©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Methodol. Mar 20, 2026; 16(1): 107426
Published online Mar 20, 2026. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v16.i1.107426
Published online Mar 20, 2026. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v16.i1.107426
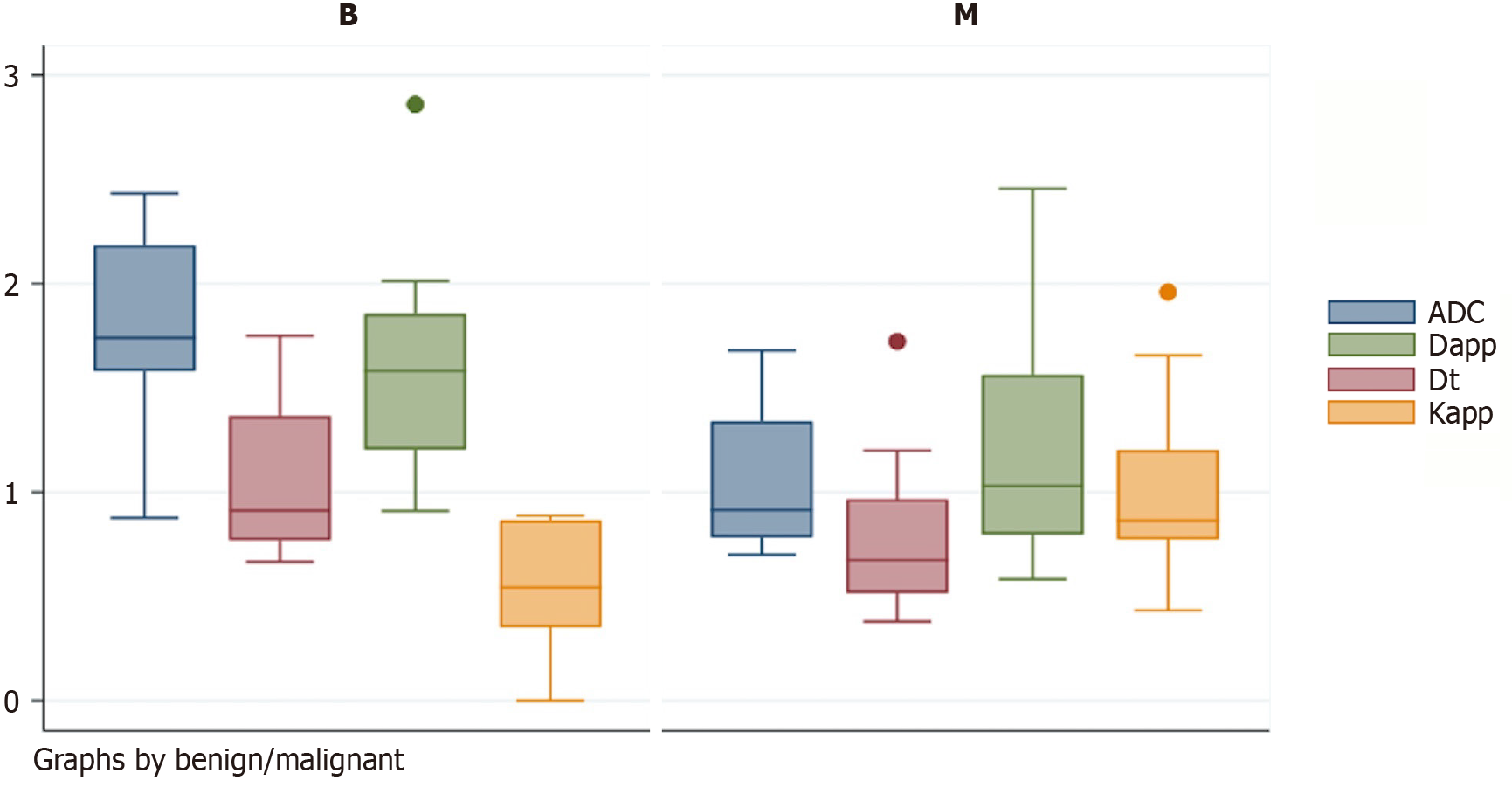
Figure 1 Box whisker plots showing distribution of apparent diffusion coefficient, intravoxel incoherent motion imaging and diffusion kurtosis imaging parameters in benign and malignant sinonasal masses.
ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient; Dapp: Diffusion coefficient; Dt: True Diffusion coefficient; Kapp: Kurtosis coefficient; B: Benign; M: Malignant.
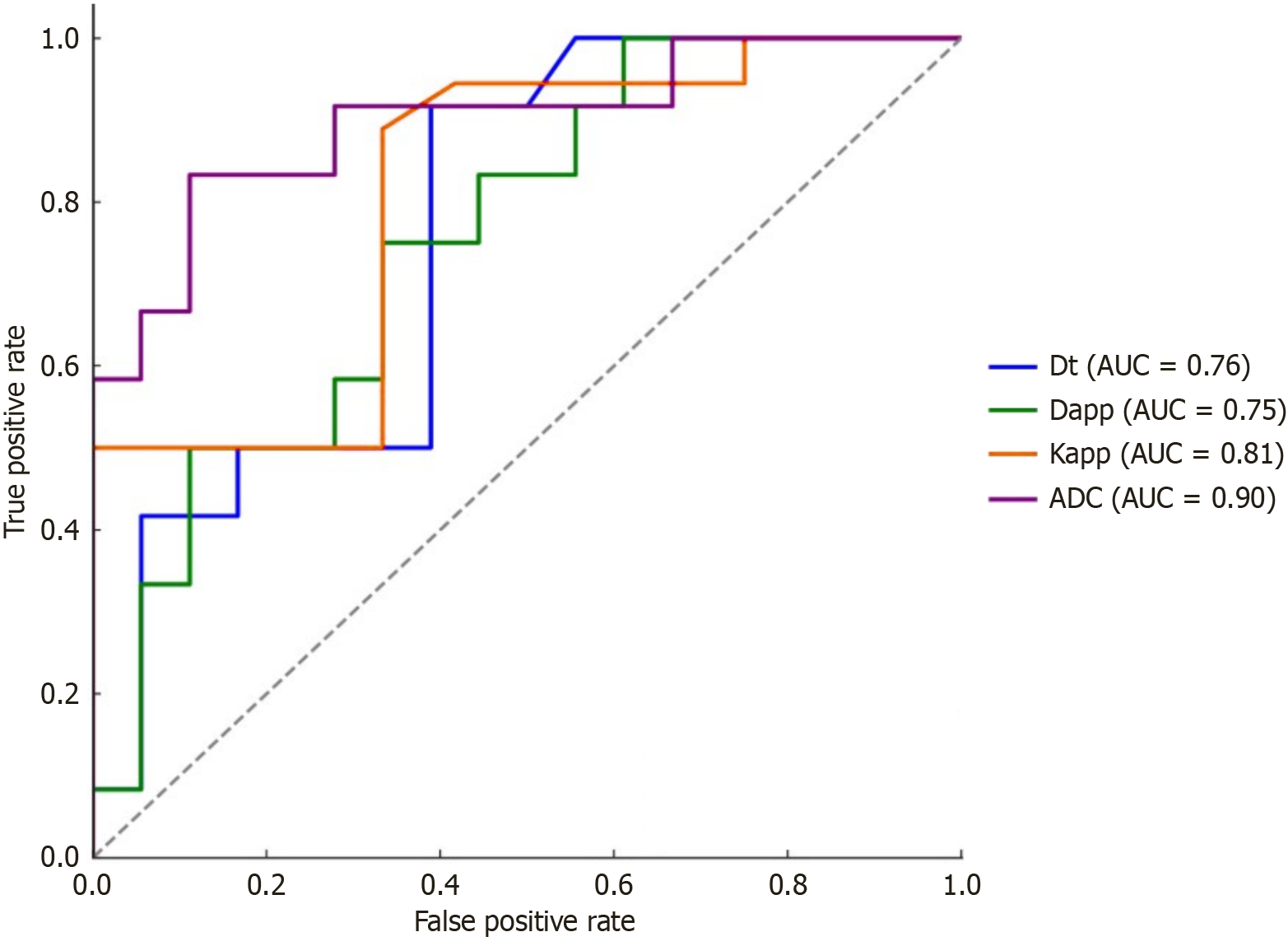
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient, intravoxel incoherent motion imaging and diffusion kurtosis imaging parameters to differentiate benign and malignant sinonasal masses.
ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient; Dapp: Apparent diffusion coefficient derived from diffusion kurtosis imaging; Dt: Diffusion coefficient; Kapp: Apparent kurtosis coefficient.
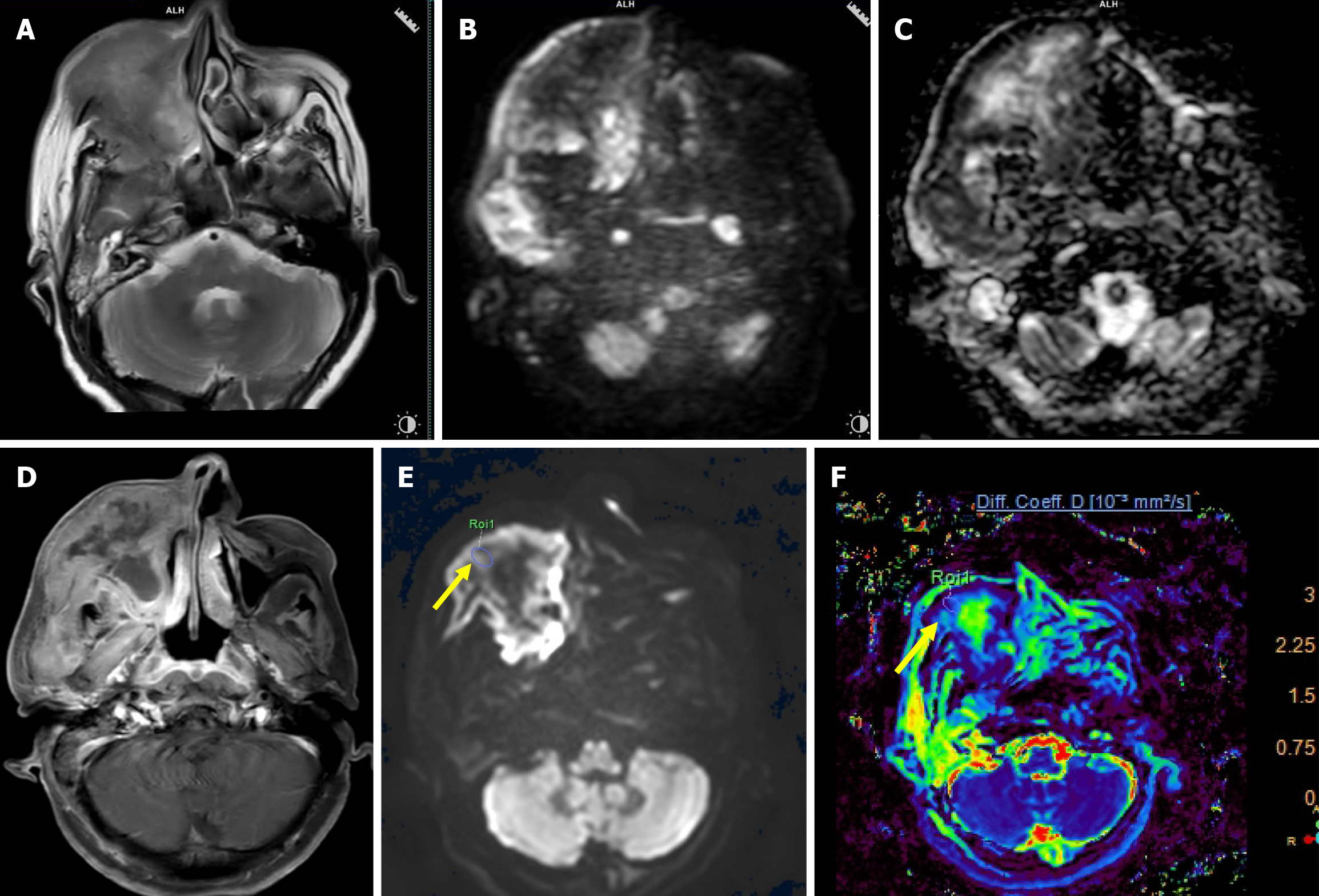
Figure 3 A 55-year-old female with undifferentiated carcinoma of the right maxillary sinus.
A: Axial T2-weighted image (T2WI) shows an ill-defined intermediate signal intensity mass epicentered in the right maxillary sinus with infiltration of the subcutaneous plane and skin; B: High b-value (b = 1000 seconds/mm2) image shows areas of high signal intensity; C: On corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map, similar areas showed hypointensity suggestive of true diffusion restriction (mean ADC value of 0.77 × 10-3 mm2/second); D: Axial post contrast T1WI image shows heterogeneous enhancement with central nonenhancing areas; E: High b-value image (b = 2000 seconds/mm2) of intravoxel incoherent motion imaging/diffusion kurtosis imaging sequence with region of interest (ROI) drawn (arrow) over the mass; F: True diffusion coefficient map after drawing ROI showed low value (0.68 × 10-3 mm2/second).
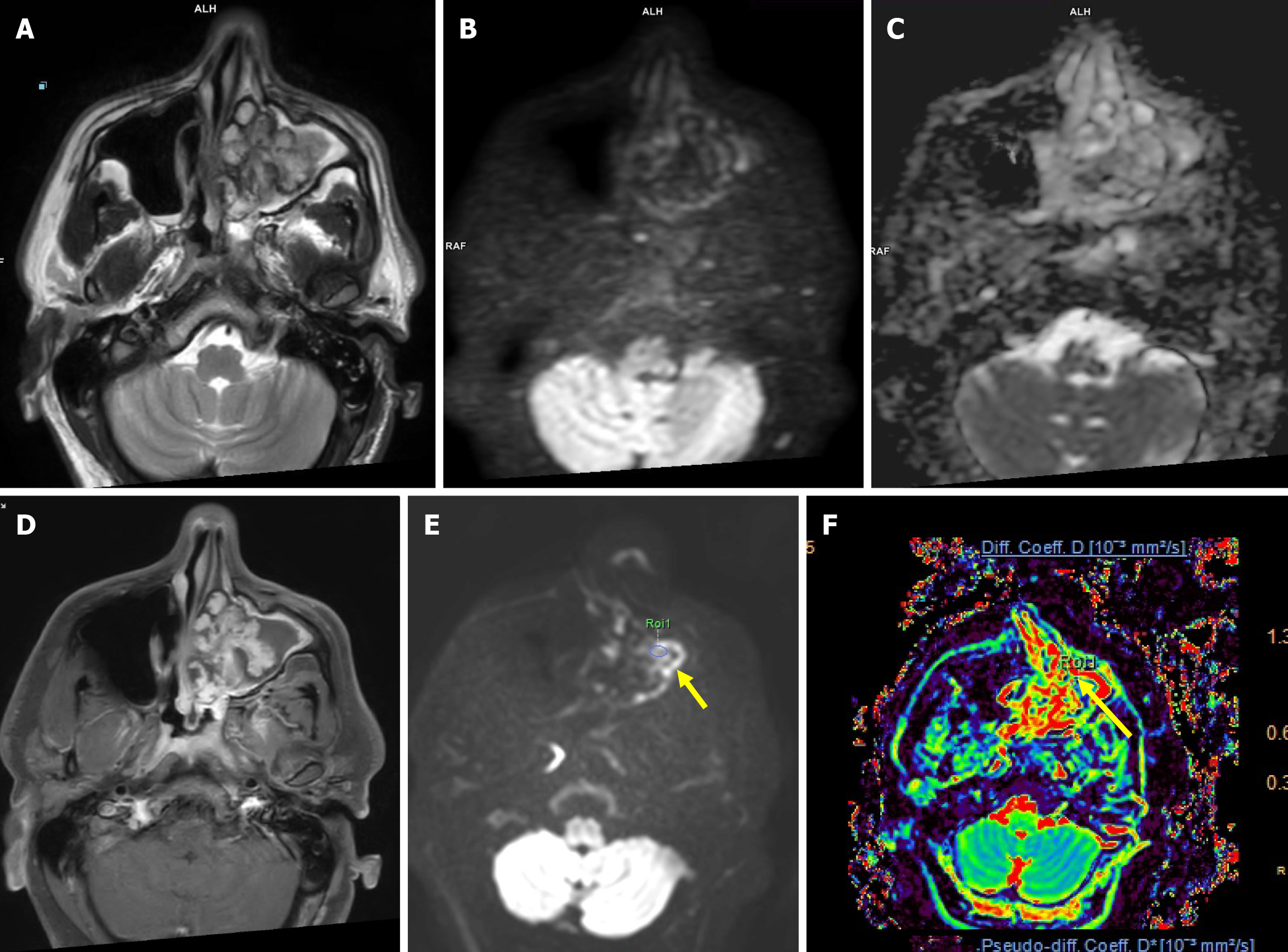
Figure 4 A 42-year-old male with inflammatory polyp of the left maxillary sinus.
A: Axial T2-weighted image (T2WI) shows a heterogeneous signal intensity mass epicentered in the left maxillary sinus with widening of the osteomeatal complex; B: High b-value (b = 1000 seconds/mm2) image does not show any areas of high signal intensity; C: On corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map, no true diffusion restriction was seen (mean ADC value of 1.89 × 10-3 mm2/second); D: Axial post contrast T1WI image shows lobular pattern of enhancement; E: High b-value image (b = 2000 seconds/mm2) of intravoxel incoherent motion imaging diffusion kurtosis imaging sequence with region of interest (ROI) drawn (arrow) over the mass after correlating with the post contrast images; F: True diffusion coefficient (Dt) map after drawing ROI showed value of 0.76 × 10-3 mm2/second.
- Citation: Saini M, Manchanda S, Bhalla AS, Kandasamy D, Kakkar A, Thakar A. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating benign and malignant sinonasal masses: A prospective study and literature review. World J Methodol 2026; 16(1): 107426
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v16/i1/107426.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v16.i1.107426