©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Nov 19, 2025; 15(11): 109332
Published online Nov 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.109332
Published online Nov 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.109332
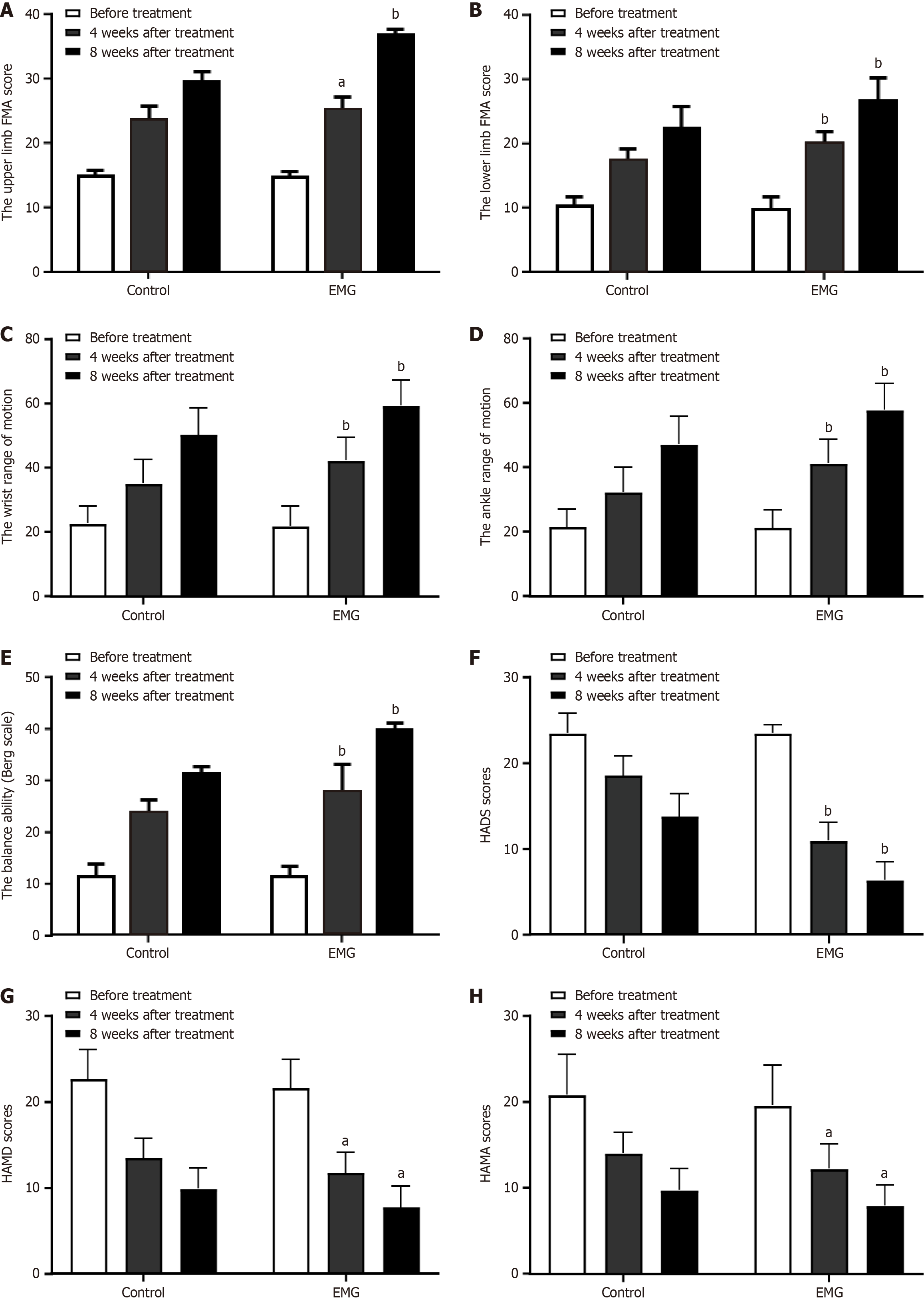
Figure 1 Comparison of motor function, motion range, balance ability, anxiety and depression between the two groups.
A: Comparison of pre- and post-treatment upper limb Fugl-Meyer assessment scores between the two groups; B: Comparison of pre- and post-treatment lower limb Fugl-Meyer assessment scores between the two groups; C: Comparison of wrist joint range of motion before and after treatment between the two groups; D: Comparison of ankle joint range of motion before and after treatment between the two groups; E: Comparison of balance ability (Berg scores) before and after treatment between the two groups; F: Comparison of Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale scores before and after treatment between the two groups; G: Comparison of Hamilton Depression Rating Scale scores before and after treatment between the two groups; H: Comparison of Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale scores before and after treatment between the two groups. aP < 0.01 compared to the control group; bP < 0.001 compared to the control group. FMA: Fugl-Meyer assessment; EMG: Electromyographic; HADS: Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; HAMD: Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; HAMA: Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale.
- Citation: Yu L, Niu H, Ji WB, Liu ZG, Jiang B, Wang WY. Application of electromyographic biofeedback therapy in physical dysfunction rehabilitation and post-stroke anxiety reduction in stroke survivors. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(11): 109332
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i11/109332.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.109332