©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Virol. Jun 25, 2025; 14(2): 101693
Published online Jun 25, 2025. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i2.101693
Published online Jun 25, 2025. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i2.101693
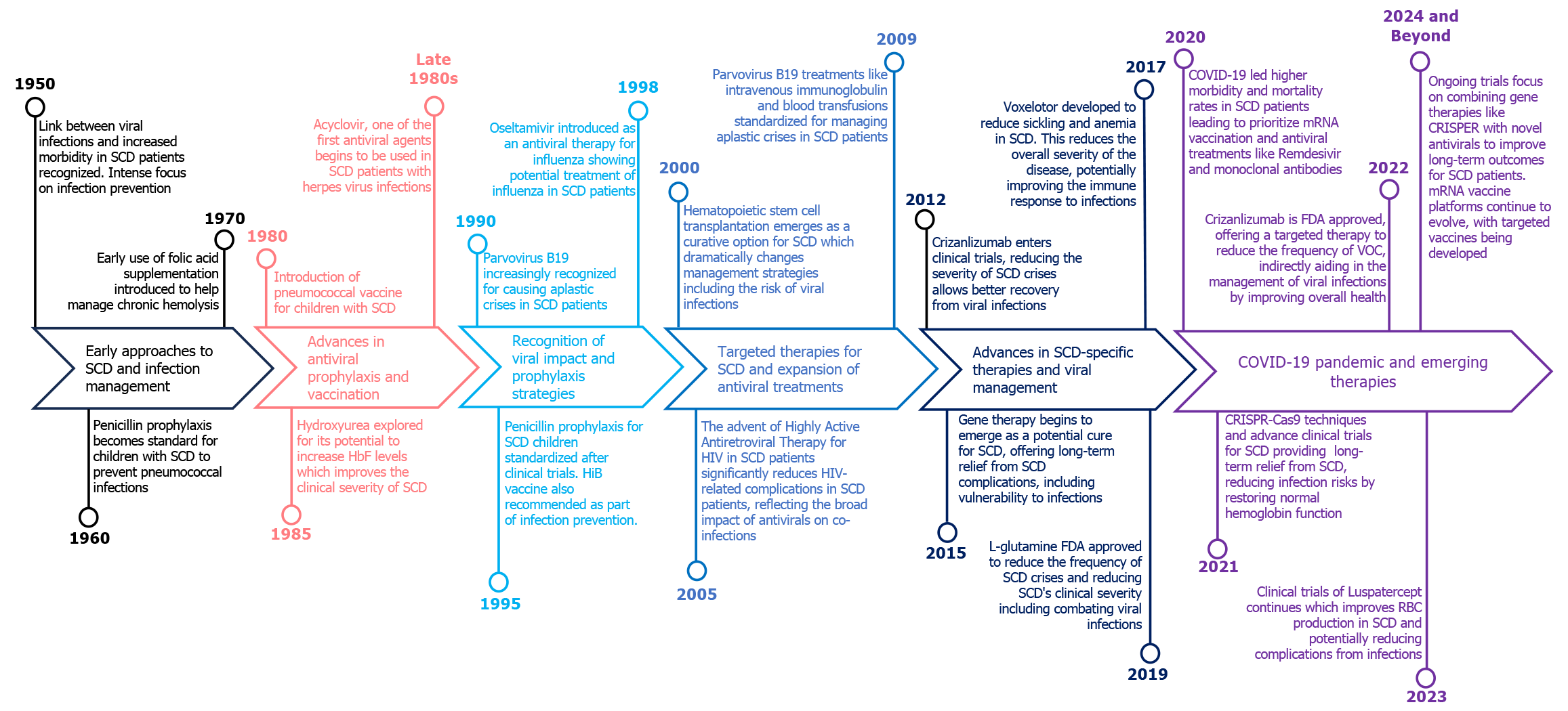
Figure 1 Historical management of sickle cell disease and viral infections.
COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; CRISPR-cas9: Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; SCD: Sickle cell disease; VOC: Vaso-occlusive crisis.
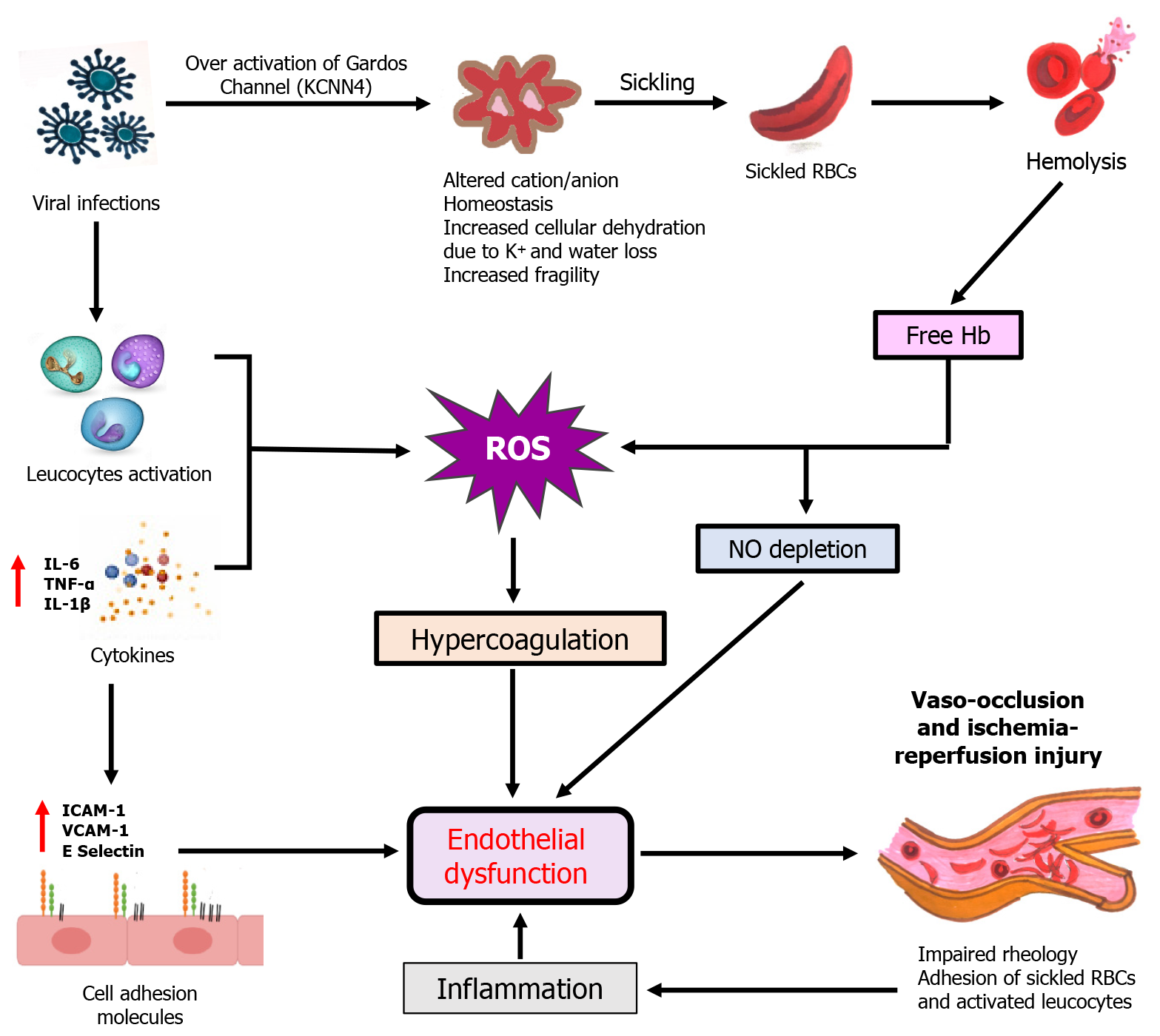
Figure 2 Mechanisms of viral infection-related exacerbation in sickle cell disease.
Hb: Hemoglobin; IL: Interleukin; NO: Nitric oxide; RBCs: Red blood cells; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
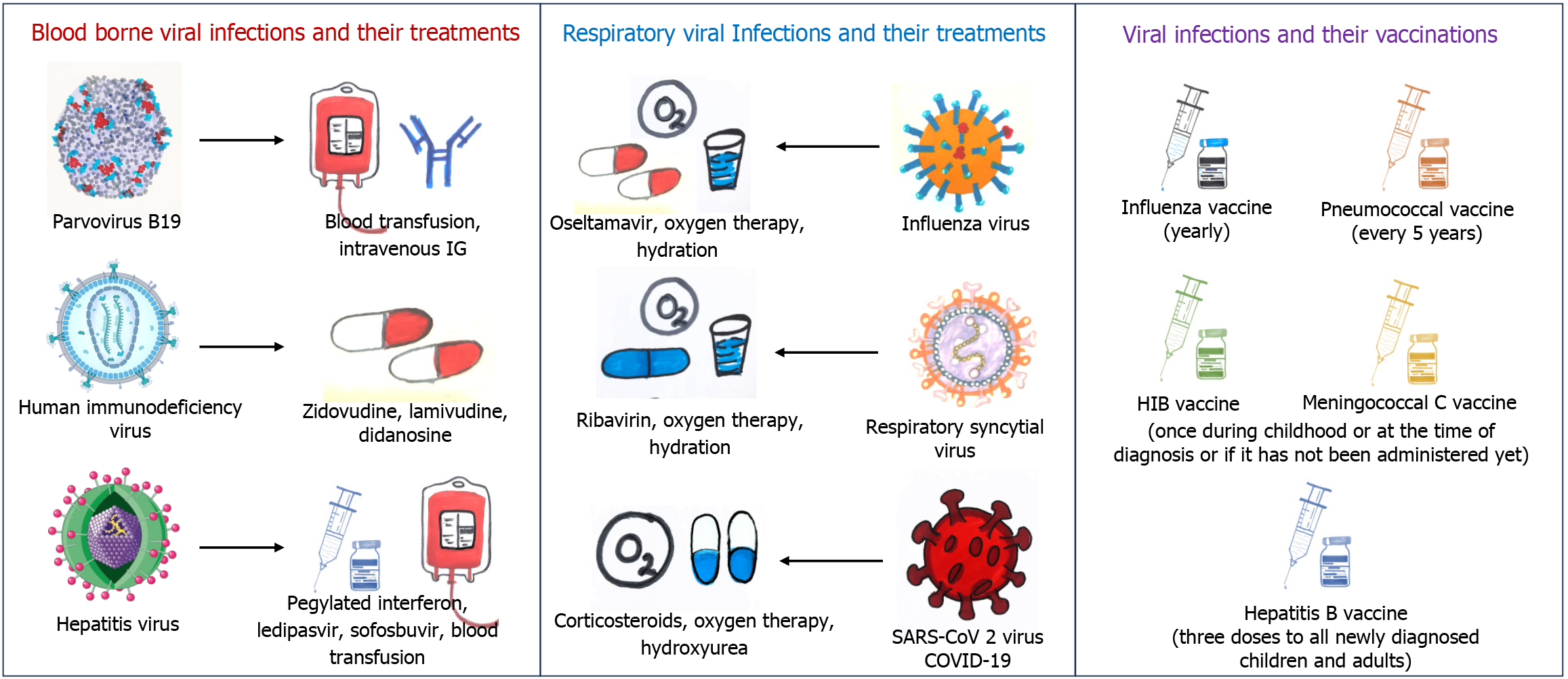
Figure 3 Treatments and prophylaxis for viral infections in sickle cell disease.
COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; IG: Immunoglobulin; SARS-CoV 2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2.
- Citation: Sahu T, Jagzape AT, Sinha M, Sinha R, Verma HK. New frontiers in sickle cell disease: The role of antiviral therapies and emerging drugs in managing viral infections. World J Virol 2025; 14(2): 101693
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v14/i2/101693.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v14.i2.101693