©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Psychiatry. Jan 19, 2026; 16(1): 112973
Published online Jan 19, 2026. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v16.i1.112973
Published online Jan 19, 2026. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v16.i1.112973
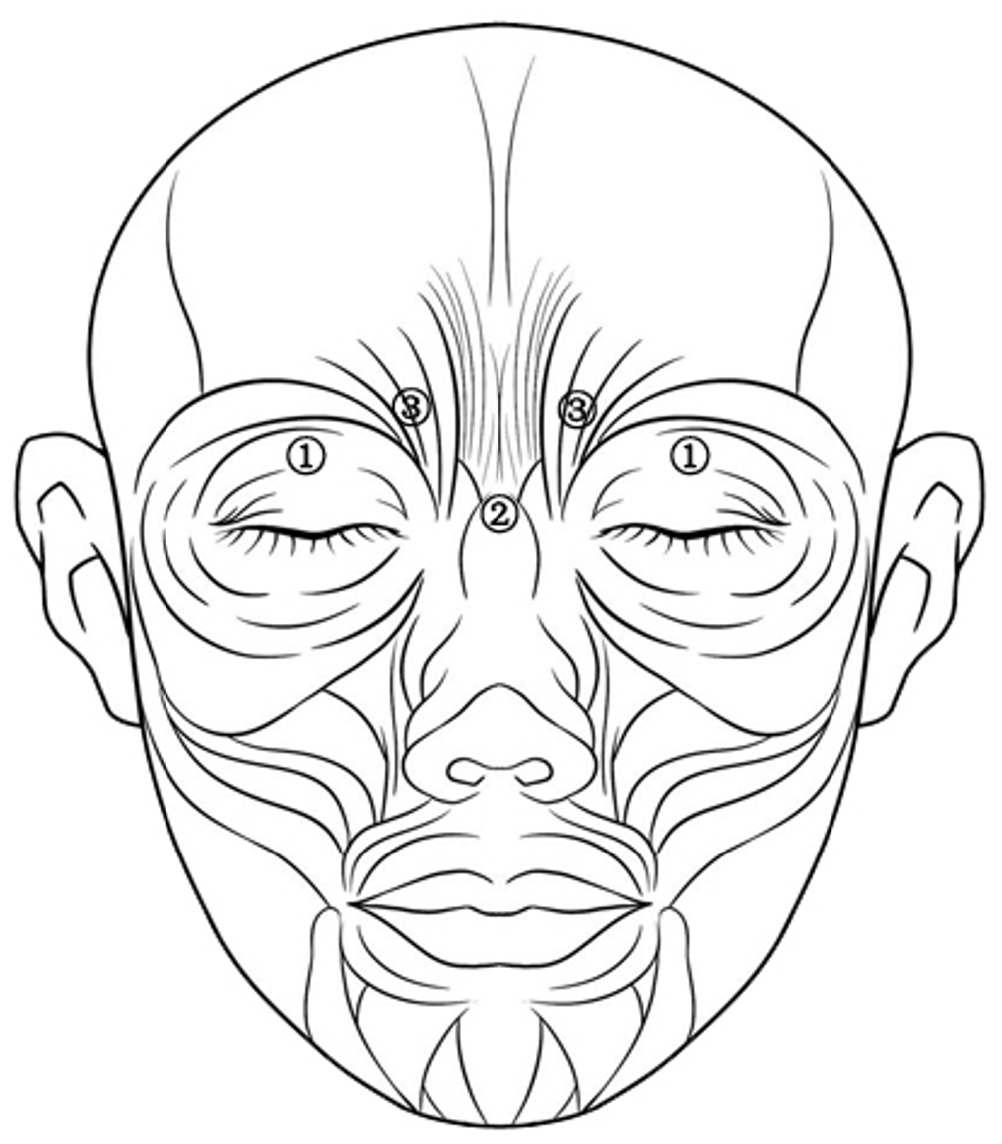
Figure 1 Schematic representation of botulinum toxin A injection muscle.
①: Orbicularis oculi; ②: Procerus; ③: Corrugator.
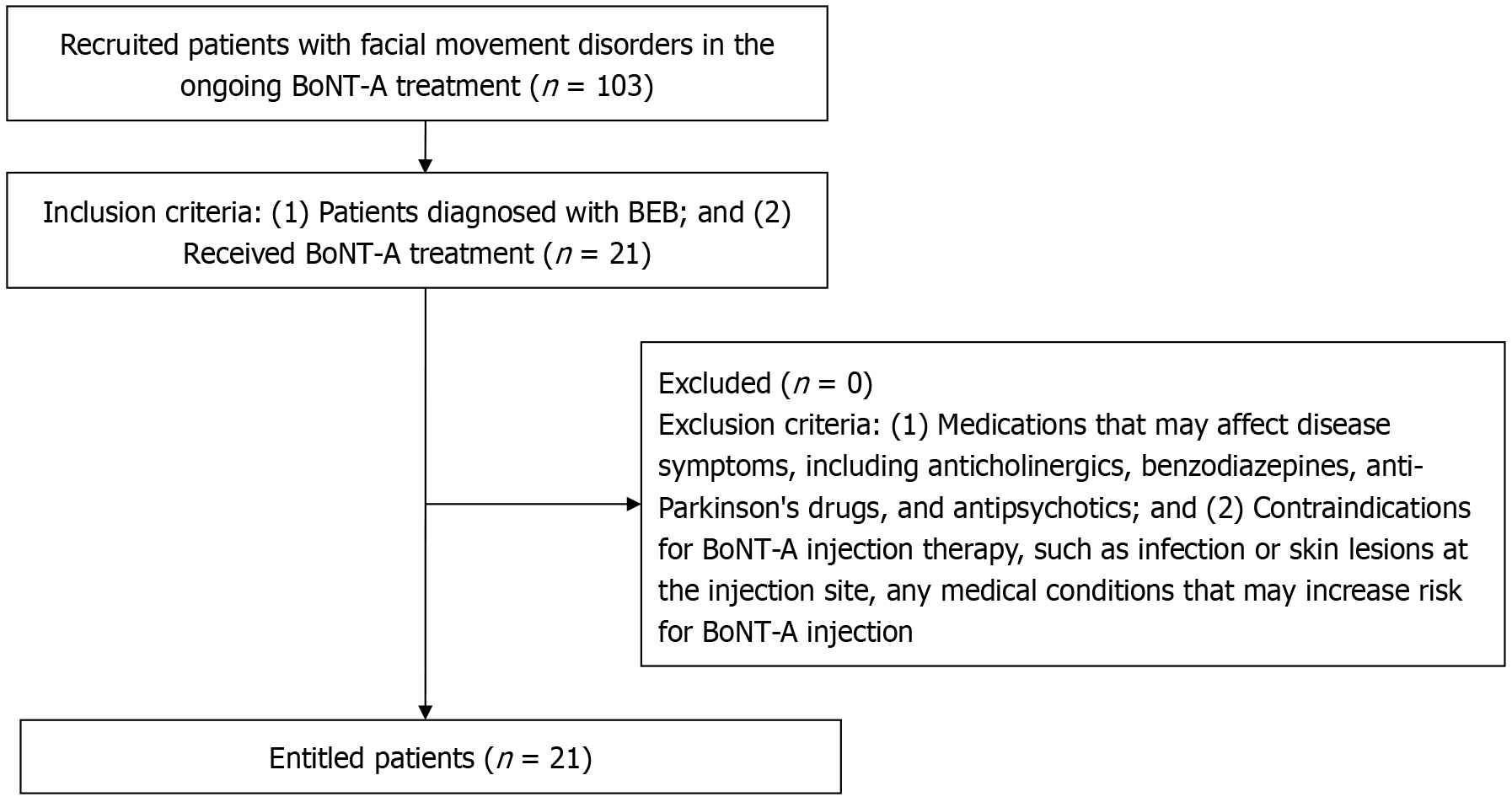
Figure 2 Flow diagram describing the study population, number included and excluded.
BoNT-A: Botulinum toxin A; BEB: Benign essential blepharospasm.
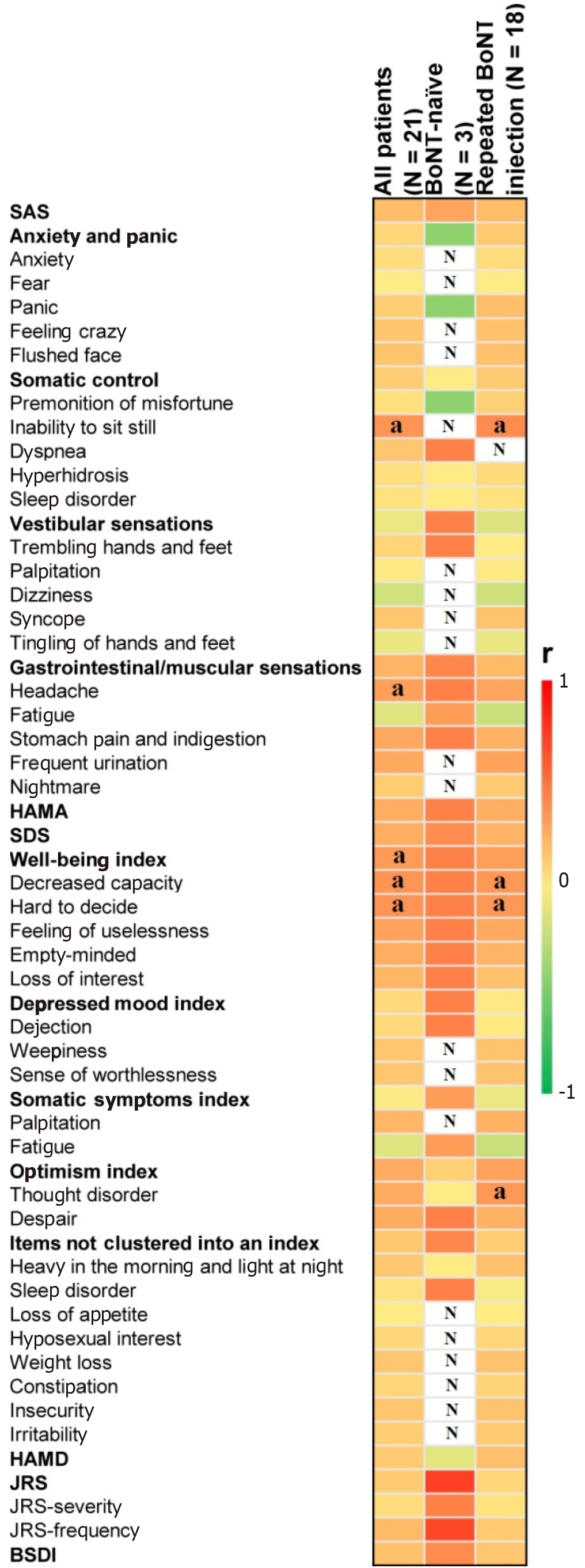
Figure 3 Heat map of correlation between botulinum toxin A therapy and Jankovic Rating Scale, Blepharospasm Disability Index, Self-rating Anxiety Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Scale, Self-rating Depression Scale and Hamilton Depression Scale total and their subscale scores in a whole group and subgroups.
aP < 0.05, N: No significance. BoNT-A: Botulinum toxin A; SAS: Self-rating Anxiety Scale; HAMA: Hamilton Anxiety Scale; SDS: Self-rating Depression Scale; HAMD: Hamilton Depression Scale; JRS: Jankovic Rating Scale; BSDI: Blepharospasm Disability Index.
- Citation: He XY, Xu MY, Feng LY, Zhang JT, Jin LZ, Jin L, Ge JC, Zhang L, Zhang WB, Zhang L, Shen H, Yan J. Sustained anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of botulinum toxin A in blepharospasm patients beyond motor symptom control. World J Psychiatry 2026; 16(1): 112973
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v16/i1/112973.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v16.i1.112973