©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Psychiatry. Sep 19, 2022; 12(9): 1169-1182
Published online Sep 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i9.1169
Published online Sep 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i9.1169
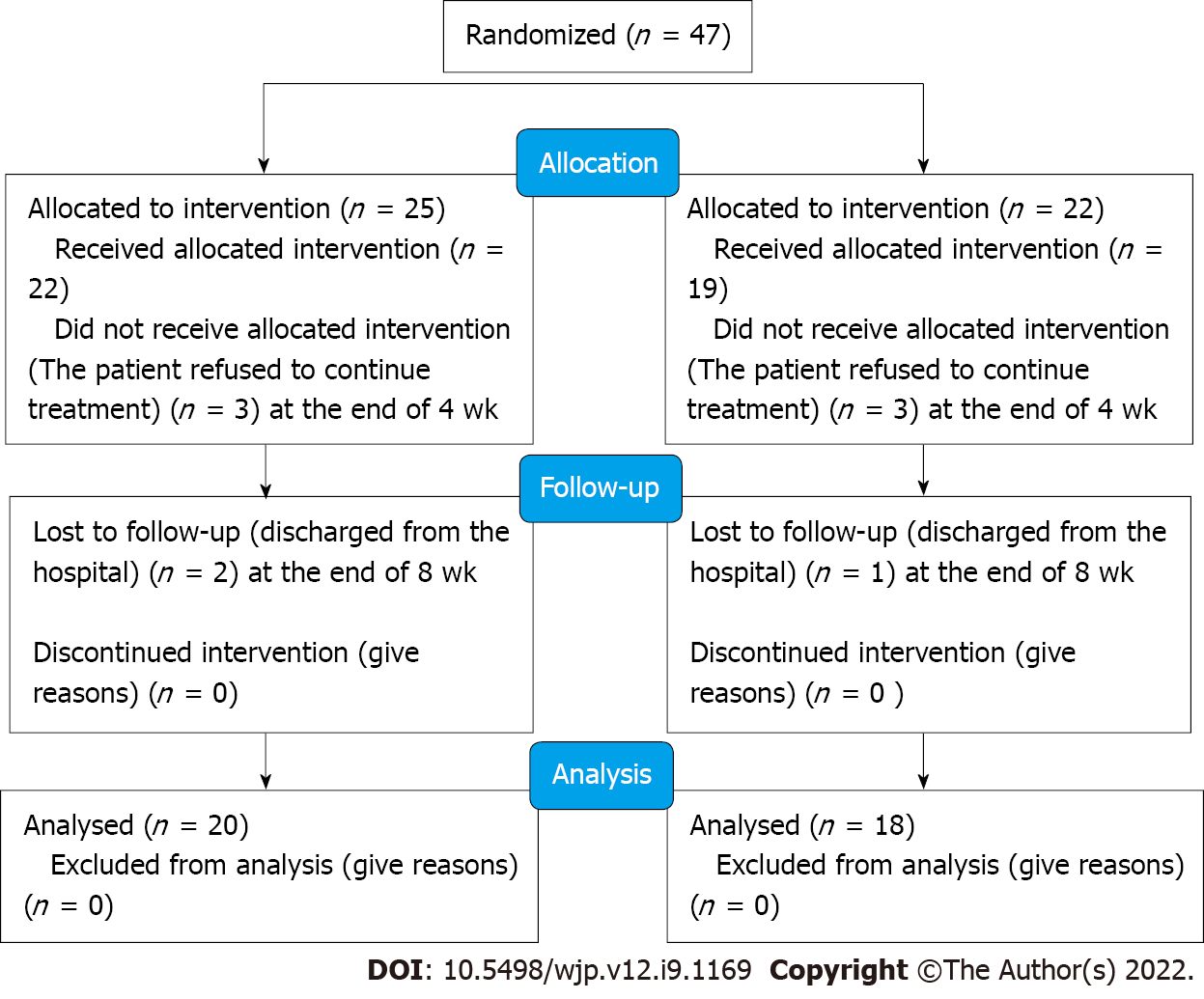
Figure 1 Flow diagram.
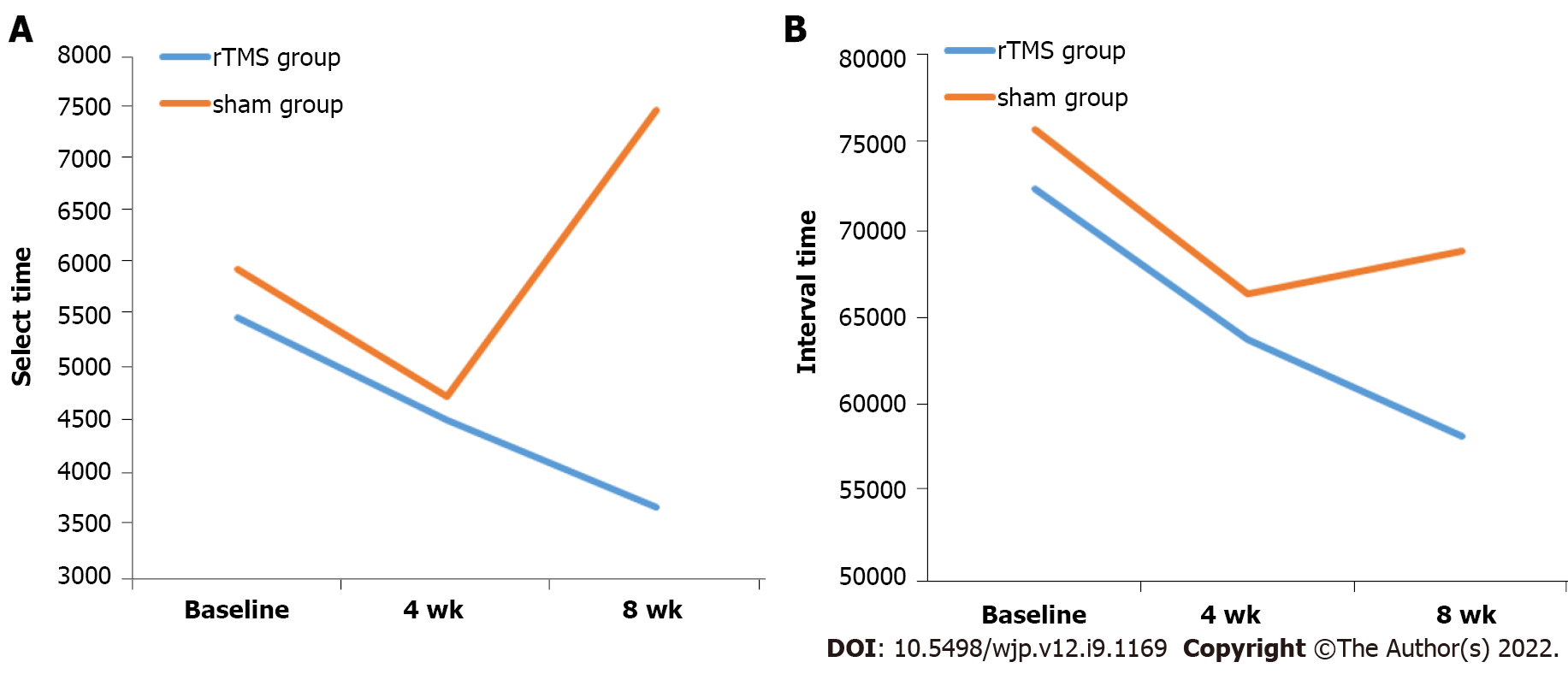
Figure 2 Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation treatment also significantly shortened select and interval time in pattern recognition memory from baseline to week 8 compared to the sham group.
A: Select time; B: Interval time. rTMS: Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation.
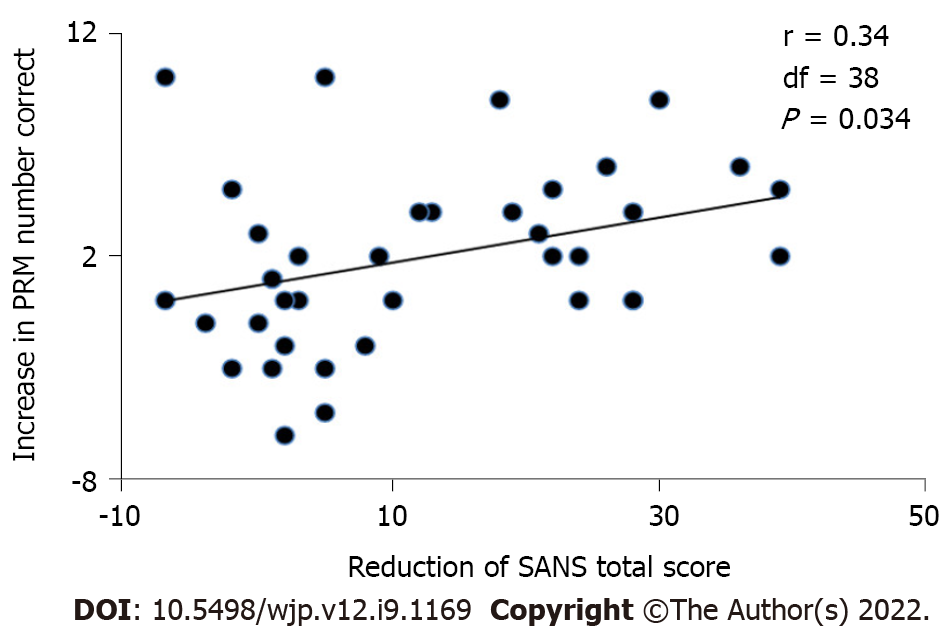
Figure 3 The increase in pattern recognition memory-number correct from baseline to week 8 was significantly correlated with the reduction in Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms total score (P < 0.
05). This association was confirmed by multiple regression analysis (beta = 0.42, t = 2.53, P = 0.017). PRM: Pattern recognition memory; SANS: Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms.
- Citation: Du XD, Li Z, Yuan N, Yin M, Zhao XL, Lv XL, Zou SY, Zhang J, Zhang GY, Li CW, Pan H, Yang L, Wu SQ, Yue Y, Wu YX, Zhang XY. Delayed improvements in visual memory task performance among chronic schizophrenia patients after high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. World J Psychiatry 2022; 12(9): 1169-1182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v12/i9/1169.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i9.1169