©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Nov 19, 2025; 15(11): 111917
Published online Nov 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.111917
Published online Nov 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.111917
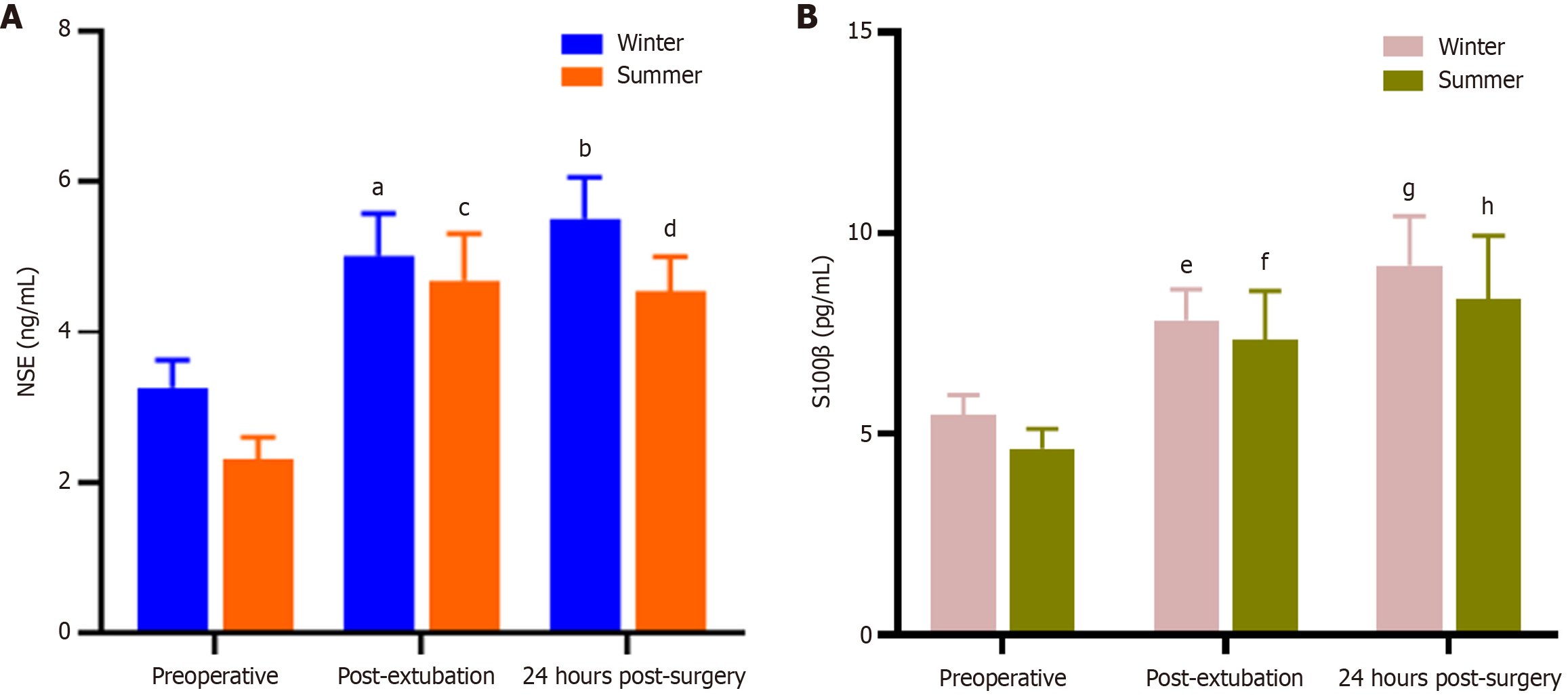
Figure 1 Expression levels of S100 calcium binding protein B and Neuron-specific enolase at various time points.
A: Neuron-specific enolase; B: S100 calcium binding protein B. aP value = 0.003. Post-extubation vs preoperative serum neuron-specific enolase levels in winter surgical patients. bP value = 0.02. Postoperative 24 hours vs preoperative neuron-specific enolase levels in winter surgical patients. cP value = 0.05. Post-extubation vs preoperative serum neuron-specific enolase levels in summer surgical patients. dP value = 0.04. Postoperative 24 hours vs preoperative neuron-specific enolase levels in summer surgical patients. eP value = 0.06. Post-extubation vs preoperative serum S100 calcium binding protein B levels in winter surgical patients. fP value = 0.02. Postoperative 24 hours vs preoperative S100 calcium binding protein B levels in winter surgical patients. gP value = 0.003. Post-extubation vs preoperative serum S100 calcium binding protein B levels in summer surgical patients. hP value = 0.01. Postoperative 24 hours vs preoperative S100 calcium binding protein B levels in summer surgical patients. NSE: Neuron-specific enolase; S100β: S100 calcium binding protein B.
- Citation: Liu M, Song WL, Shen HJ, Liu YM. Impact of ambient temperature on postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients surgery: A seasonal comparison in tropical regions. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(11): 111917
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i11/111917.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.111917