©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jul 19, 2025; 15(7): 106023
Published online Jul 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.106023
Published online Jul 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.106023
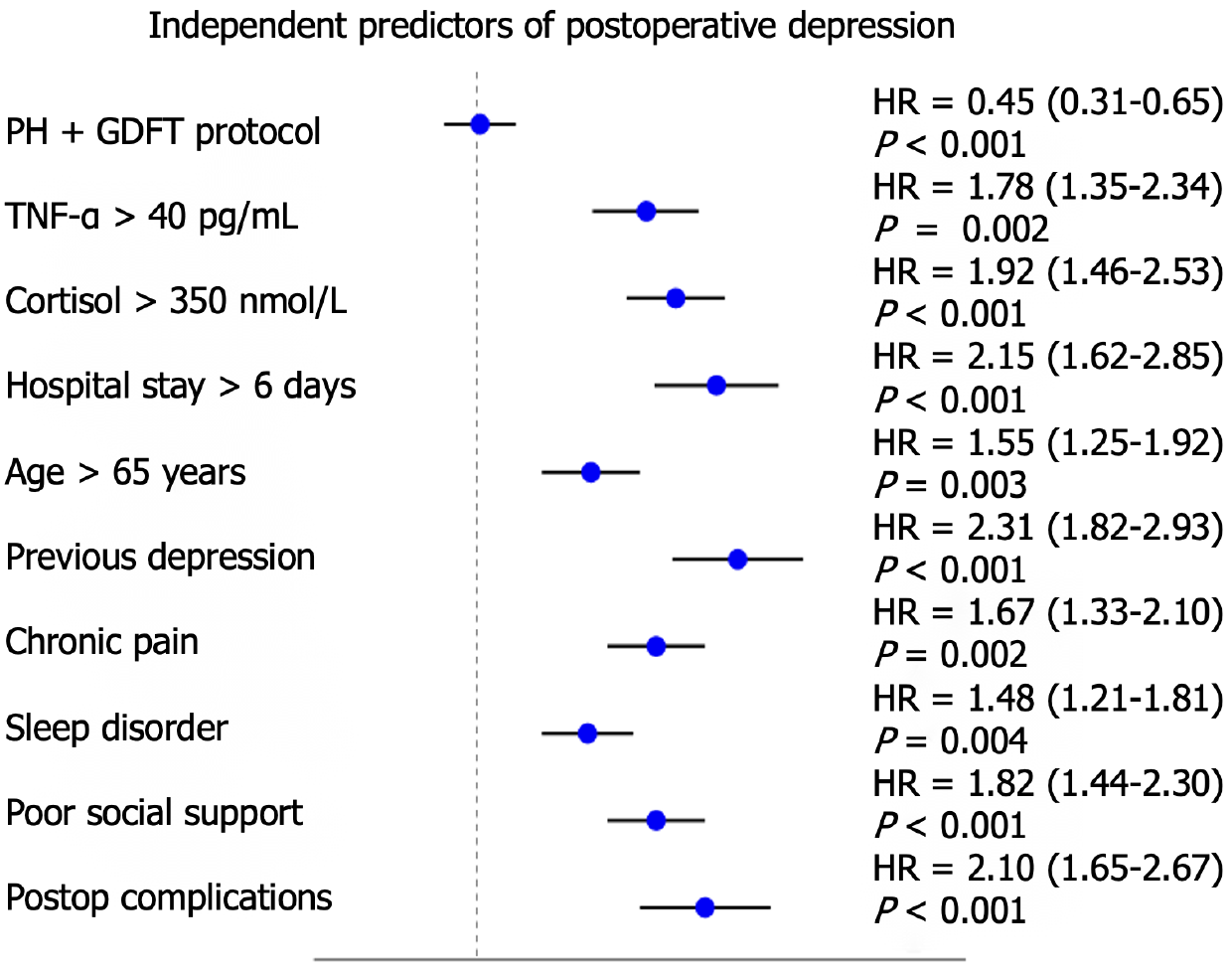
Figure 1 Independent predictors of postoperative depression.
The analysis shows that the permissive hypercapnia + goal-directed fluid therapy protocol significantly reduced the risk of depression during the 7-day follow-up (hazard ratio = 0.45). Other factors linked to higher depression risk included high tumor necrosis factor α levels (> 40 pg/mL), high cortisol levels (> 350 nmol/L), and longer hospital stays (> 6 days). PH: Permissive hypercapnia; GDFT: Goal-directed fluid therapy; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; HR: Hazard ratio.
- Citation: Yuan L, Zhang XM, Liu N, Shi JQ, Sun XJ, Li GL, Teng JL. Permissive hypercapnia combined with goal-directed fluid therapy improve postoperative mental health in elderly patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(7): 106023
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i7/106023.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.106023