©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Transplant. Dec 18, 2025; 15(4): 106938
Published online Dec 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i4.106938
Published online Dec 18, 2025. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v15.i4.106938
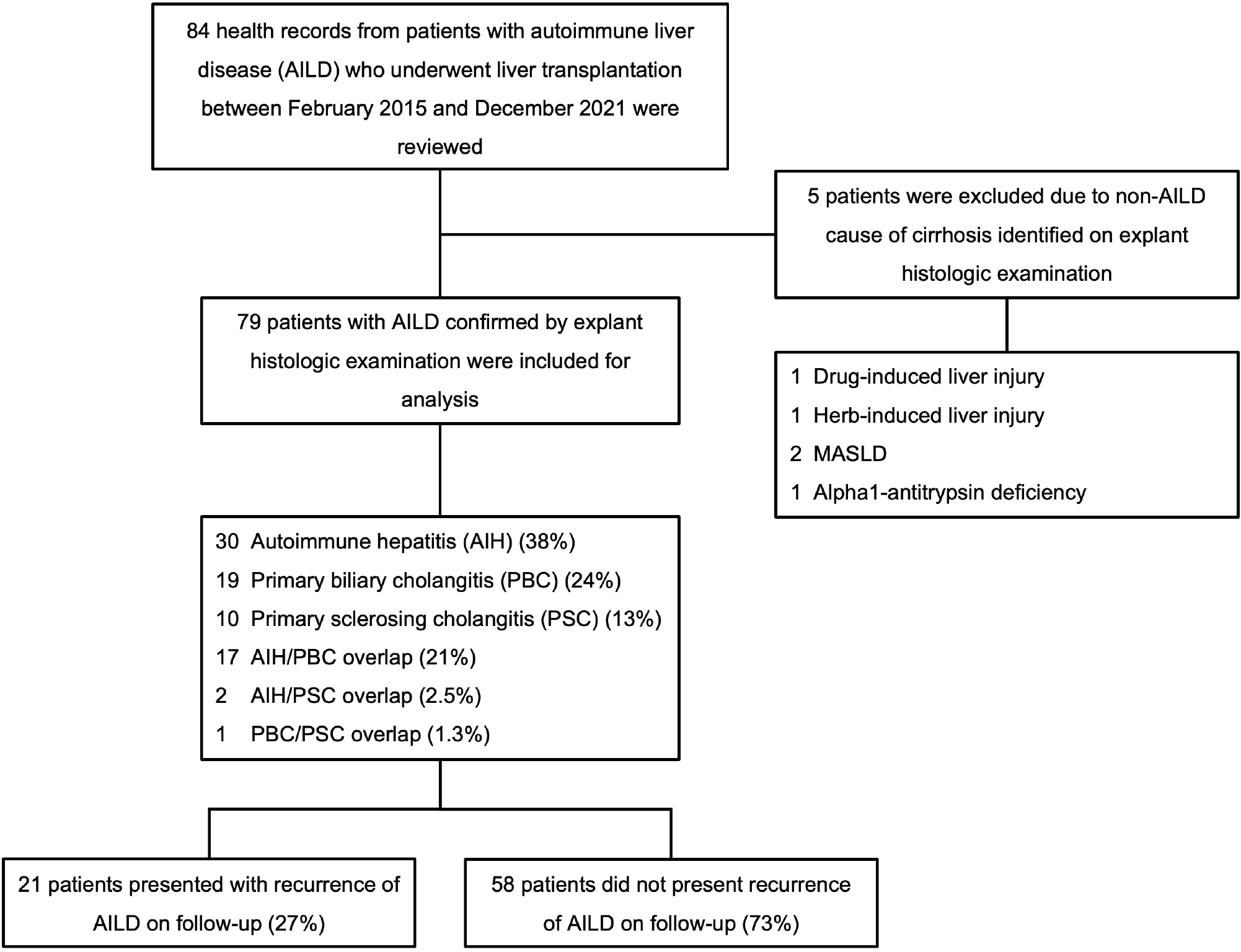
Figure 1 Patient inclusion and exclusion, cirrhosis etiology, and disease recurrence rate.
AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis; AILD: Autoimmune liver disease; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; PBC: Primary biliary cholangitis; PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis.
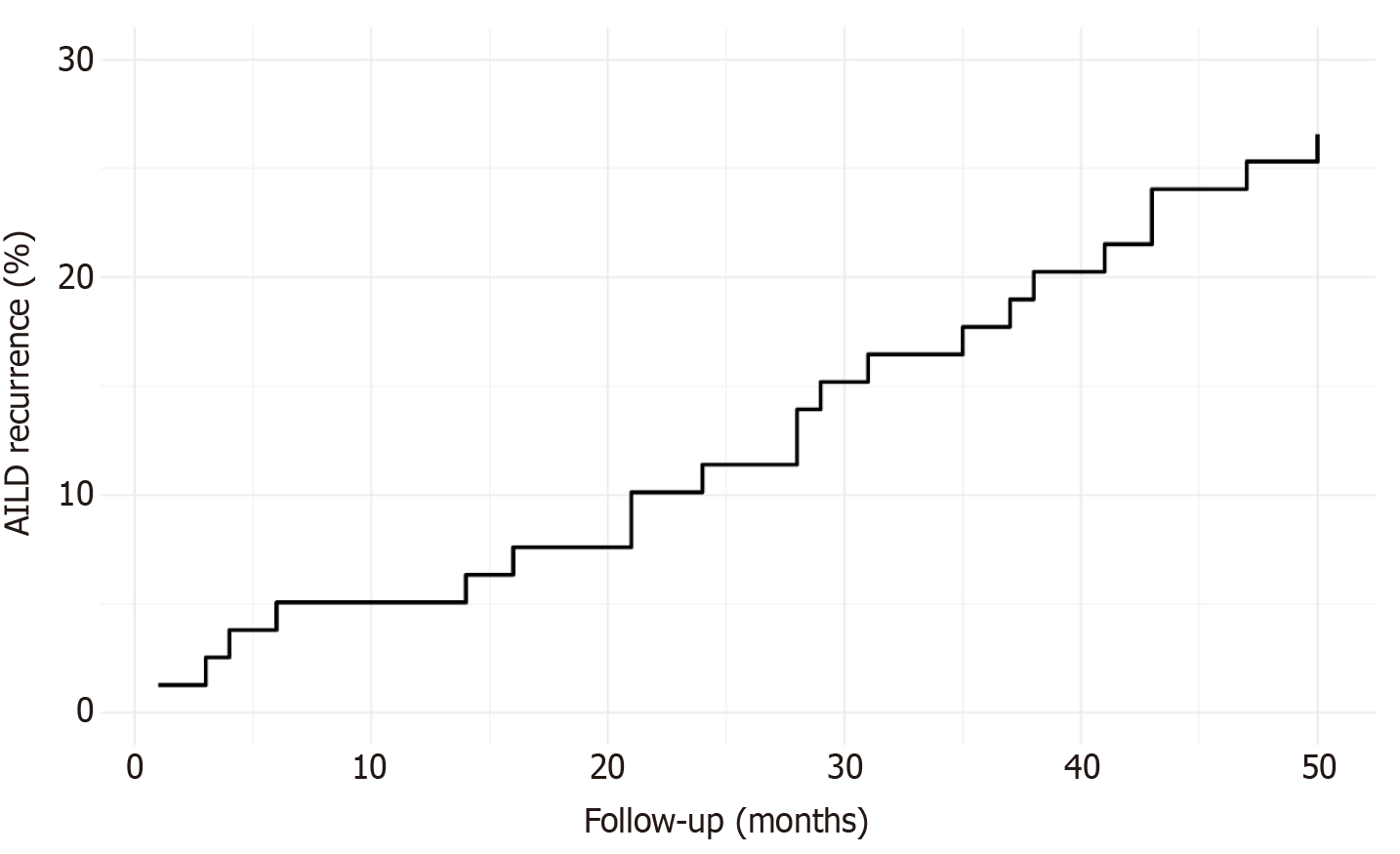
Figure 2 Cumulative incidence of autoimmune liver disease recurrence following liver transplantation.
AILD: Autoimmune liver disease.
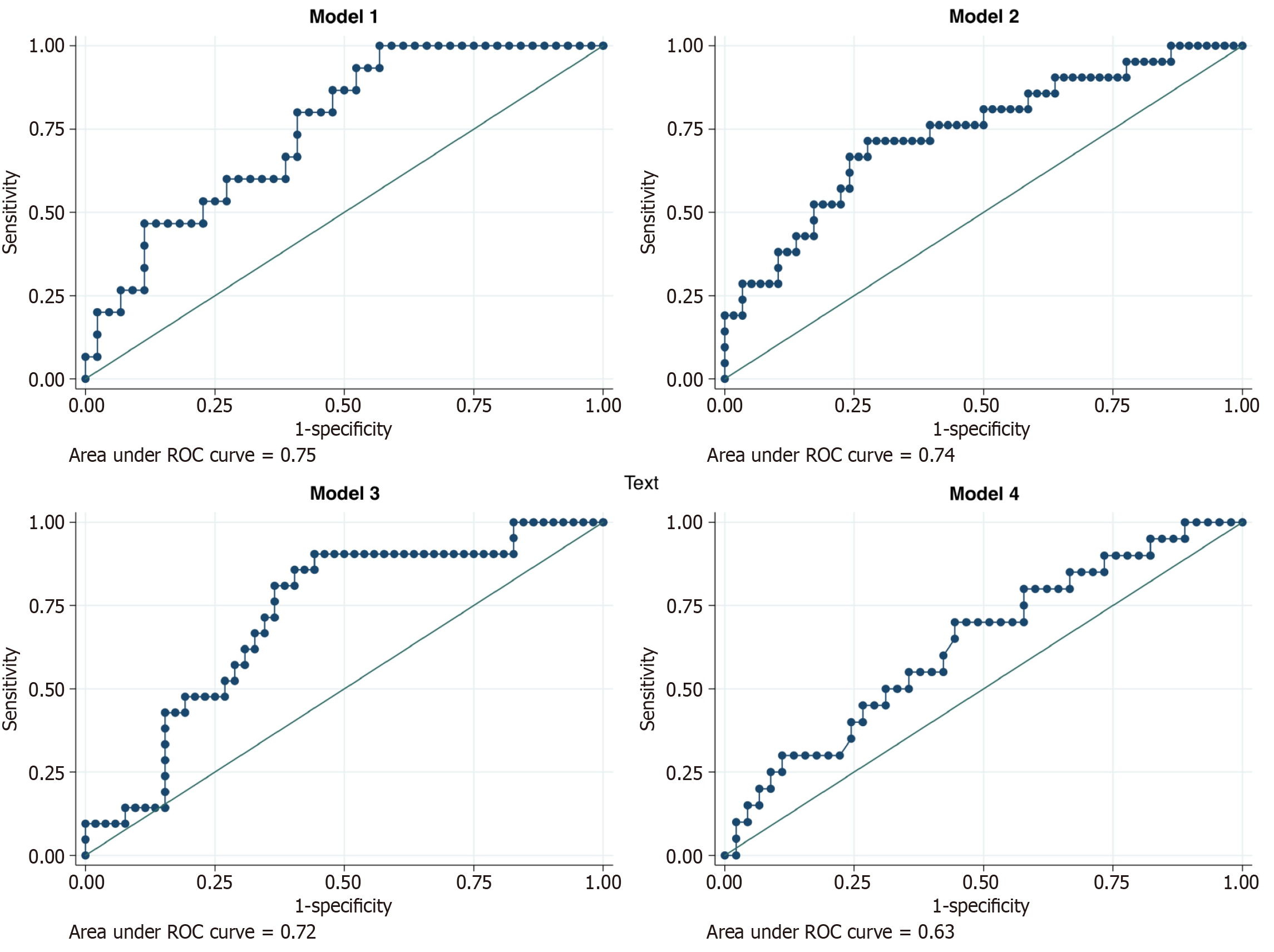
Figure 3 Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve curves of exploratory models predicting autoimmune liver disease recurrence.
Model 1 assessed the duration and severity of autoimmune liver disease. Models 2 and 3 analyzed surrogates of liver disease activity and systemic inflammation based on laboratory values at baseline (model 2) and three months after transplantation (model 3). Model 4 evaluated potential factors associated with reduced treatment adherence and the need for dose adjustments. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic.
- Citation: Salgado-de la Mora M, Mendez-Guerrero O, Torre A, Vilatoba M, Castro Narro GE, Lumbreras Márquez MI, Navarro-Alvarez N. Risk factors for autoimmune liver disease recurrence after liver transplantation. World J Transplant 2025; 15(4): 106938
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v15/i4/106938.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v15.i4.106938