©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Nephrol. Dec 25, 2025; 14(4): 111343
Published online Dec 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i4.111343
Published online Dec 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i4.111343
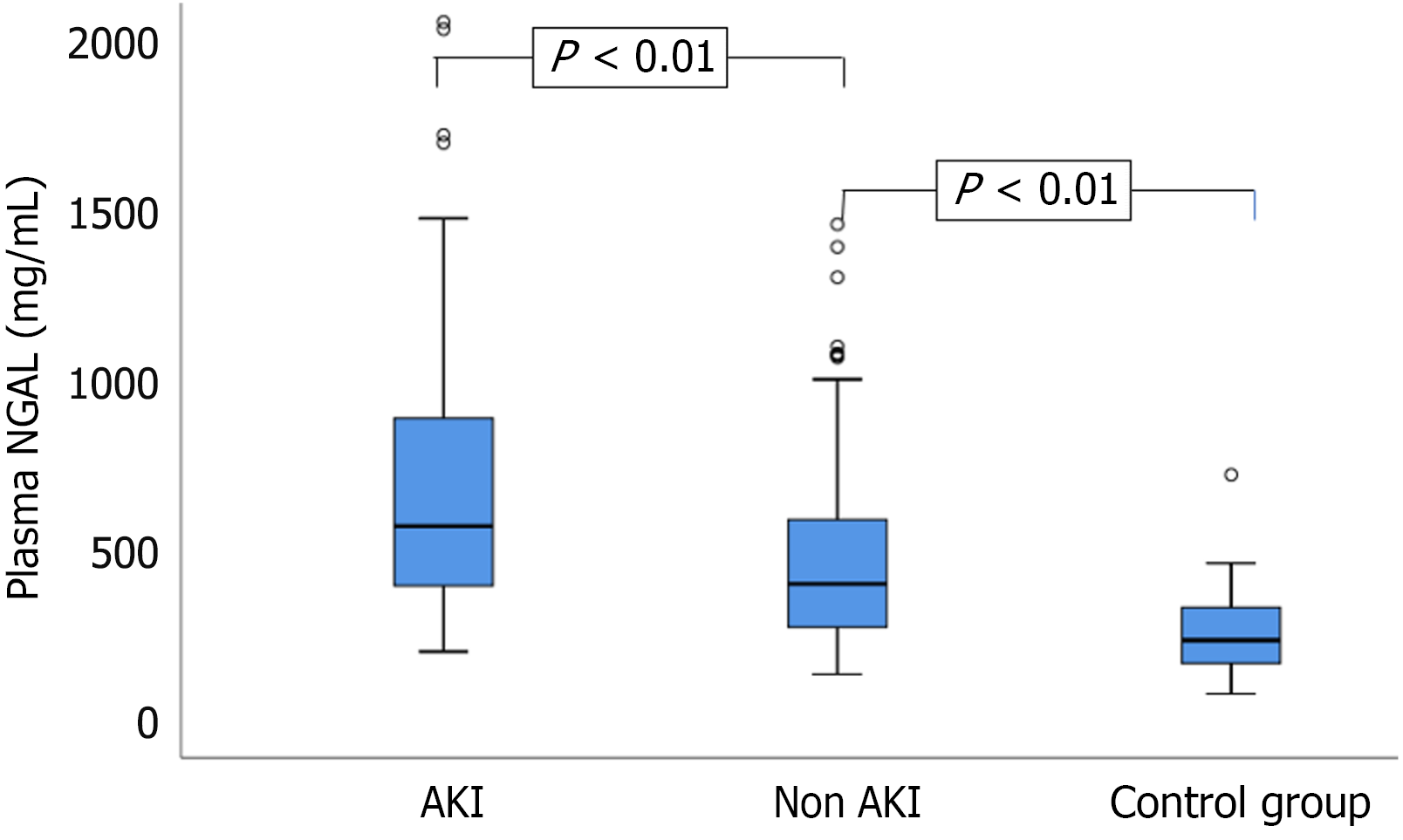
Figure 1 Comparison of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations between study groups (n = 257).
Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels were significantly higher in patients with acute kidney injury than in those without acute kidney injury or healthy controls (P < 0.01). NGAL: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; AKI: Acute kidney injury.
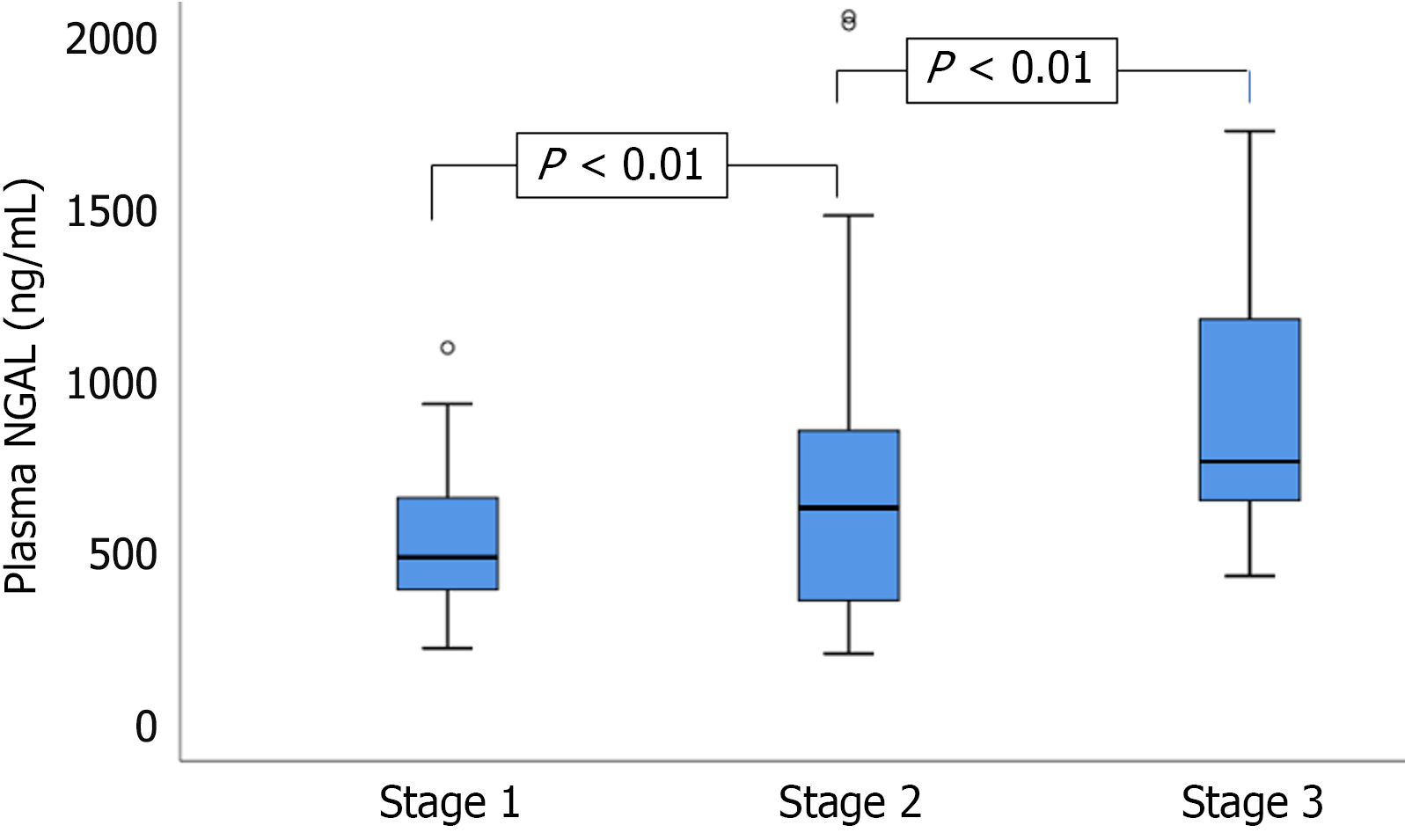
Figure 2 Comparison of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels between acute kidney injury stages.
Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels were significantly different across acute kidney injury stages 1-3 (P < 0.01), increasing with severity. NGAL: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin.
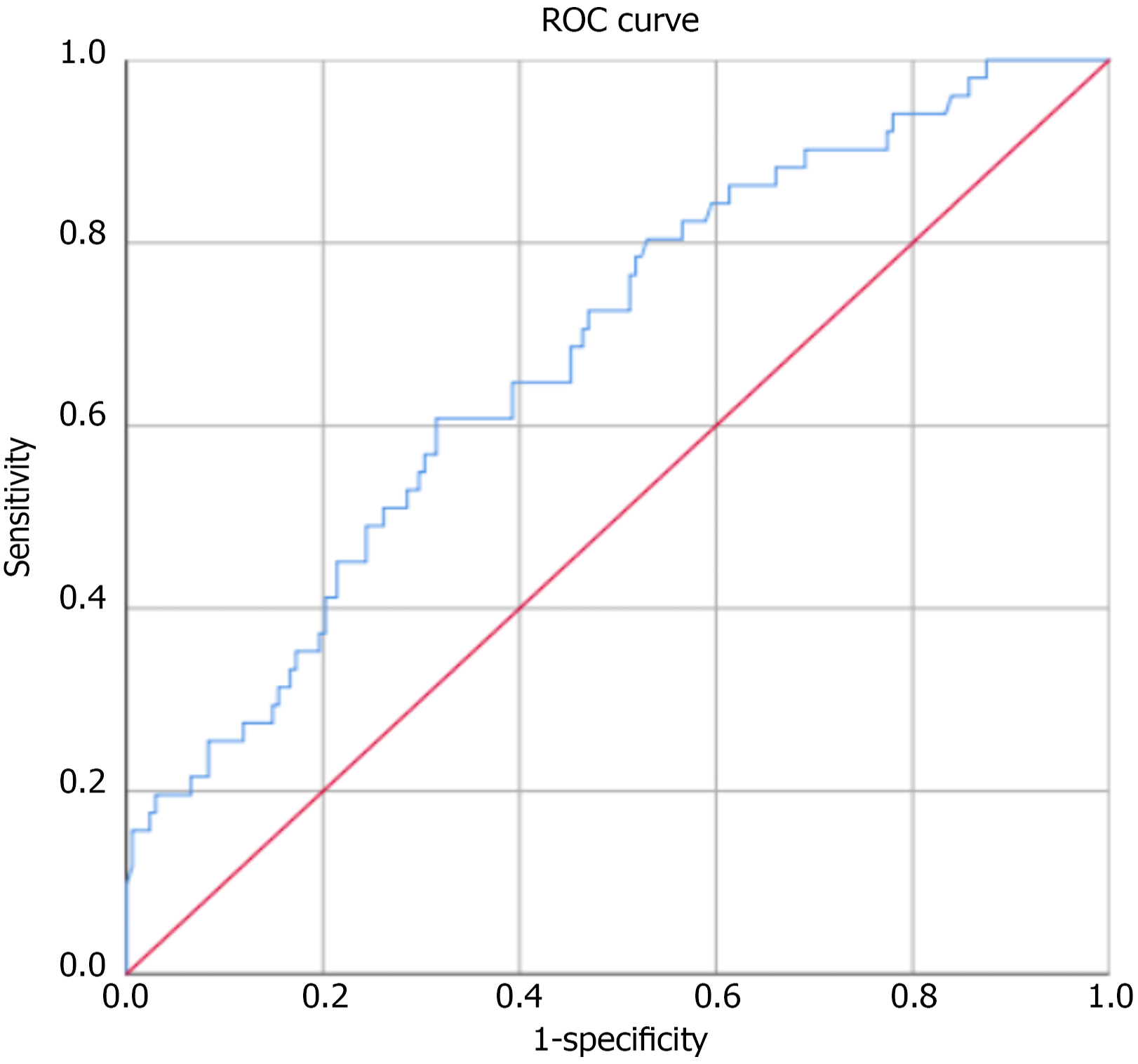
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting acute kidney injury in patients with acute pancreatitis (n = 219).
The area under the curve shows the diagnostic performance of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic.
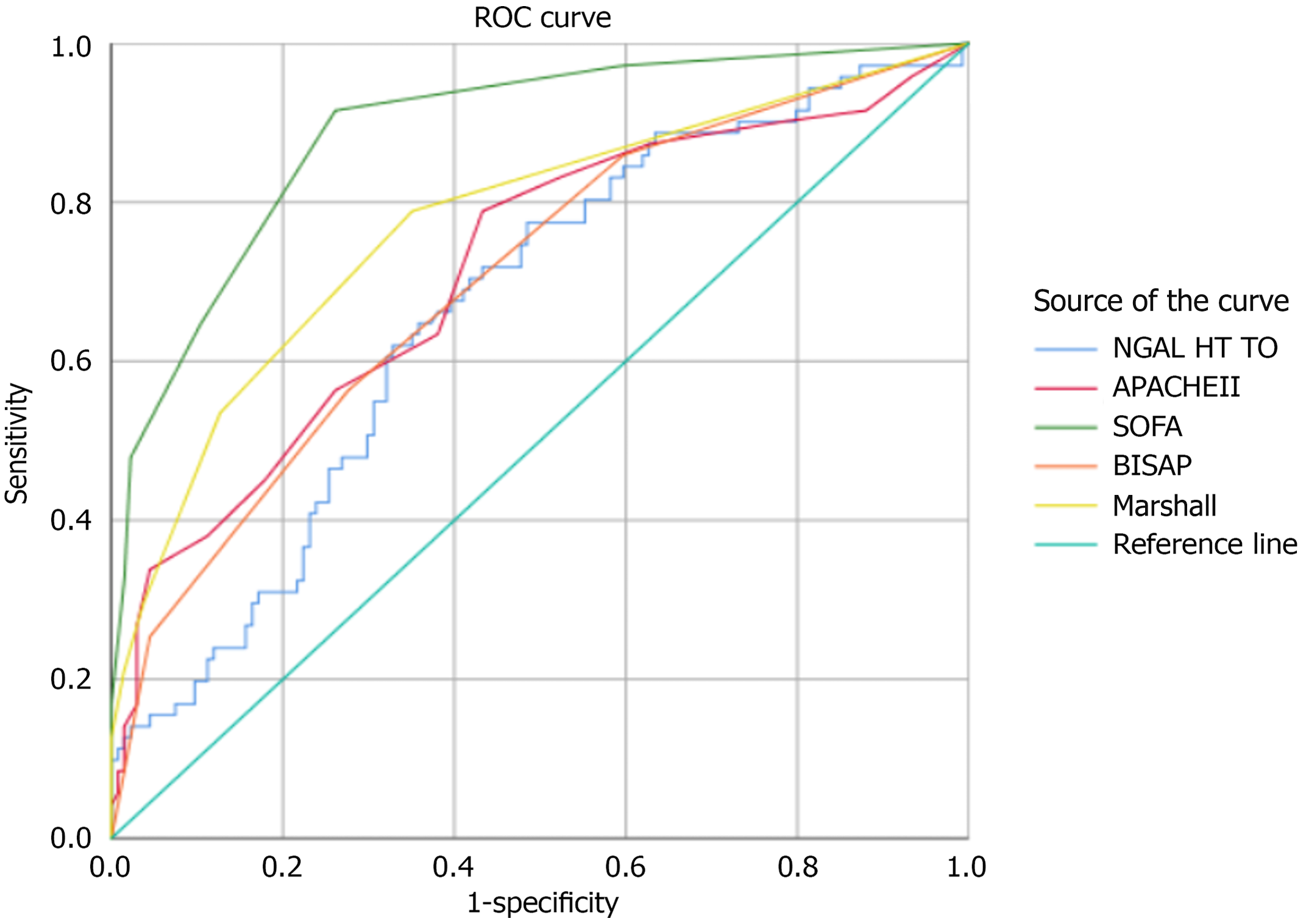
Figure 4 Comparison of the predictive value of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin with clinical severity scores.
Receiver operating characteristic analysis comparing neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin with the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II, the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment, the bedside index for severity in acute pancreatitis, and Marshall scores in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; NGAL: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; APACHE: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; BISAP: Bedside index for severity in acute pancreatitis.
- Citation: Nguyen KT, Le NH, Le TV, Pham DT, Nguyen TA, Nguyen LC, Do SN. Concentration and predictive value of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in patients with acute pancreatitis and acute kidney injury. World J Nephrol 2025; 14(4): 111343
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v14/i4/111343.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v14.i4.111343