©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 7, 2022; 10(1): 117-127
Published online Jan 7, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.117
Published online Jan 7, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.117
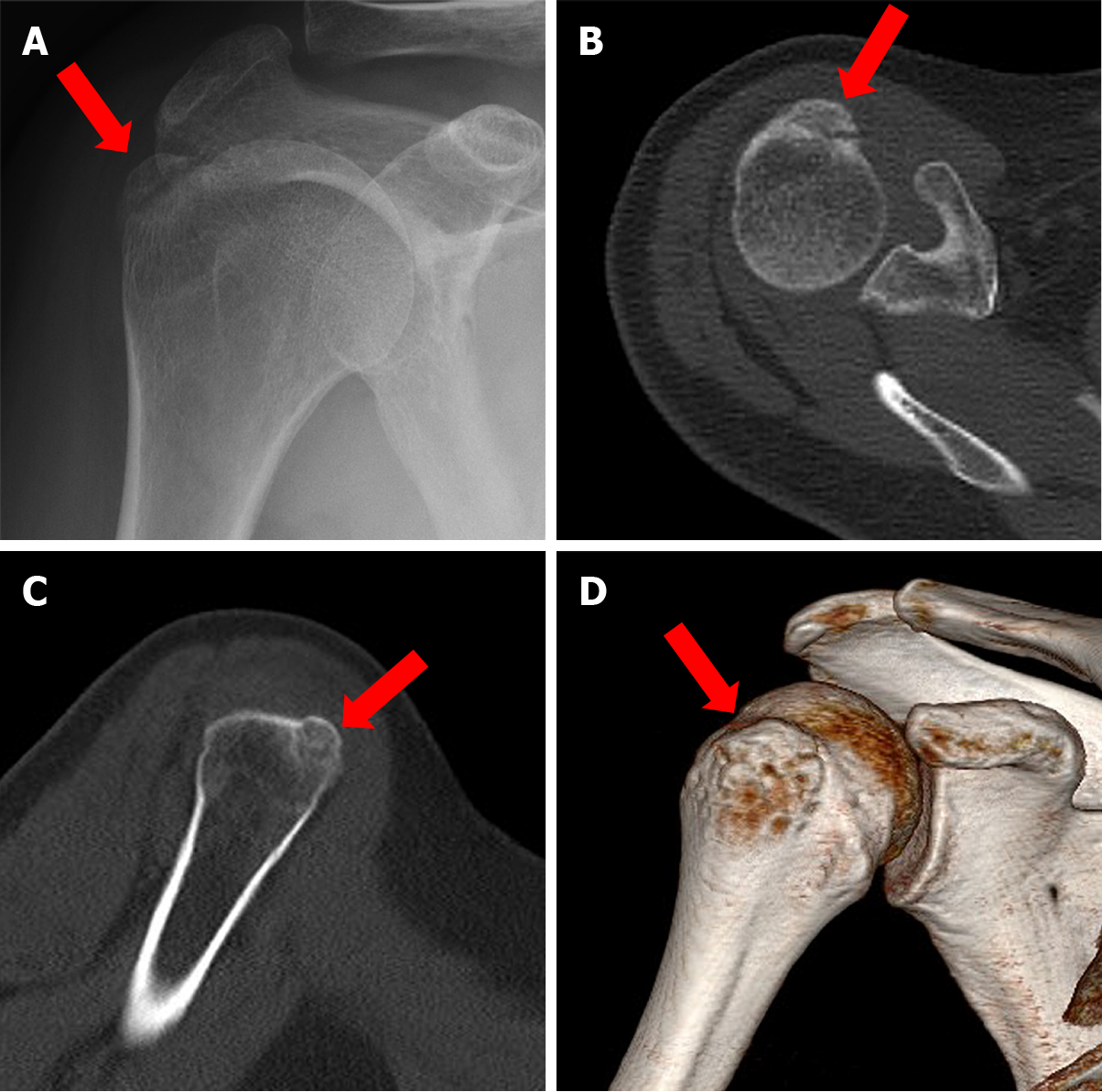
Figure 1 Imaging shows significant displacement of the fracture block of the humeral greater tuberosity of the patient.
A: Shoulder joint X-ray orthotopic film; B: Axial computed tomography (CT) scan; C: Coronal CT scan; D: Three-dimensional reconstruction image of the humerus.
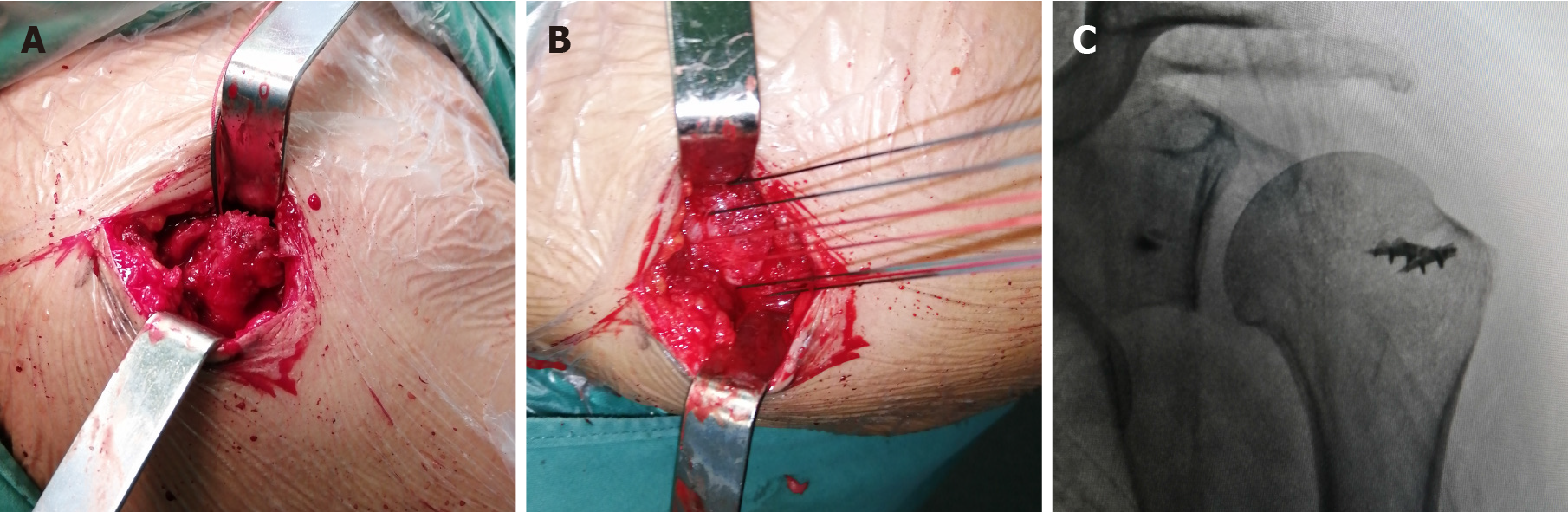
Figure 2 Intraoperative procedures and perspective.
A: Avulsion fracture of supraspinatus and infraspinatus stopper, greater tuberosity fracture, multiple fracture fragments, rotator cuff tear; B: Anchor lines were passed through the rotator cuff tissue and knotted; C: Intraoperative fluoroscopy shows good reduction of the fracture block.
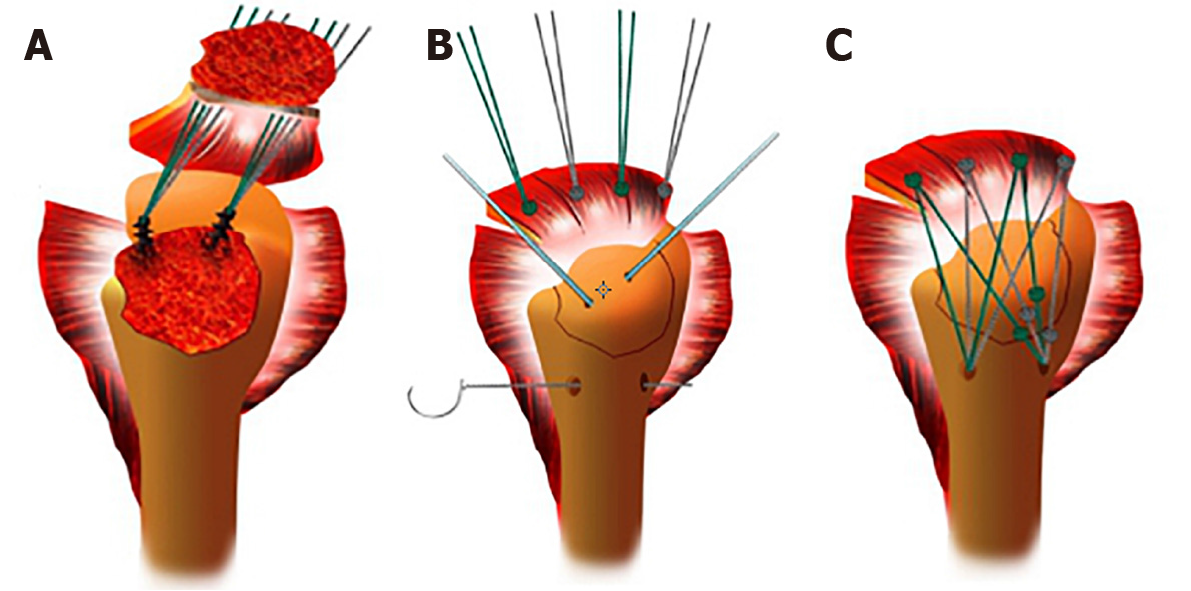
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the operation procedure.
A: Two 5.0-mm anchors were inserted into the cartilaginous margin of the humeral head, and then the anchor lines were threaded through the rotator cuff tissue; B: A Kirschner wire was used for temporary fixation of the greater tuberosity and a bone tunnel of appropriate length was drilled at the distal outer edge of the fracture line at approximately 5-10 mm, depending on the size of the fracture block; C: The larger tuberosity fracture block was reduced and fixed by the suture bridge technique, to repair the torn rotator cuff tissue. Because there should not be too many knots, the number of sutures used depended on the size of the fracture fragment. Generally, three sutures can be firmly fixed for avulsion fractures.
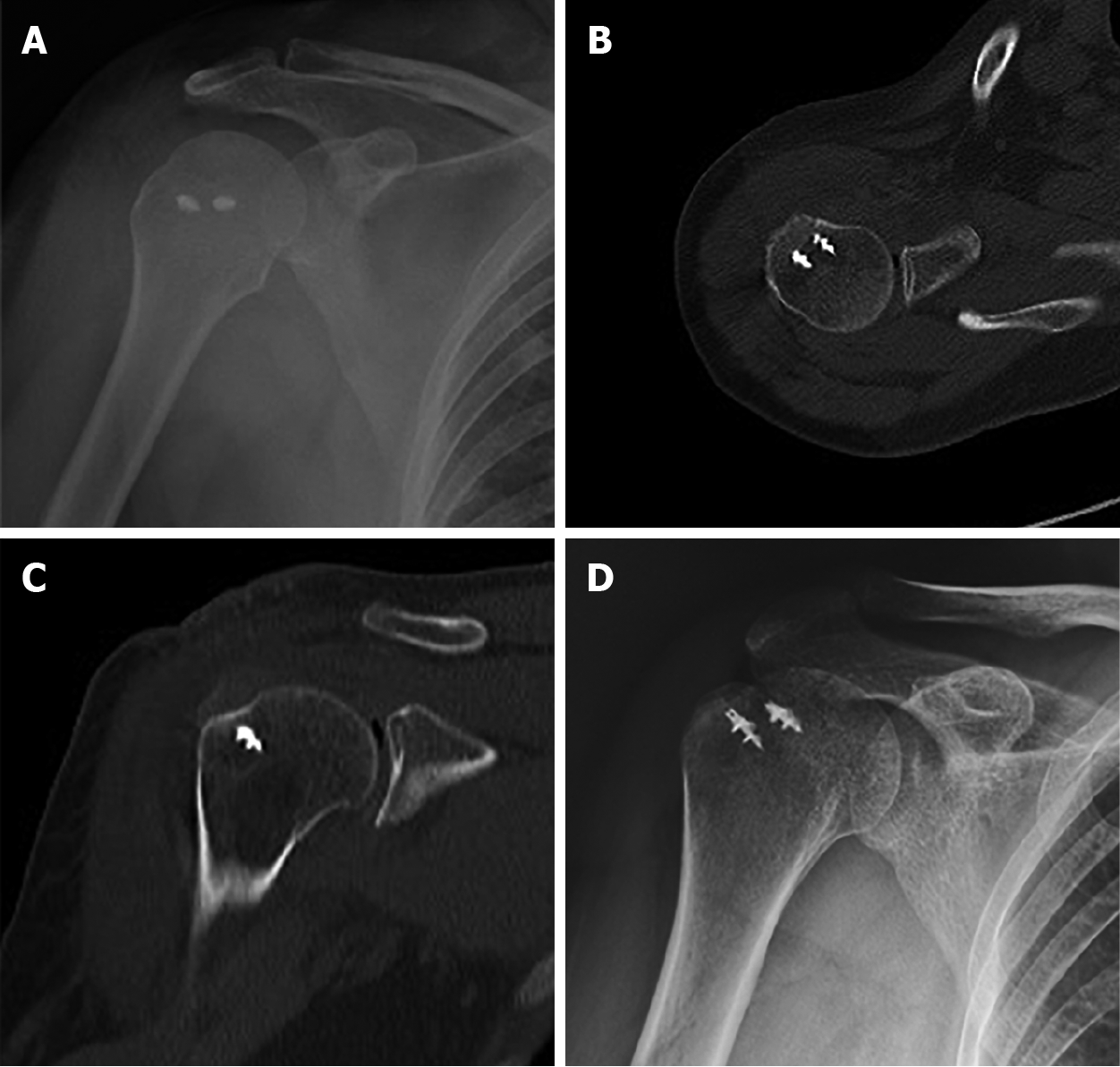
Figure 4 Postoperative radiograph and computed tomography showed good reduction of the greater tuberosity.
Fracture block alignment was good 1 d after surgery. A: Shoulder joint X-ray orthotopic film; B: Axial computed tomography (CT) scan; C: Coronal CT scan; D: The patient achieved bone union 1 mo after surgery.
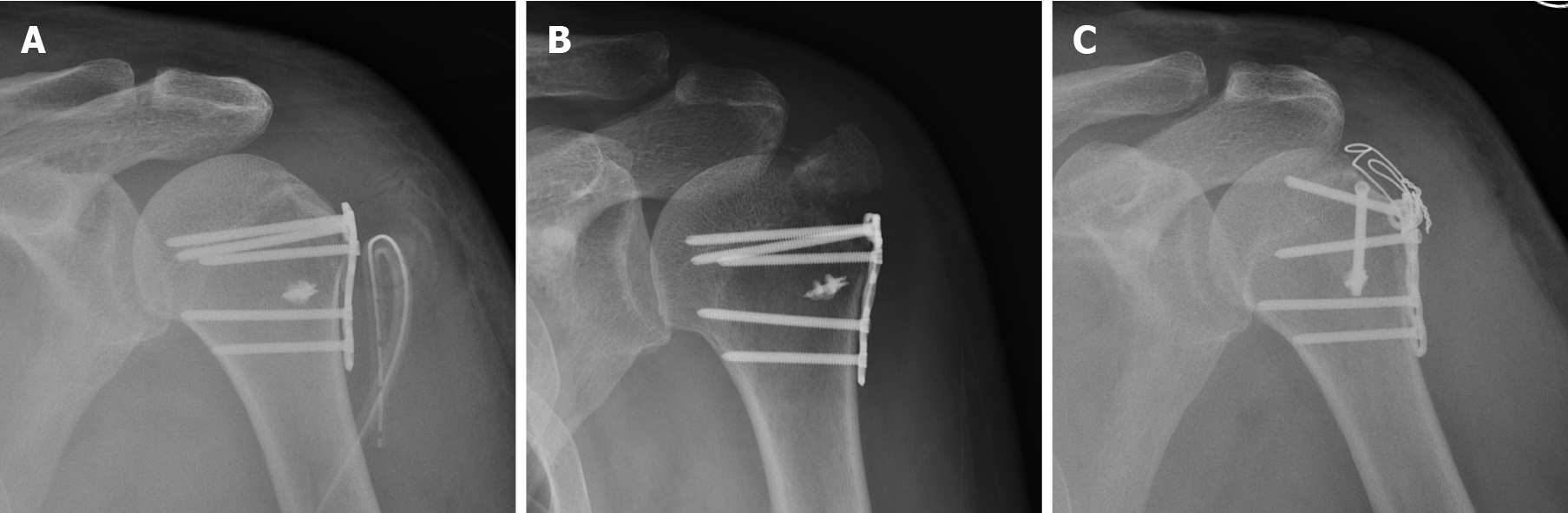
Figure 5 Failure of steel plate treatment for a greater tuberosity fracture.
A: Because of the anatomical position, it is difficult to appropriate the position of a traditional steel plate; B: The greater tuberosity became displaced due to rotator cuff traction being neglected; C: After a second operation, the fracture was fixed with screws and steel wire against rotator cuff pull, and a satisfactory result was obtained.
- Citation: Kong LP, Yang JJ, Wang F, Liu FX, Yang YL. Minimally invasive open reduction of greater tuberosity fractures by a modified suture bridge procedure. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(1): 117-127
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i1/117.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.117