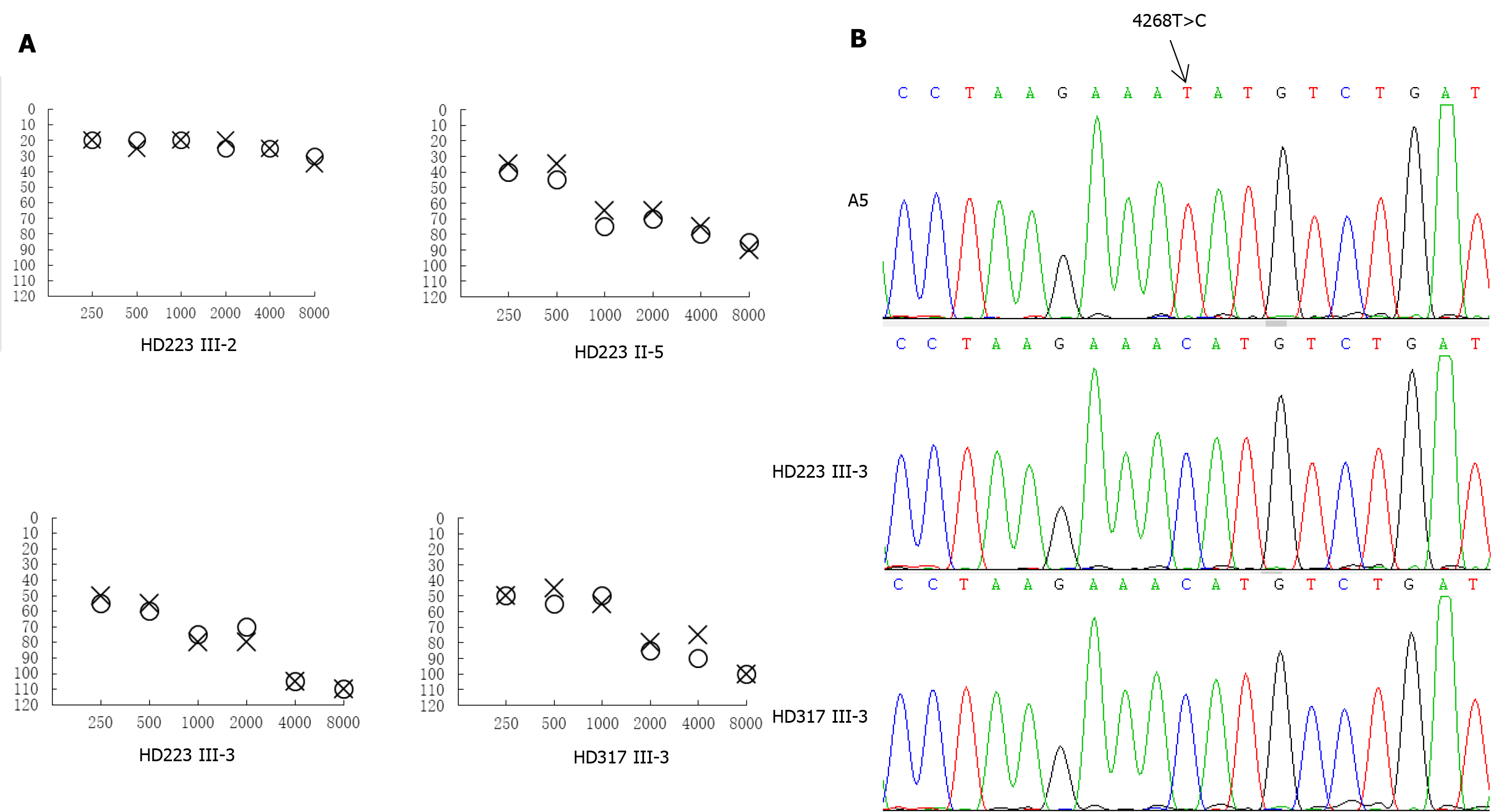
Figure 2 Clinical and genetic characterization of the two Chinese families.
A: Air conduction audiogram of four subjects. Symbols: X-left, O-right ear; B: Partial sequence chromatograms of tRNAIle gene from two probands and a control subject, respectively.
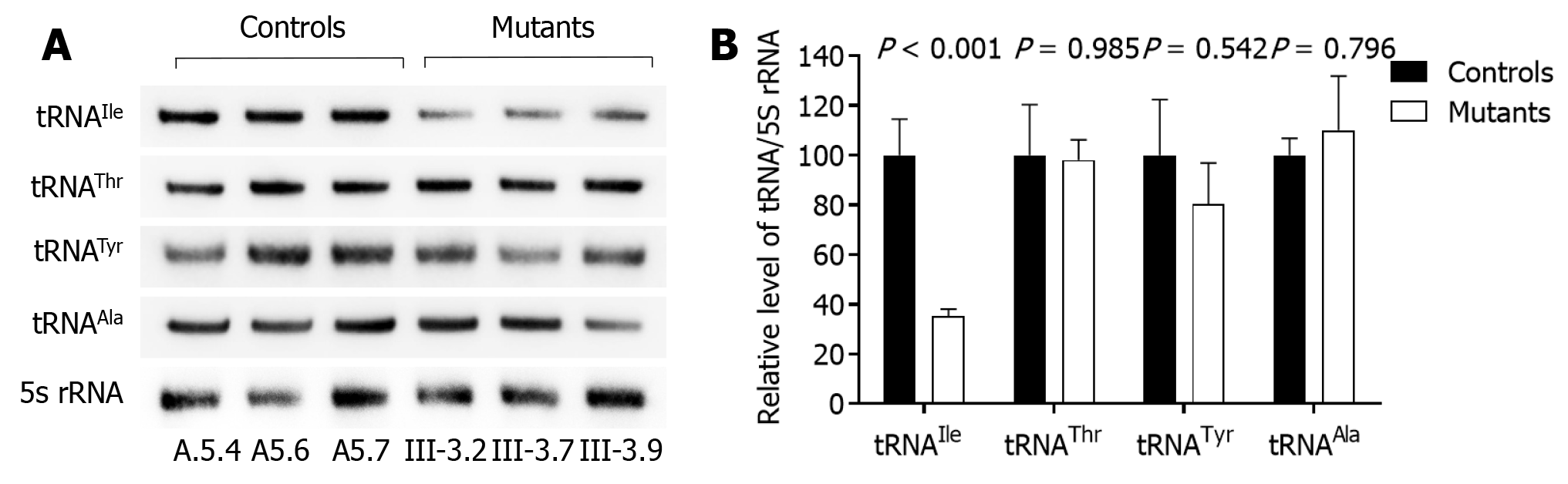
Figure 3 Northern blot analysis of mitochondrial tRNA.
A: Equal amounts (2 μg) of total mitochondrial RNA from various cell lines were electrophoresed through a denaturing polyacrylamide gel, electroblotted and hybridized with DIG-labeled oligonucleotide probes; B: Quantification of mitochondrial tRNA levels. The calculations were based on three independent determinations of the tRNA content in each cell line and three determinations of the content in the reference tRNA marker in each cell line. The horizontal dashed lines represent the average value for each group.
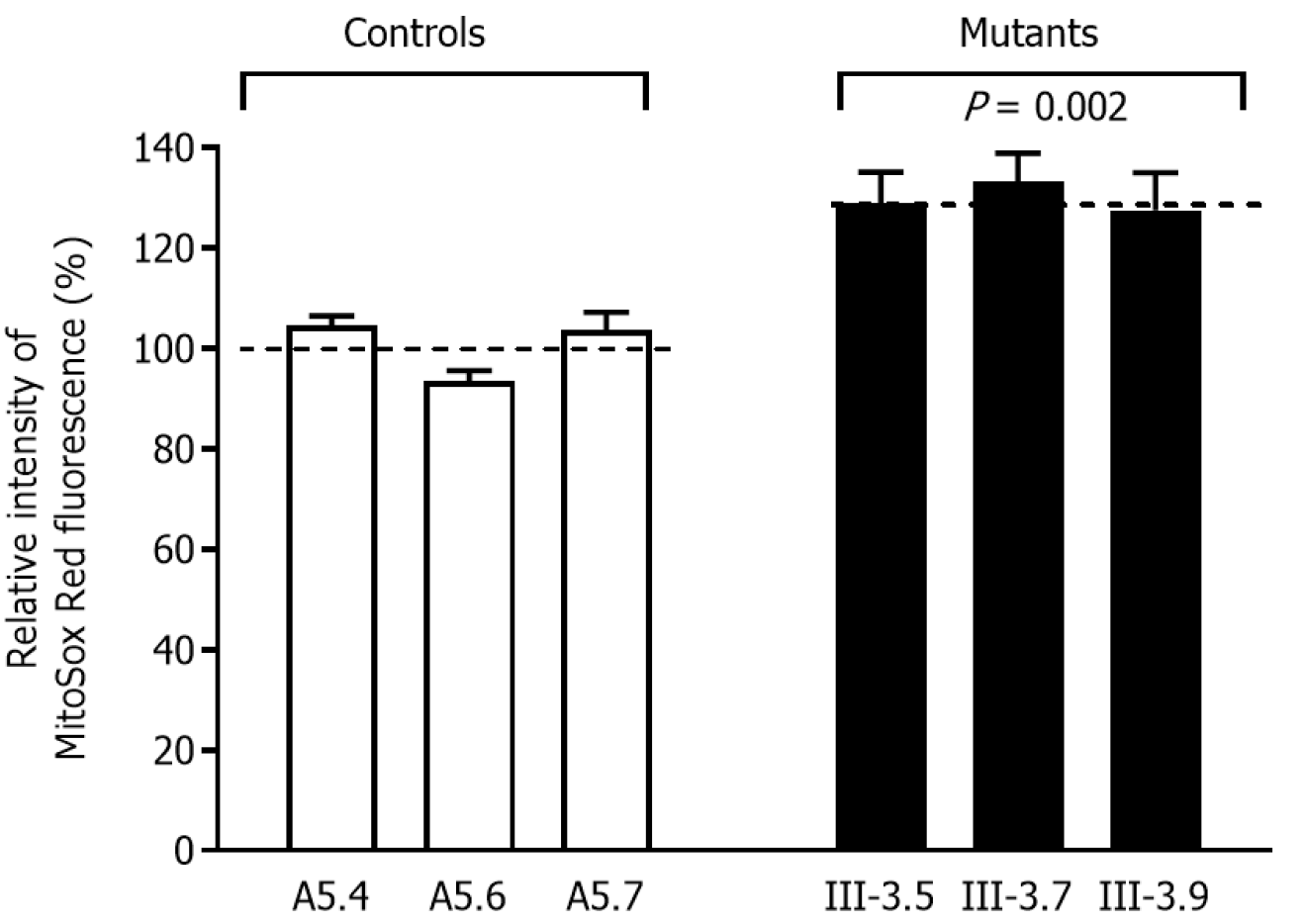
Figure 4 Measurement of reactive oxygen species production.
The relative ratio of intensity was calculated in three cybrid cell lines derived from one Chinese control subject and cybrid cell lines. The values for the latter are expressed as percentages of the average values for the control cell lines. The average of three determinations for each cell line is shown. The error bars indicate two standard errors of the means. A P value indicates significance, according to the t-test, of the differences between mutant and control cell lines.
- Citation: Zhao LJ, Zhang ZL, Fu Y. Novel m.4268T>C mutation in the mitochondrial tRNAIle gene is associated with hearing loss in two Chinese families. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(1): 205-216
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i1/205.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.205