©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Dec 19, 2025; 15(12): 112479
Published online Dec 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i12.112479
Published online Dec 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i12.112479
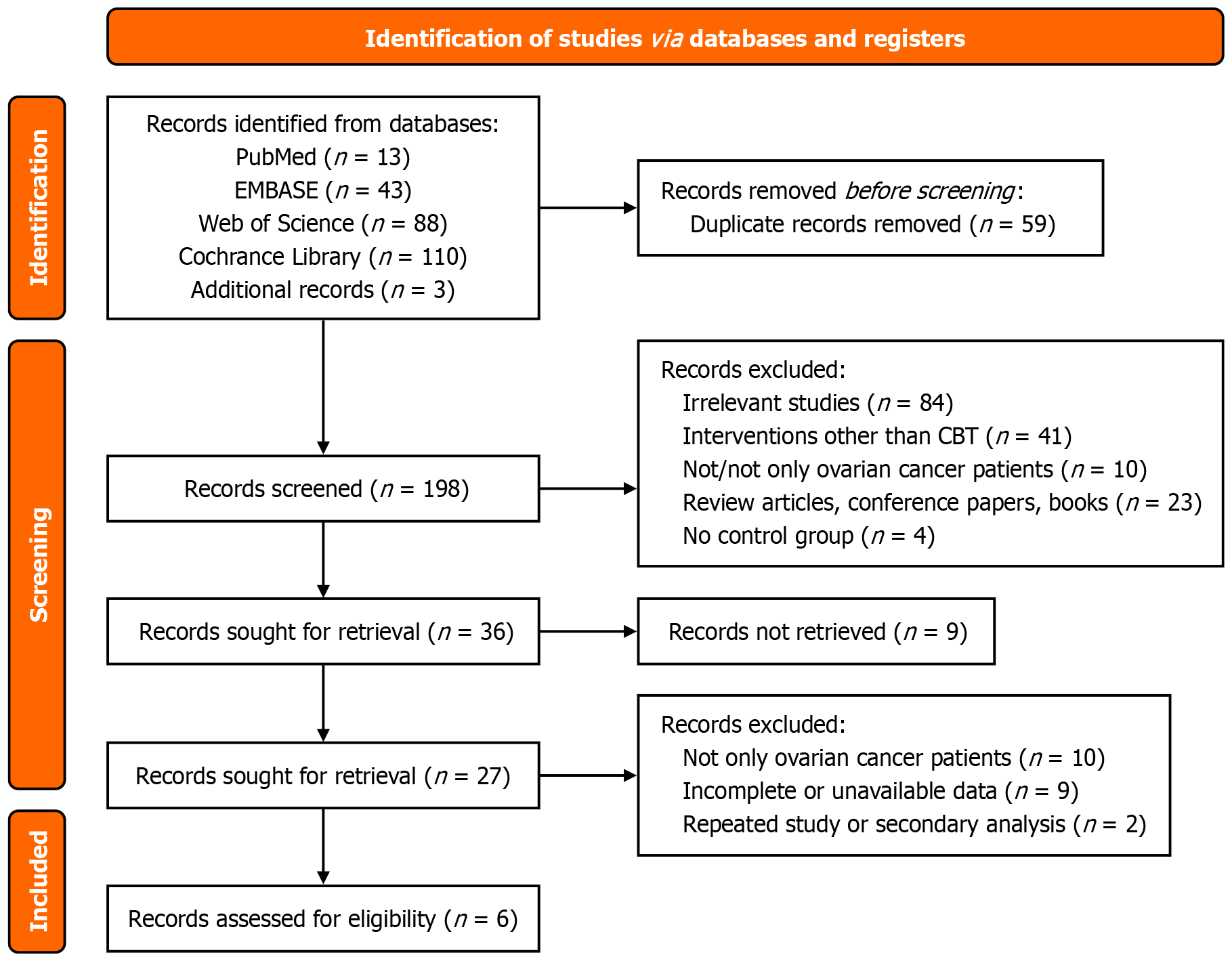
Figure 1
Literature screening flow chart.
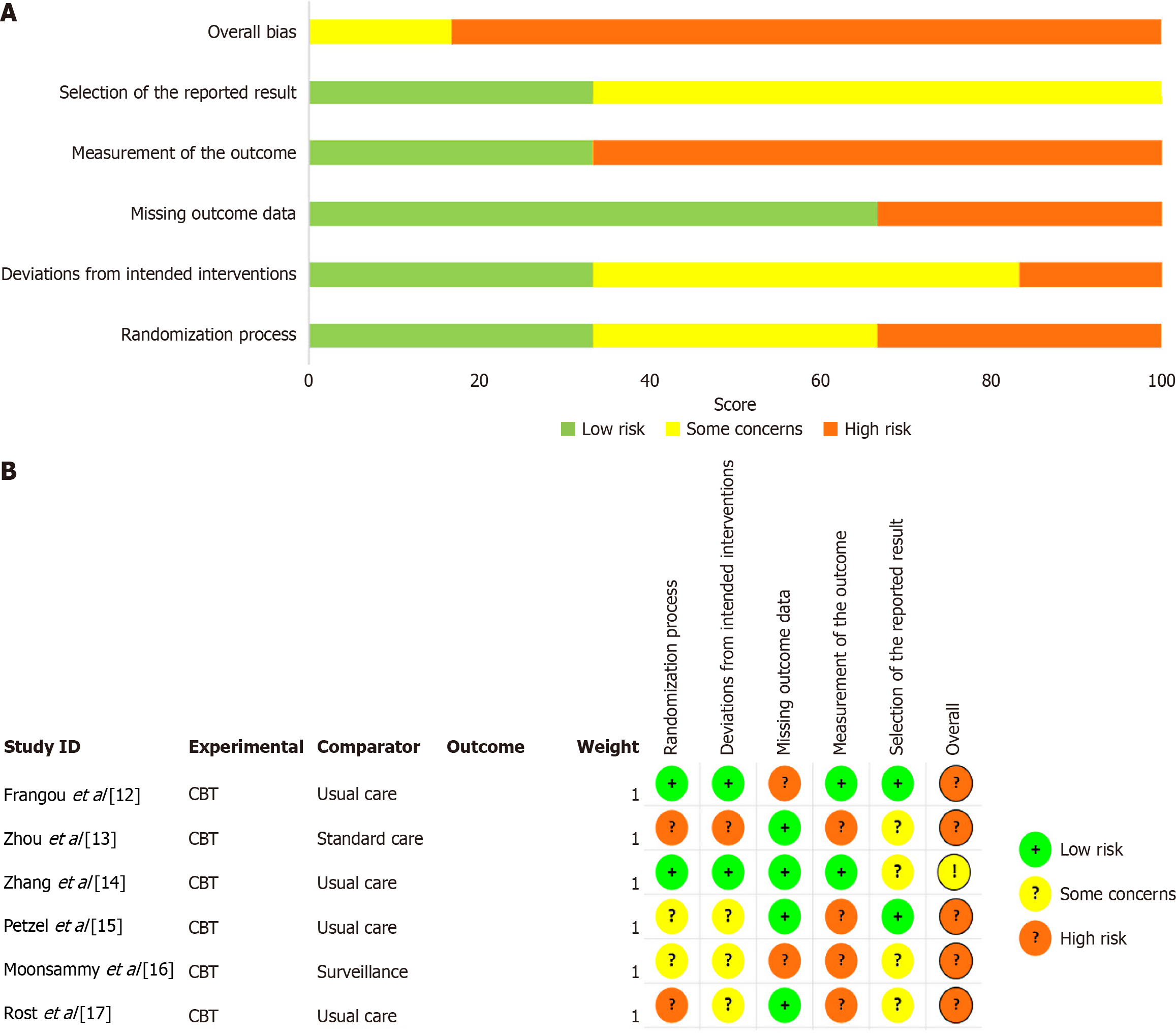
Figure 2 Risk of bias of the included studies by the Cochrane RoB 2.
0 tool. A: Risk of bias graph; B: Risk of bias summary. CBT: Cognitive behavioral therapy.
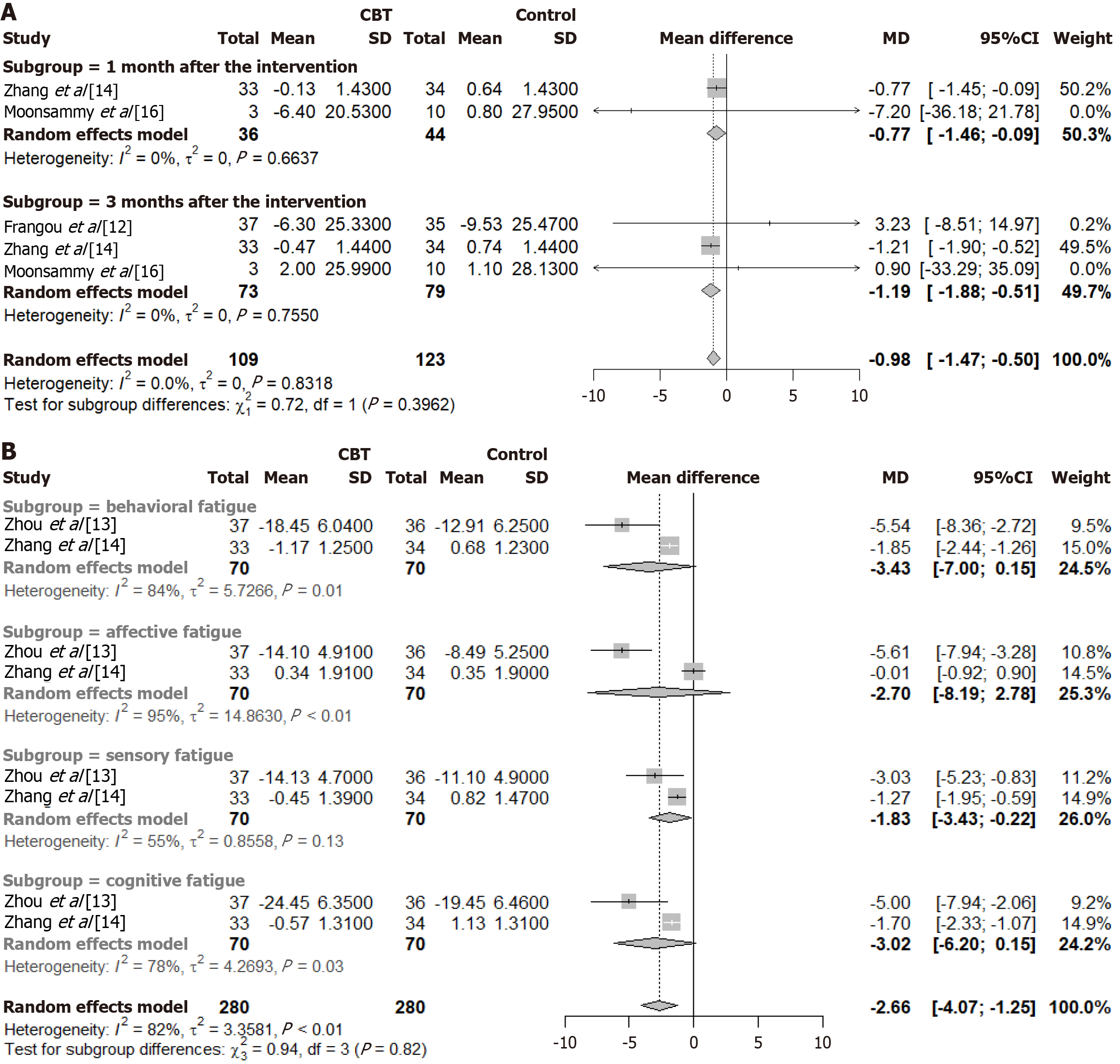
Figure 3 Meta-analysis of cancer-related fatigue of ovarian cancer patients after cognitive behavioral therapy treatment.
A: Total cancer-related fatigue; B: Subscales of cancer-related fatigue (negative values indicate a reduction in cancer-related fatigue). CBT: Cognitive behavioral therapy; CI: Confidence interval.
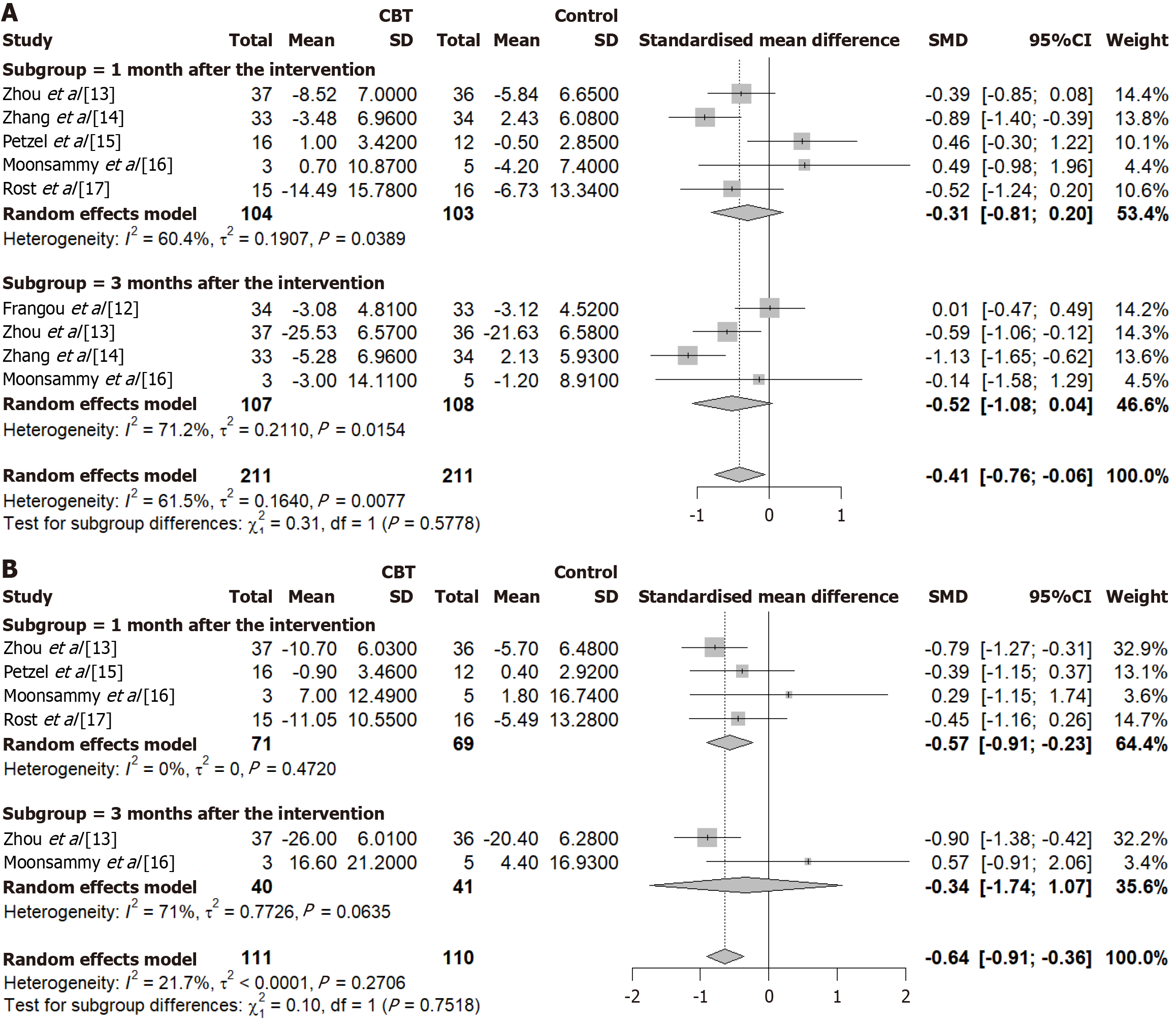
Figure 4 Meta-analysis of depression and anxiety of patients with ovarian cancer after cognitive behavioral therapy treatment.
A: Depression; B: Anxiety (negative values indicate a reduction in depression or anxiety). CBT: Cognitive behavioral therapy; CI: Confidence interval.
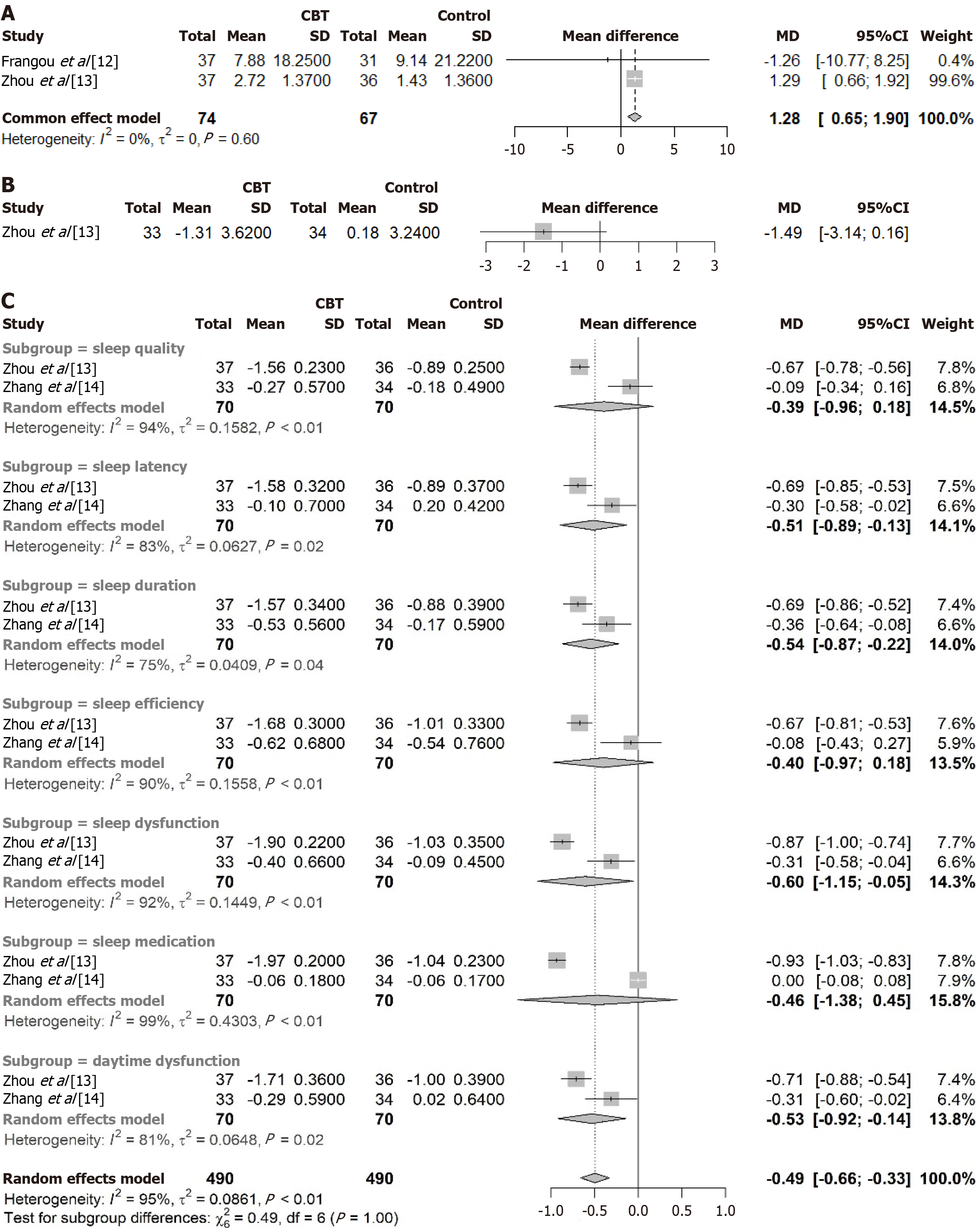
Figure 5 Meta-analysis of quality of life and quality of sleep.
A: Quality of life-general health; B: Quality of sleep; C: Subscales of quality of sleep (positive value indicates an improvement in quality of life or quality of sleep). CBT: Cognitive behavioral therapy; CI: Confidence interval.
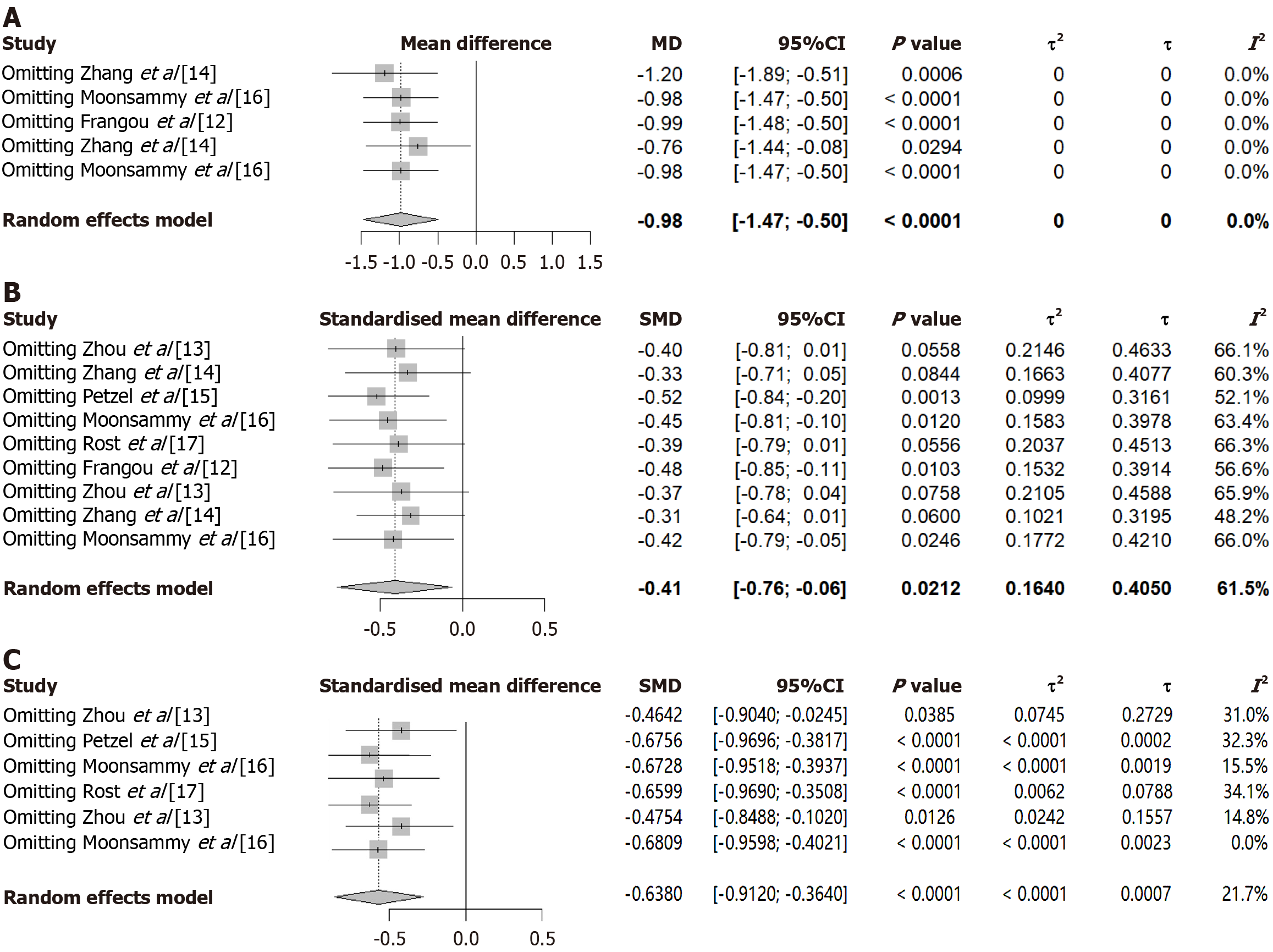
Figure 6 Sensitivity analysis of cancer-related fatigue, depression, and anxiety of patients with ovarian cancer after cognitive behavioral therapy treatment.
A: Cancer-related fatigue; B: Depression; C: Anxiety.
- Citation: Zhao F, Bo Y, Su XL. Effect of cognitive behavioral therapy on cancer-related fatigue and psychological status in ovarian cancer patients: A meta-analysis. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(12): 112479
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i12/112479.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i12.112479