©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Nephrol. Dec 25, 2025; 14(4): 109099
Published online Dec 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i4.109099
Published online Dec 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i4.109099
Figure 1 shows various clinical utilities of donor-derived cell-free DNA.
dd-cfDNA: Donor-derived cell-free DNA; ABMR: Antibody-mediated rejection.
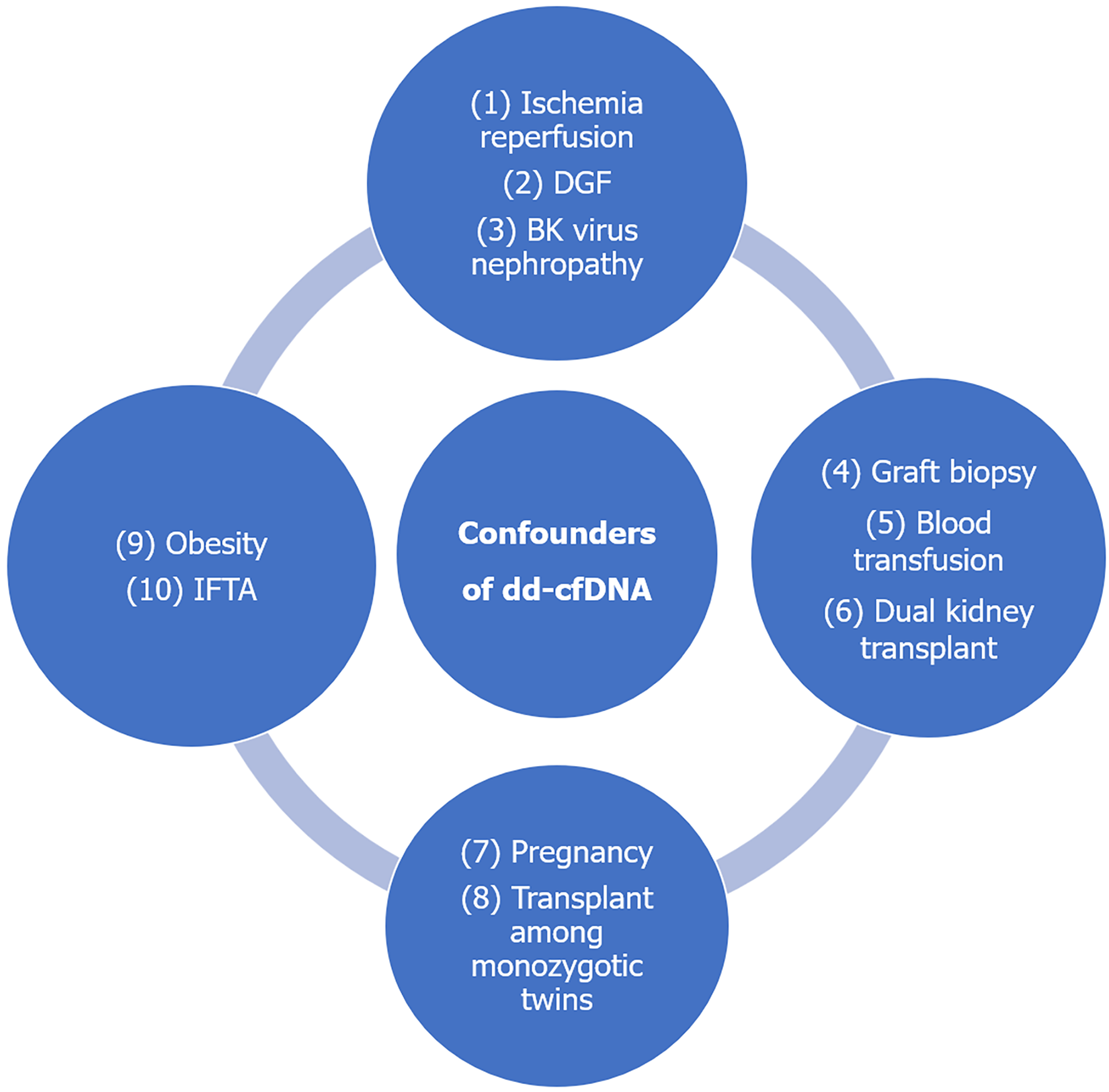
Figure 2 Shows various confounding conditions that may lead to elevated donor-derived cell-free DNA levels or interfere with the assay, independent of rejection.
dd-cfDNA: Donor-derived cell-free DNA; IFTA: Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy; DGF: Delayed graft function.
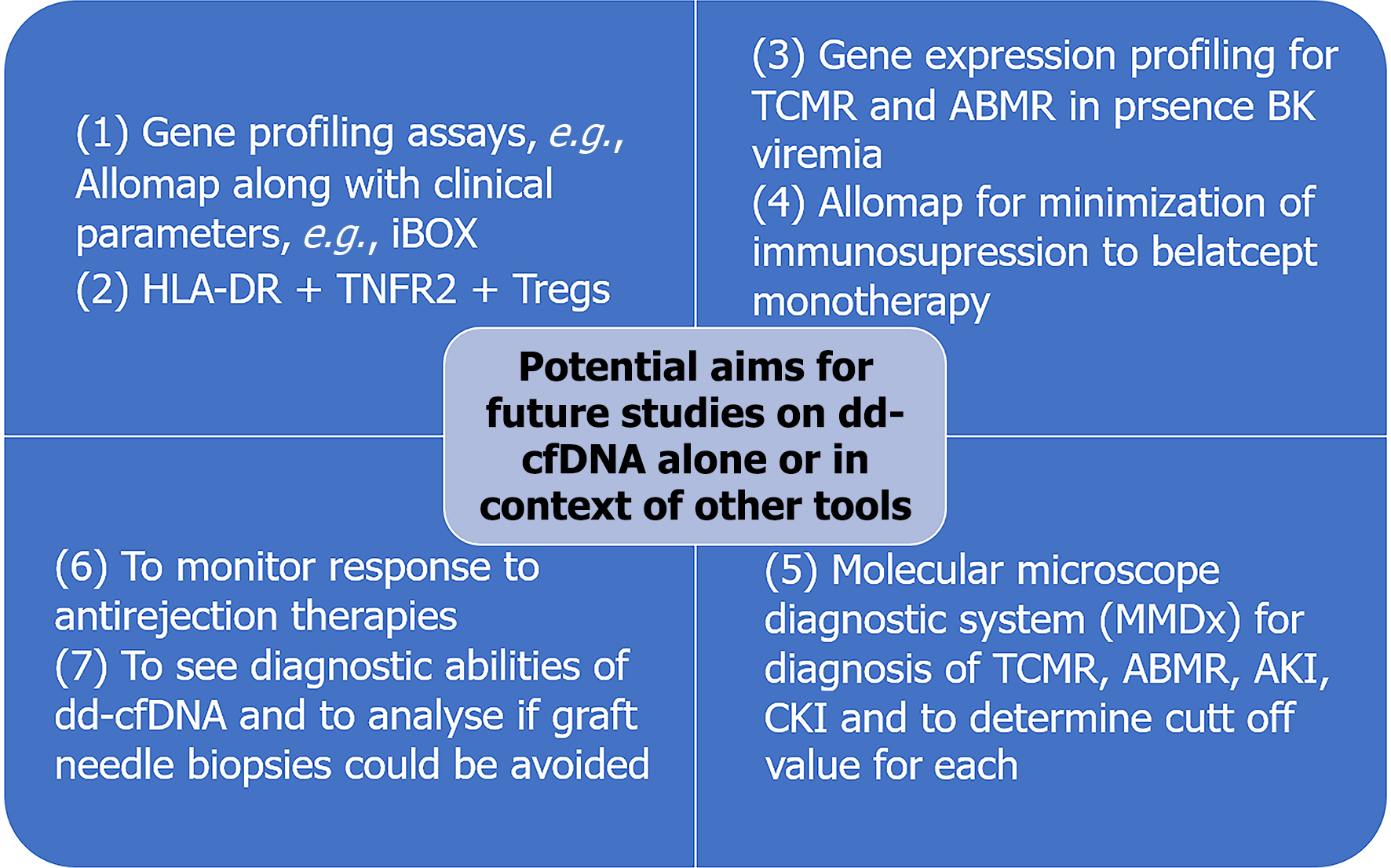
Figure 3 Potential future aims for ongoing studies.
ABMR: Antibody-mediated rejection; TCMR: T cell-mediated rejection; AKI: Acute kidney injury; CKI: Chronic kidney injury; cfDNA: Cell-free DNA.
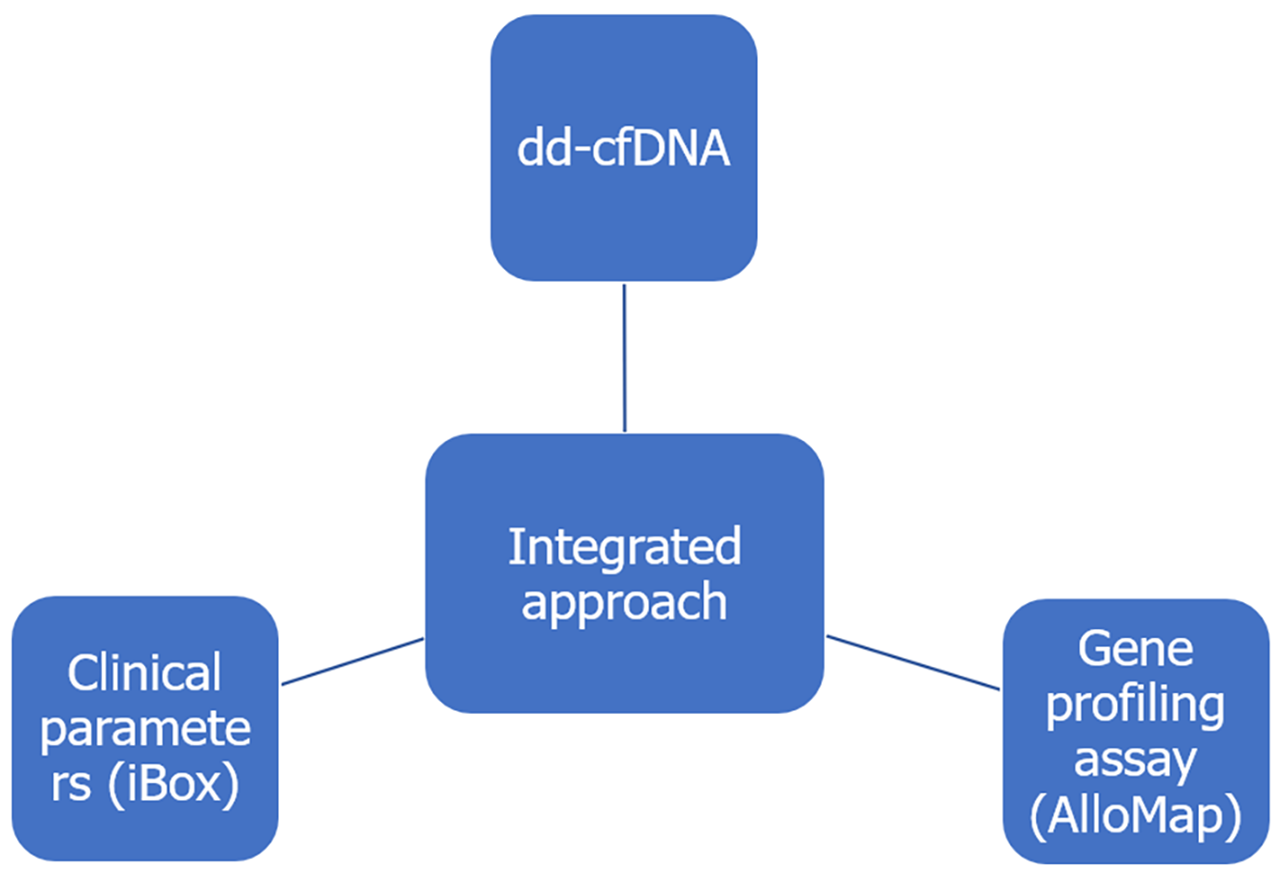
Figure 4 An integrated approach to using donor-derived cell-free DNA for the diagnosis of rejection and renal allograft surveillance.
dd-cfDNA: Donor-derived cell-free DNA.
- Citation: Khalil MAM, Sadagah NM, Mahmood HHK, Altom AA, Tan J, Al-Qurashi SH. Donor-derived cell-free DNA and its utility in kidney transplantation: A myth or a reality. World J Nephrol 2025; 14(4): 109099
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v14/i4/109099.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v14.i4.109099