©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Jan 19, 2024; 14(1): 26-35
Published online Jan 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.26
Published online Jan 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.26
Figure 1 Flow diagram describing the selection of patients involved in this retrospective study.
Dex: Dexmedetomidine.
Figure 2 Comparison of Mini-Mental State Examination scores and the incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction among the three groups.
A: Mini-Mental State Examination scores; B: The incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. aP < 0.05, dexmedetomidine + ulinastatin vs dexmedetomidine. bP < 0.01, dexmedetomidine + ulinastatin vs ulinastatin. MMSE: Mini-Mental State Examination; POCD: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction; Dex: Dexmedetomidine.
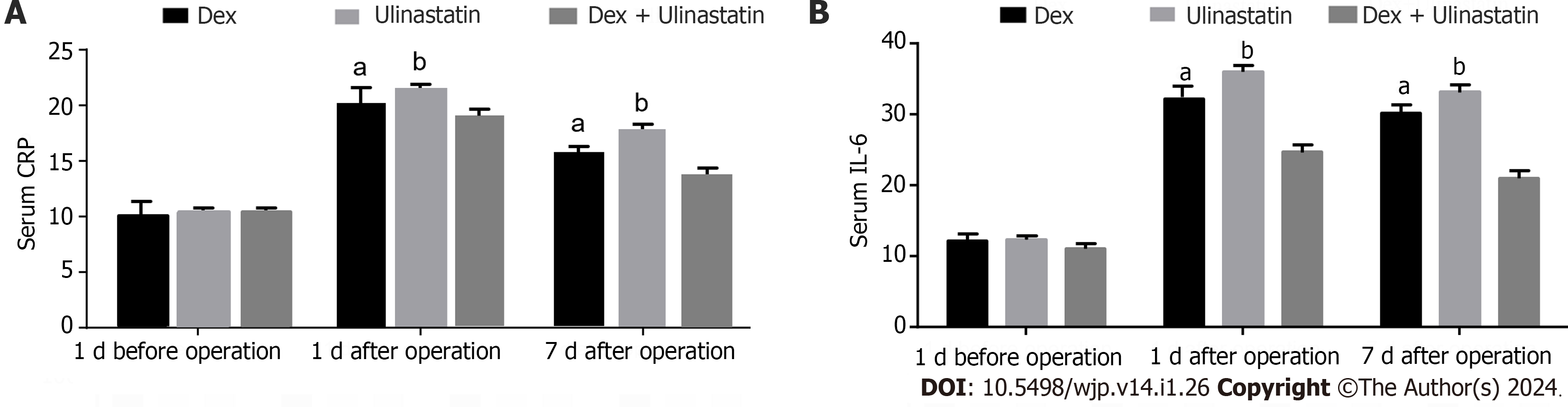
Figure 3 Comparison of serum inflammatory cytokines among the three groups.
A: Serum C-reactive protein; B: Serum interleukin-6. aP < 0.05, dexmedetomidine + ulinastatin vs dexmedetomidine. bP < 0.01, dexmedetomidine + ulinastatin vs ulinastatin. Dex: Dexmedetomidine; CRP: C-reactive protein; IL-6: Interleukin-6.
- Citation: Huo QF, Zhu LJ, Guo JW, Jiang YA, Zhao J. Effects of ulinastatin combined with dexmedetomidine on cognitive dysfunction and emergence agitation in elderly patients who underwent total hip arthroplasty. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(1): 26-35
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i1/26.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.26