©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2024; 14(3): 370-379
Published online Mar 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.370
Published online Mar 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.370
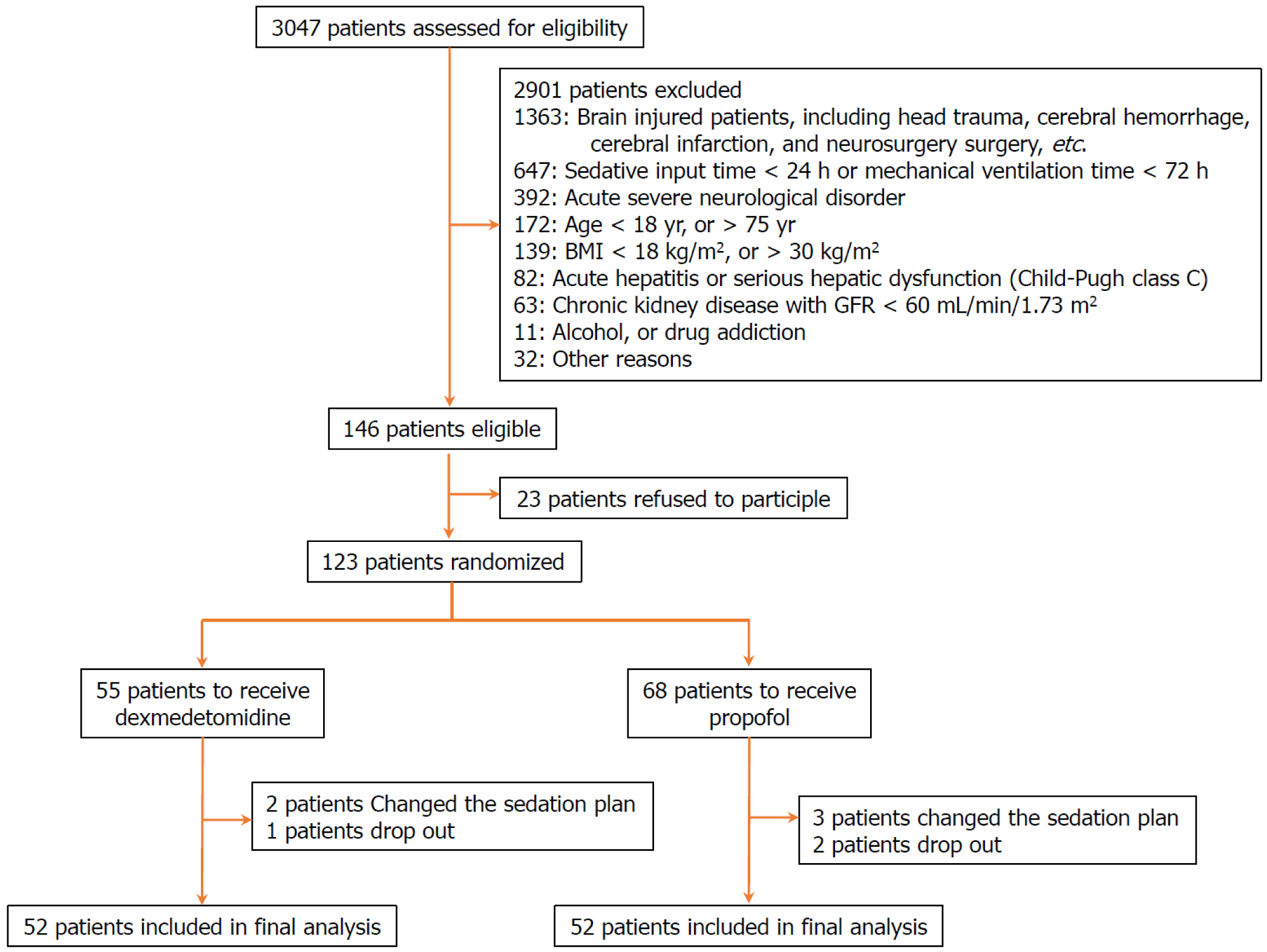
Figure 1 Flow diagrams for the trials.
BMI: Body mass index; GFR: Glomerular filtration rate.
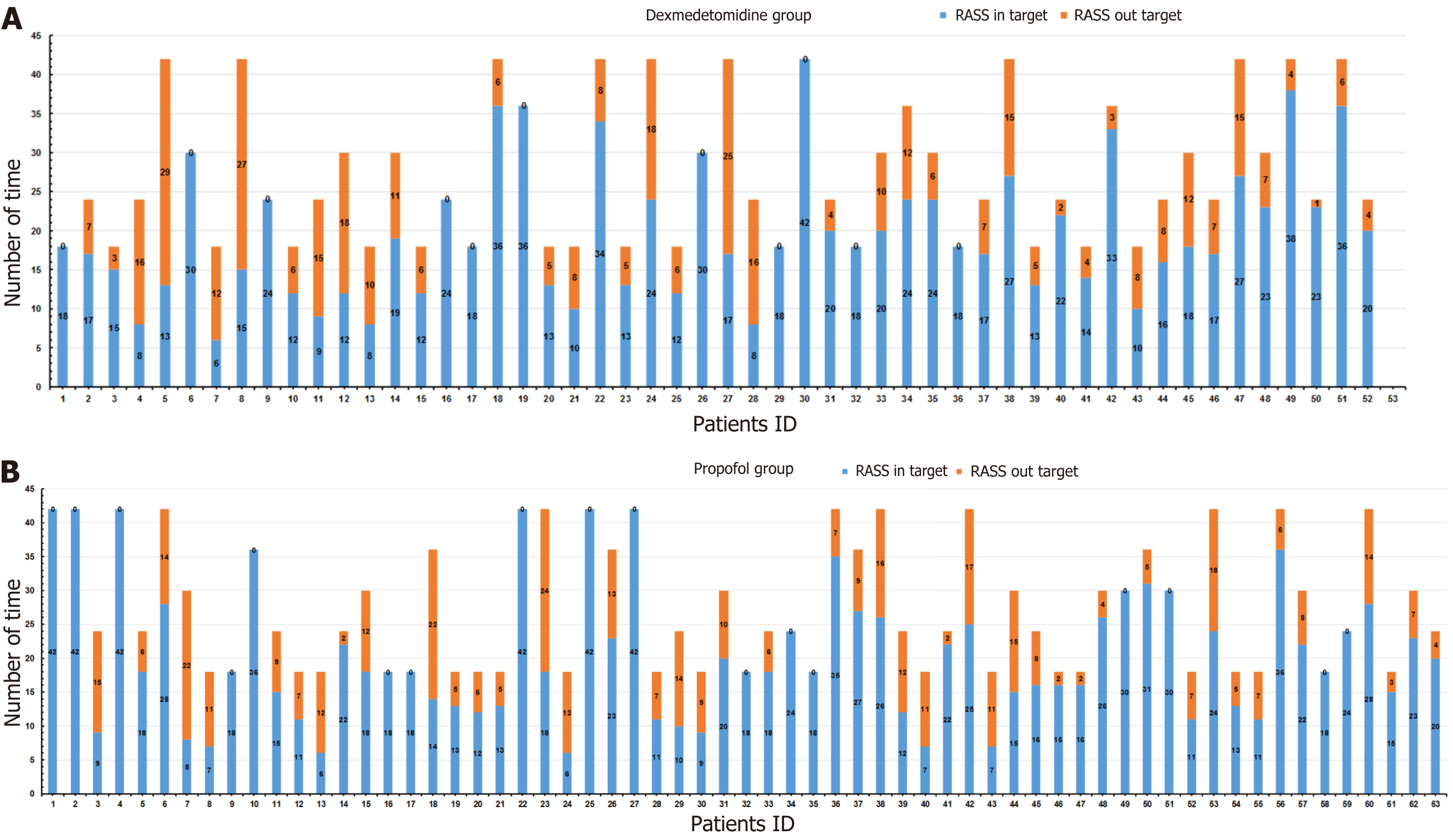
Figure 2 Number of times Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale scores in and out the target range.
A: Dexmedetomidine group; B: Propofol group. RASS: Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale scores.
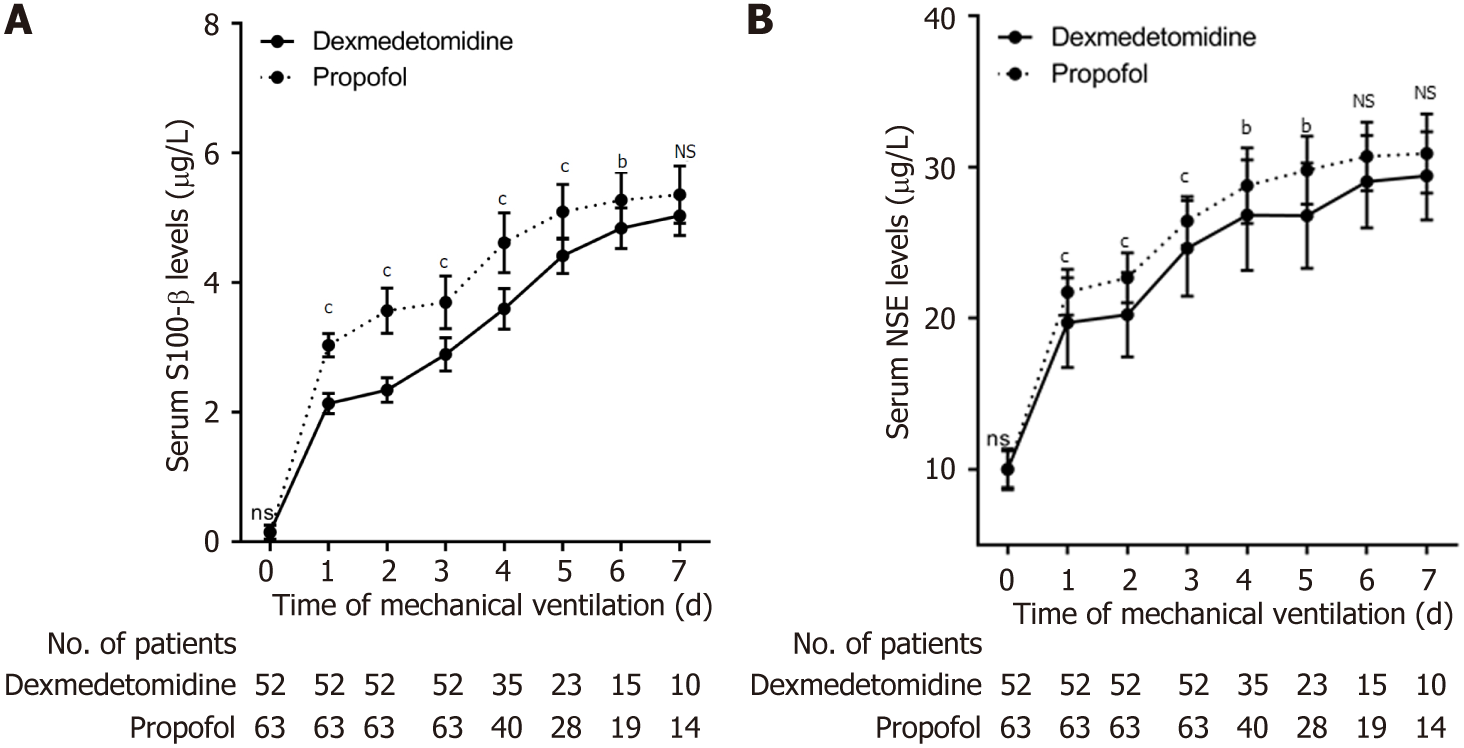
Figure 3 Dynamic changes of serum S100-β and neuron-specific enolase levels in patients with mechanical ventilation.
A: S100-β; B: Neuron-specific enolase. NSE: Neuron-specific enolase; NS: Not significant. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Yuan HX, Zhang LN, Li G, Qiao L. Brain protective effect of dexmedetomidine vs propofol for sedation during prolonged mechanical ventilation in non-brain injured patients. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(3): 370-379
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i3/370.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.370