Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Jul 19, 2024; 14(7): 1095-1105
Published online Jul 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i7.1095
Published online Jul 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i7.1095
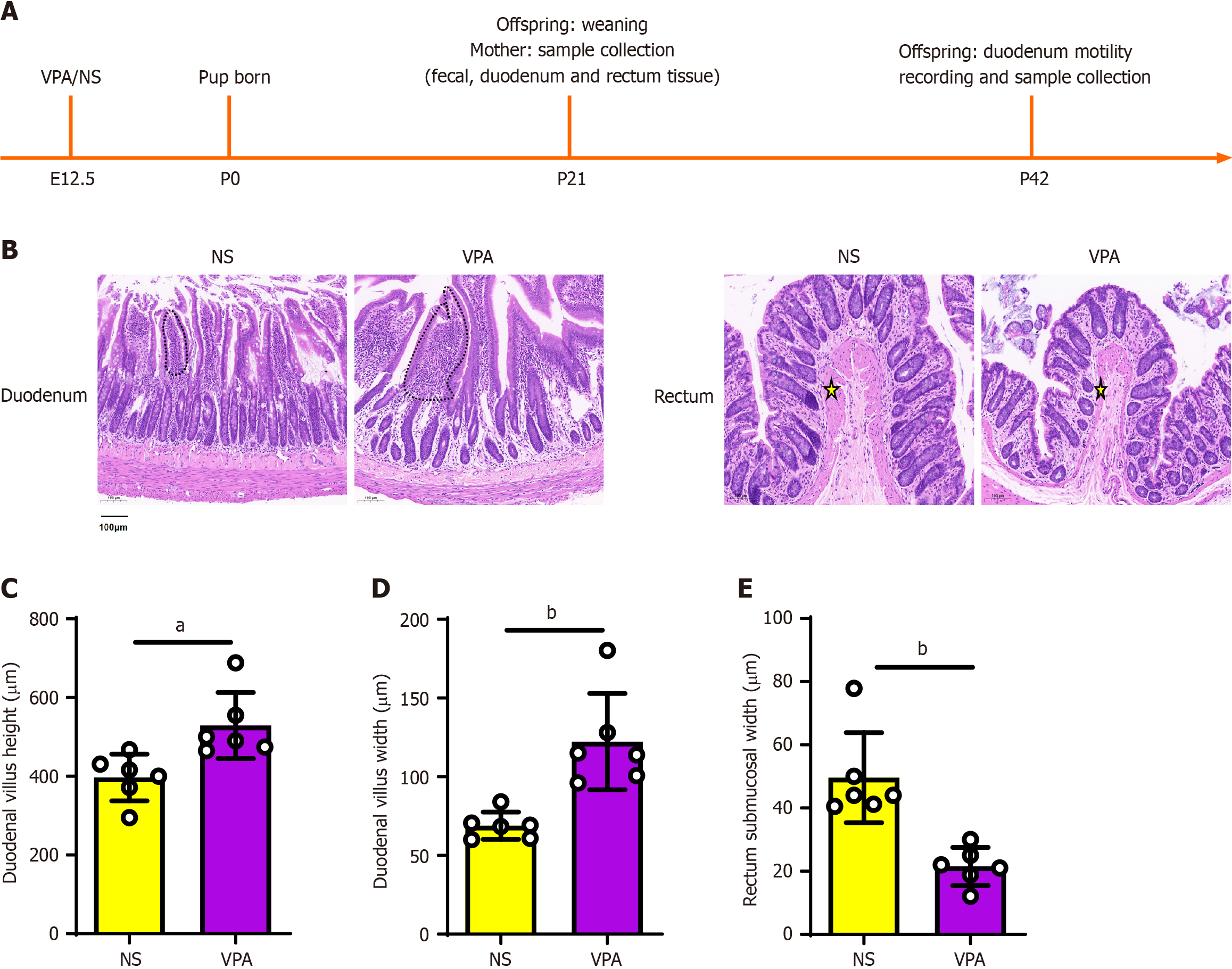
Figure 1 Histological evaluation of intestinal tissue of the normal saline and valproic acid groups (hematoxylin & eosin staining; scale bar = 100 μm; 10 ×).
A: Timeline of experimental design; B: Hematoxylin & eosin staining of the duodenum (above) and rectum (down). The duodenal villi are marked by dotted lines. The submucosa is marked by a yellow star; C and D: Histological statistics of duodenal villi height and width; E: Histological statistics of rectal submucosal width. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (normal saline group n = 6, valproic acid group n = 6). Unpaired t test, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. NA: Normal saline; VPA: Valproic acid.
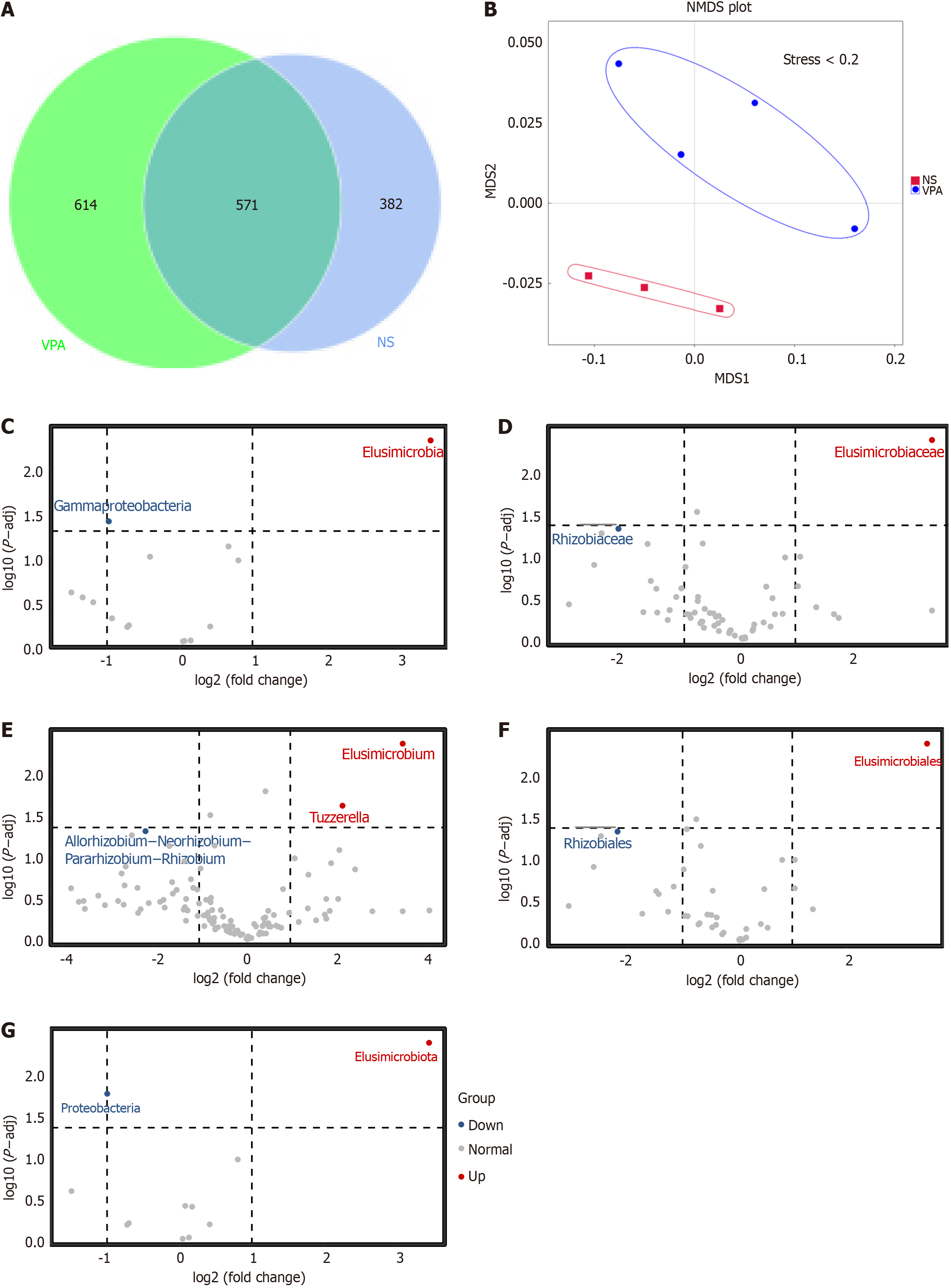
Figure 2 Alteration of gut microbiota in normal saline and valproic acid groups according to 16S rRNA data.
A: Venn diagram of observed operational taxonomic units in normal saline and valproic acid (VPA) groups; B: Beta diversity of gut microbiota based on nonmetric multidimensional scaling; C-G: Significantly different species at each taxonomic level (class, family, genus, order, and phylum) based on t-test analysis. Normal saline group n = 3, valproic acid group n = 4. P < 0.05. NA: Normal saline; VPA: Valproic acid.
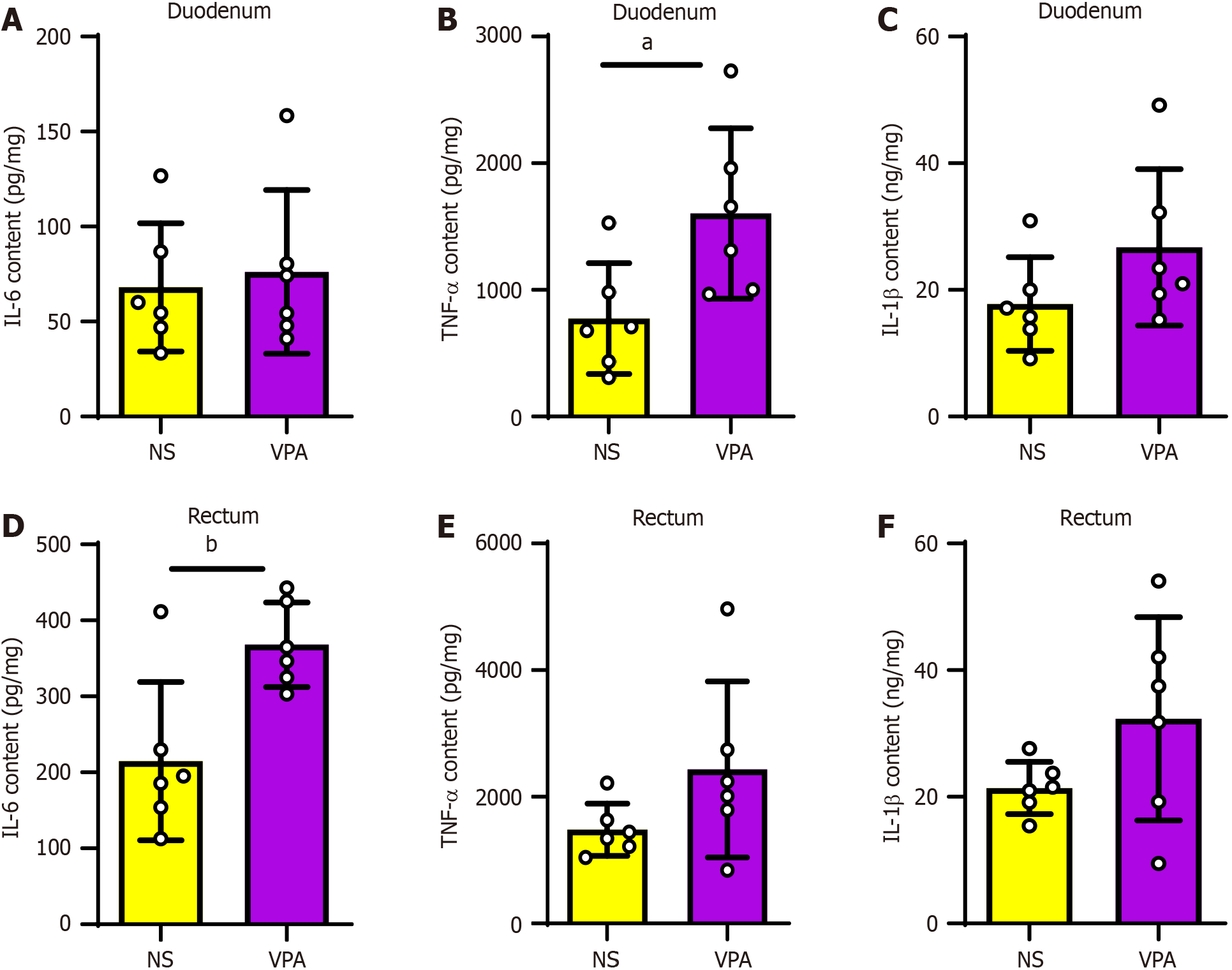
Figure 3 Levels of intestinal inflammatory factors are increased in valproic acid group.
A-C: Interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and IL-1β levels in the duodenum in normal saline (NS) and valproic acid (VPA) groups; D-F: IL-6, TNF–α, and IL-1β levels in the rectum in NS and VPA groups. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (normal saline group n = 6, valproic acid group n = 6). Unpaired t test, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL: Interleukin; NA: Normal saline; VPA: Valproic acid.
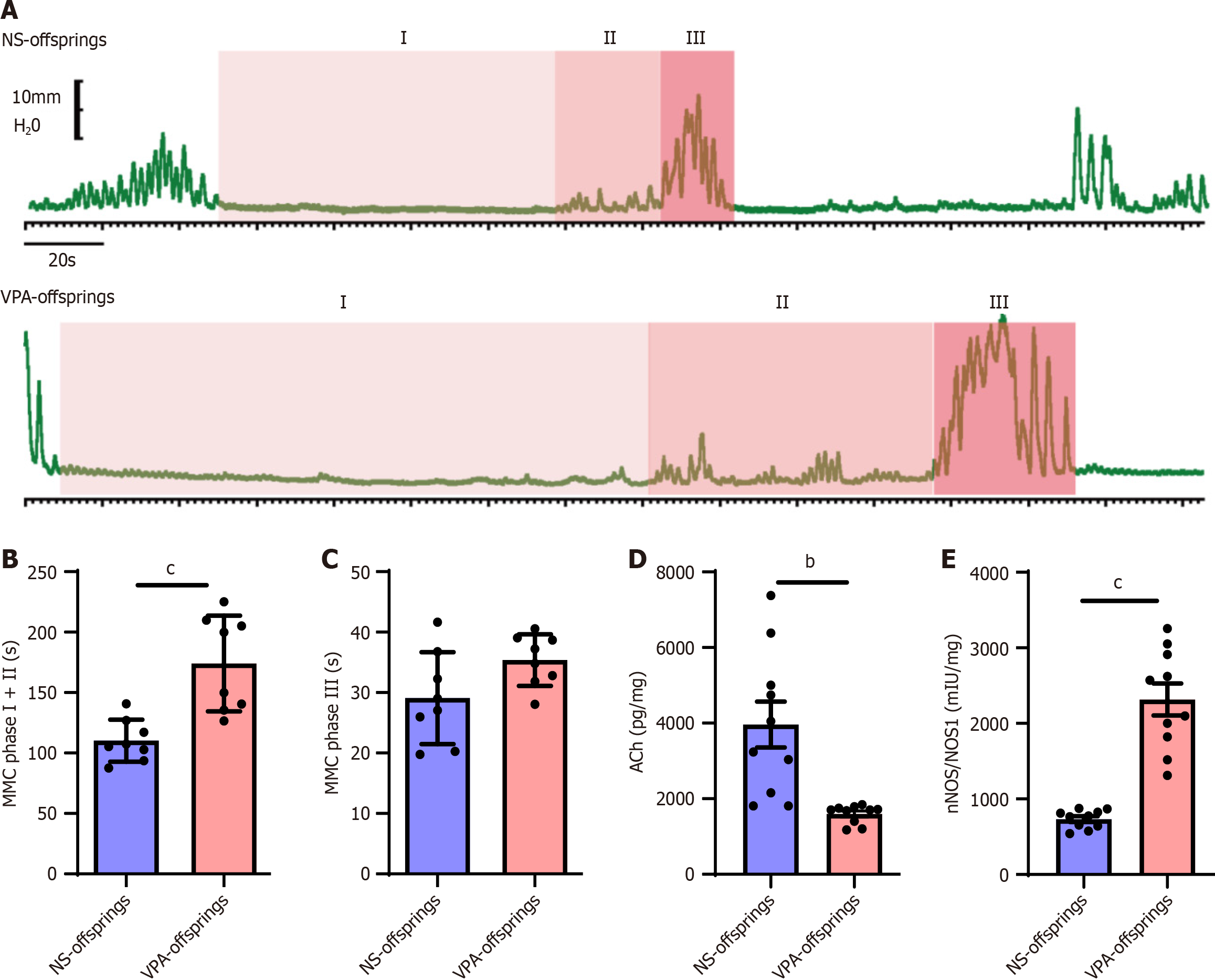
Figure 4 Duodenal motility and neurotransmitters are impaired after prenatal valproic acid exposure.
A: Duodenal motility in normal saline (NS) and valproic acid (VPA) offspring at different phases of migrating motor complex (MMC); B and C: Duration of MMC phases I + II (B) and III (C) in NS and VPA offspring groups (NS offspring group n = 8, VPA offspring group n = 8). Unpaired t test, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01; D and E: Levels of acetylcholine (D) and nitric oxide synthase (E) in NS and VPA offspring groups in the duodenum. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (normal saline offspring group n = 10, valproic acid offspring group n = 10). Unpaired t test, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. NA: Normal saline; VPA: Valproic acid; MMC: Migrating motor complex; ACh: Acetylcholine; NOS: Nitric oxide synthase.
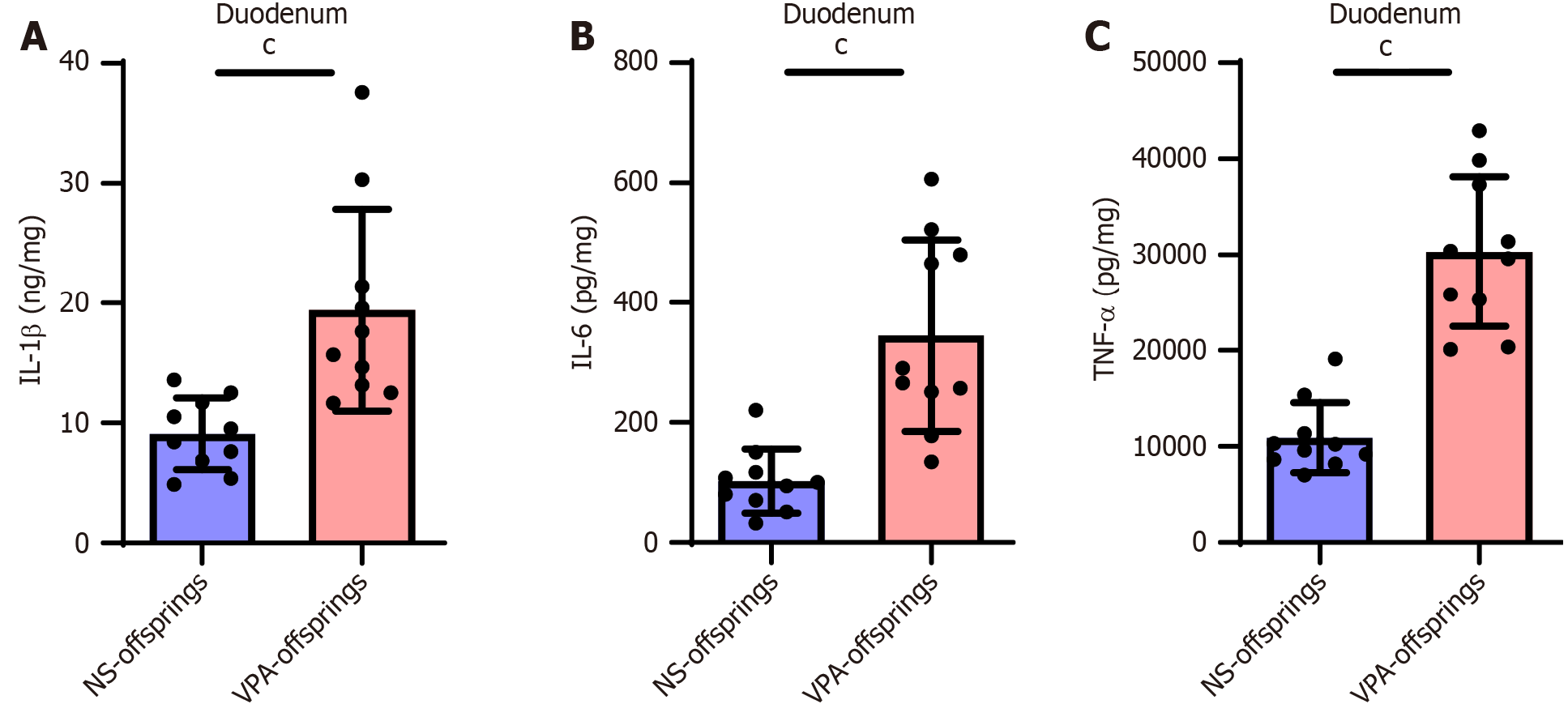
Figure 5 Levels of duodenal inflammatory factors are increased in valproic acid group.
A: Interleukin (IL)-1β levels in the duodenum in normal saline (NS) and valproic acid (VPA) groups; B: IL-6 levels in the duodenum in NS and VPA groups; C: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in the duodenum in NS and VPA groups. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (normal saline offspring group n = 8, valproic acid offspring group n = 8). Unpaired t test, cP < 0.001. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL: Interleukin; NA: Normal saline; VPA: Valproic acid.
- Citation: Li S, Zhang N, Li W, Zhang HL, Wang XX. Gastrointestinal problems in a valproic acid-induced rat model of autism: From maternal intestinal health to offspring intestinal function. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(7): 1095-1105
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i7/1095.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i7.1095