©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Nov 19, 2025; 15(11): 106956
Published online Nov 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.106956
Published online Nov 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.106956
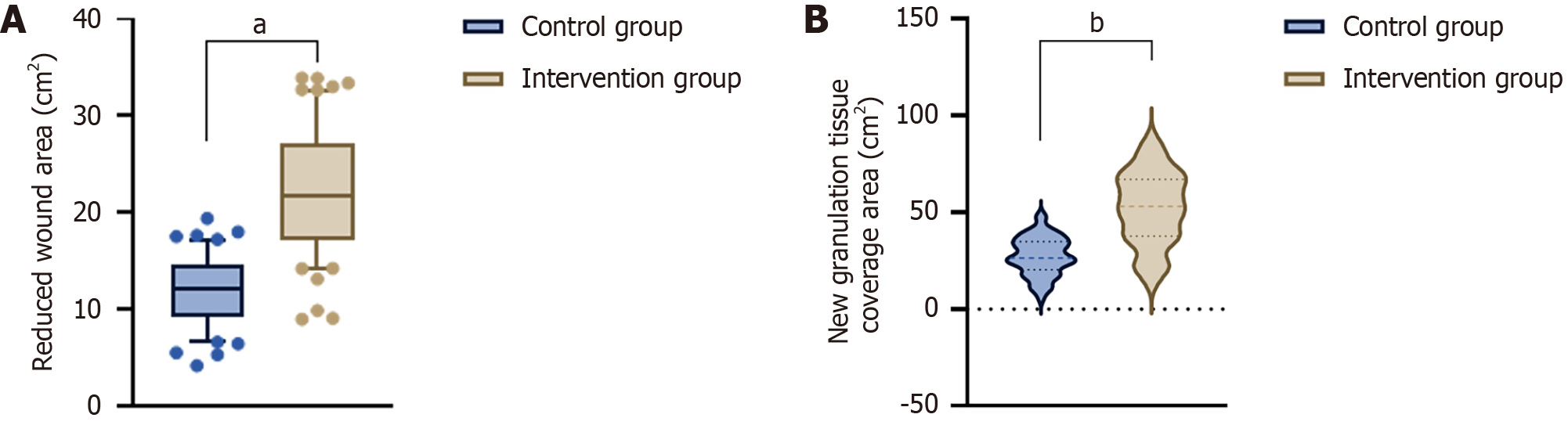
Figure 1 Comparison of reduced wound area and new granulation tissue coverage area between the two groups after 4 weeks of nursing.
aP < 0.001 vs control; bP < 0.001 vs control. A: Comparison of reduced wound area between the two groups after 4 weeks of nursing; B: New granulation tissue coverage area between the two groups after 4 weeks of nursing.
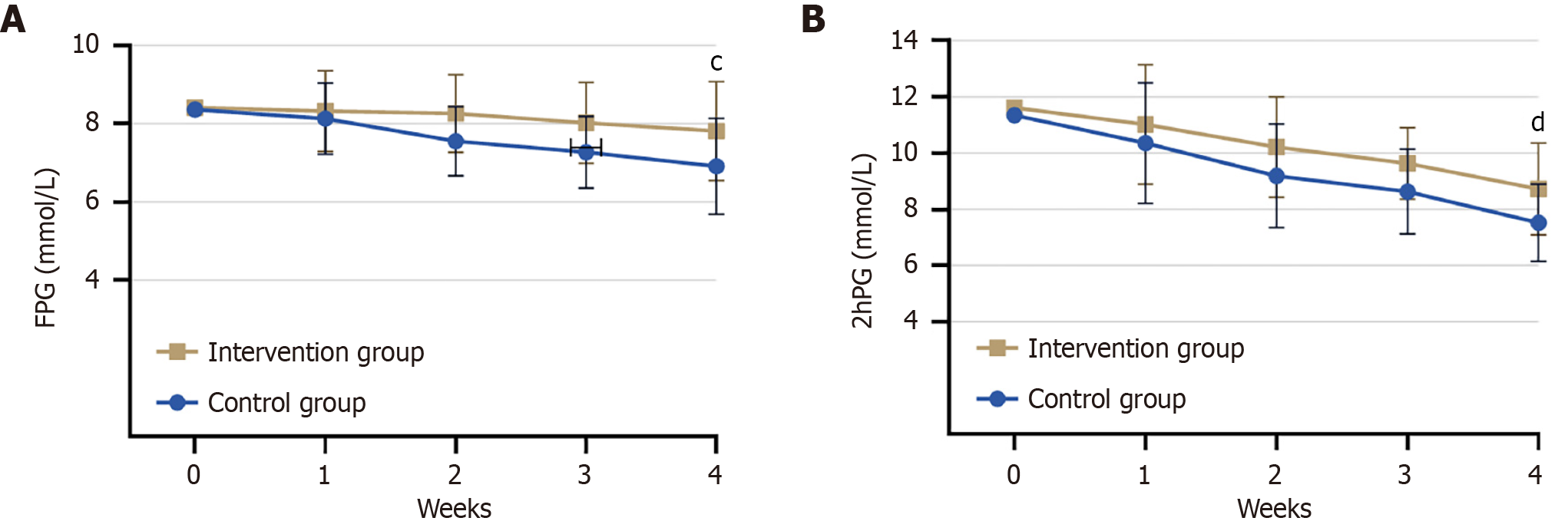
Figure 2 Comparison of blood glucose indexes between the two groups before and after intervention.
cP < 0.05 vs control; dP < 0.05 vs control. A: Comparison of fasting plasma glucose between the two groups before and after intervention; B: 2-hour postprandial blood glucose comparison between the two groups before and after intervention. FPG: Fasting plasma glucose; 2hPG: 2-hour postprandial blood glucose.
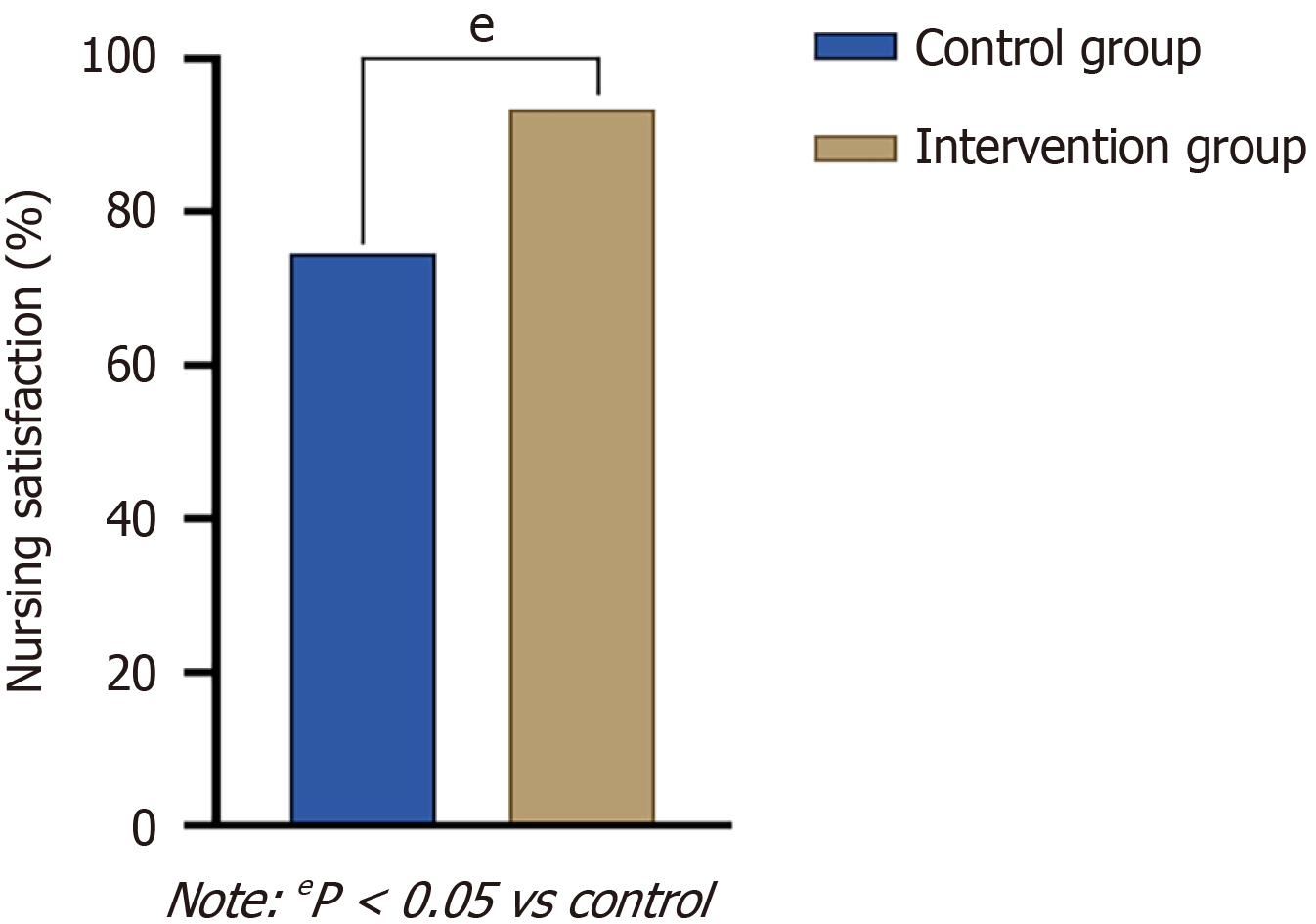
Figure 3 Comparison of nursing satisfaction between the two groups.
eP < 0.05 vs control.
- Citation: Jiang C, Guan RN, Shu Y, Zhang L, Mao XP, Nie Q, Zhu HF. Impact of multidisciplinary nursing interventions and blood glucose control on diabetic foot ulcer healing, patient emotions, and satisfaction. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(11): 106956
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i11/106956.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.106956