©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Psychiatr. Oct 19, 2021; 11(10): 841-853
Published online Oct 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i10.841
Published online Oct 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i10.841
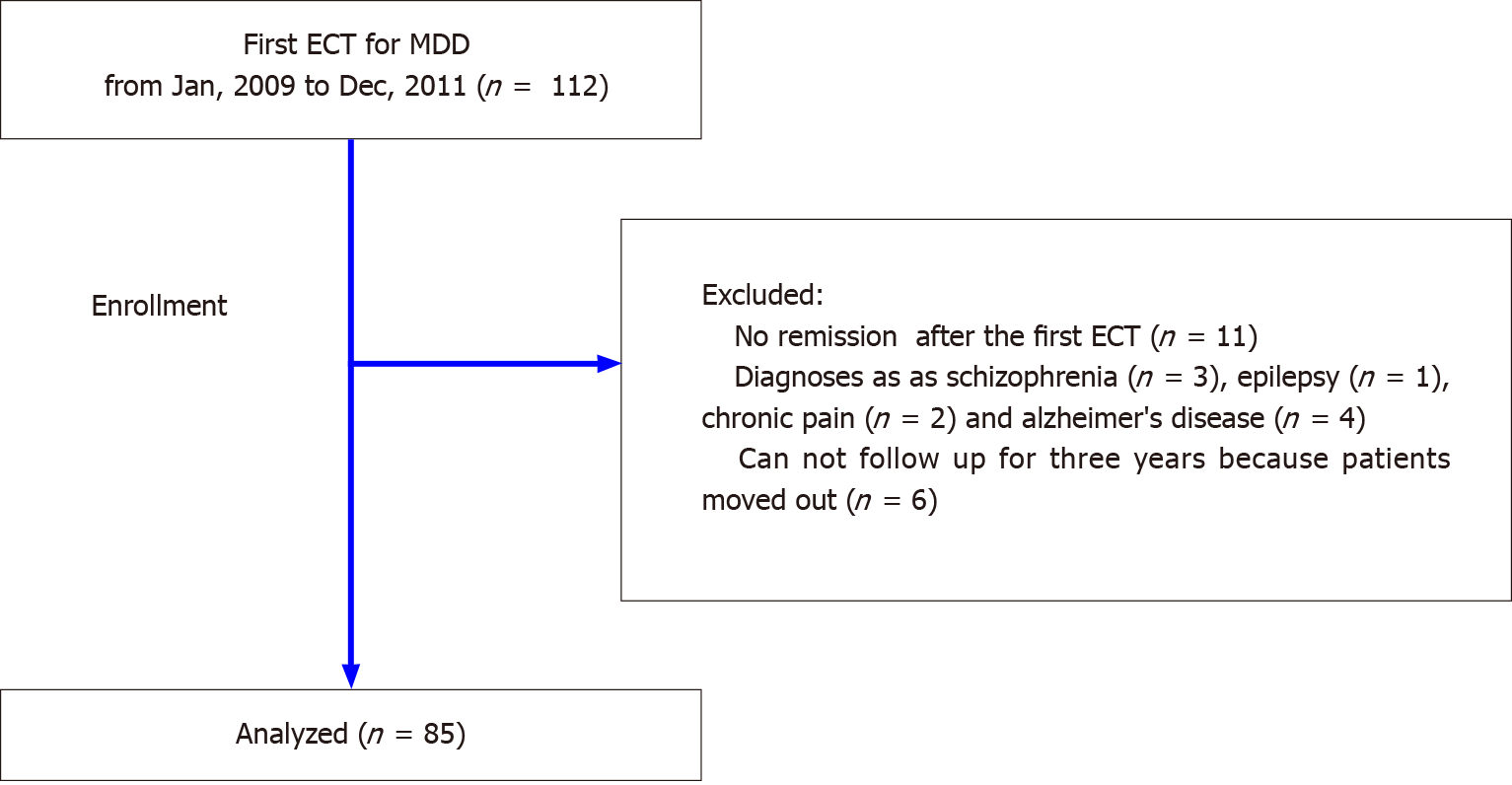
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the participants.
ECT: Electroconvulsive therapy; MDD: Major depressive disorder.
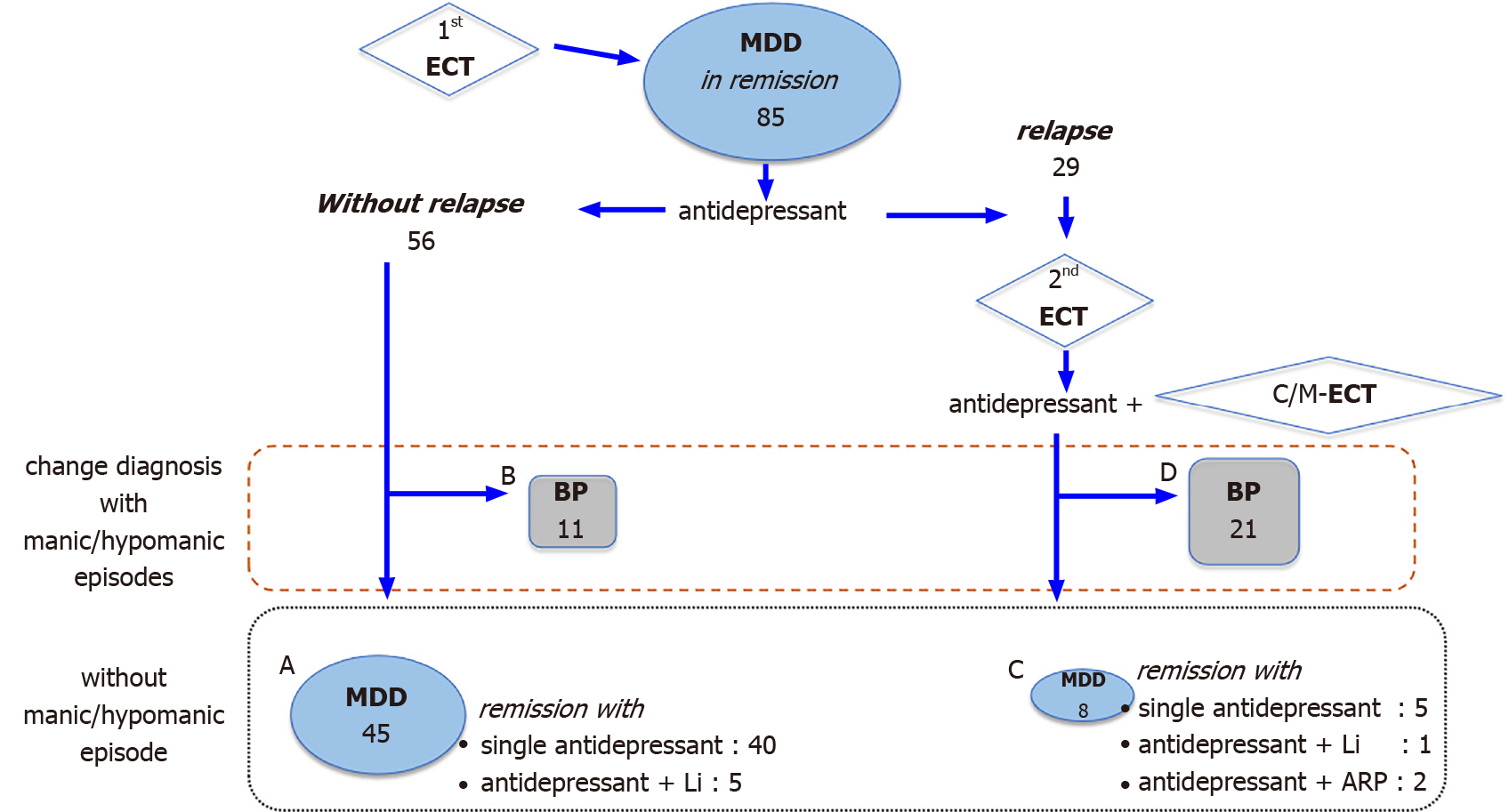
Figure 2 Changes in the treatment and diagnosis based on the relapse and manic/hypomanic episodes after remission after the first electroconvulsive therapy.
Relapses were characterized by five or more of the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Patients in groups A and B did not experience relapse after the first course of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Patients in groups C and D experienced a relapse after the first course of ECT. When there was a manic/hypomanic episode during the follow-up, the diagnosis was changed from major depressive disorder to bipolar disorder. ECT: Electroconvulsive therapy; MDD: Major depressive disorder; BP: Bipolar disorder; Li: Lithium; ARP: Aripiprazole.
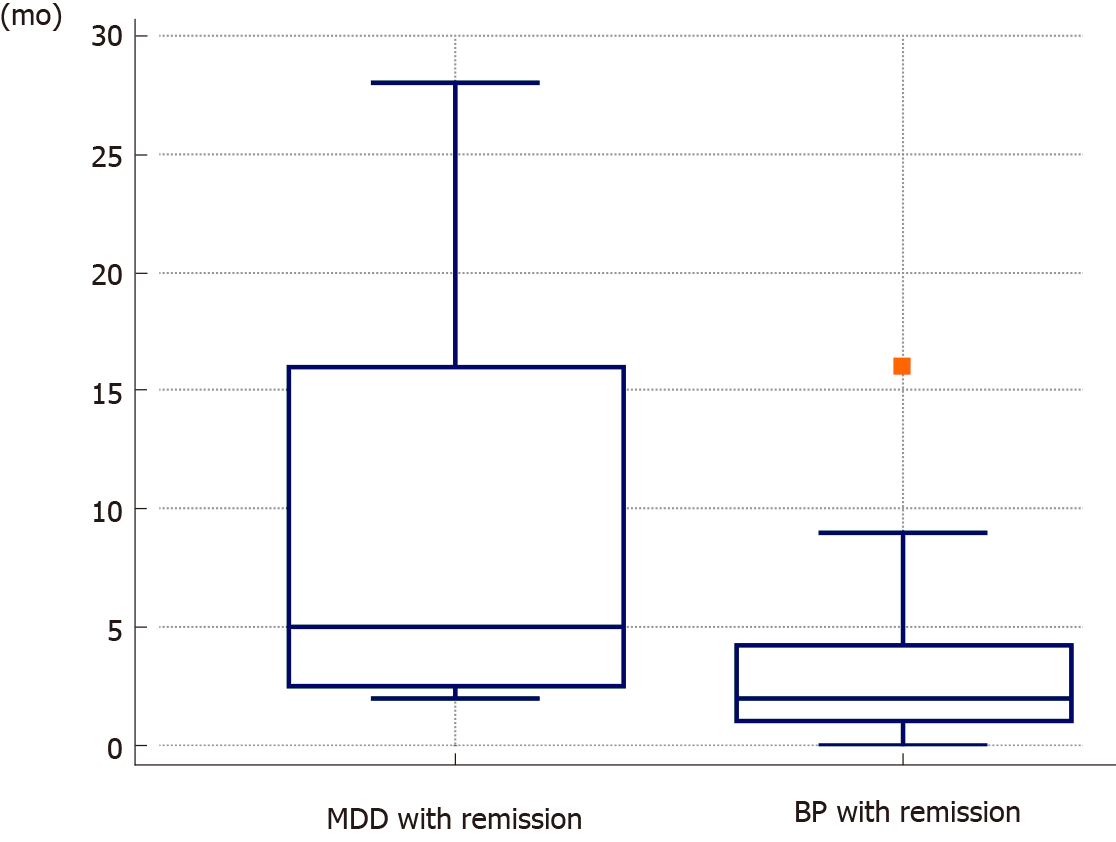
Figure 3 Period to relapse in the continuation and/or maintenance electroconvulsive therapy group.
The box-and-whisker plot displays the statistical summary of the variables. The central box shows values from the lower to the upper quartiles. The middle line represents median values. The horizontal line extends from the minimum to the maximum value, excluding the outliers, which are displayed as separate points. The BP participants in group D experienced relapse significantly earlier than the major depressive disorder participants in group C.
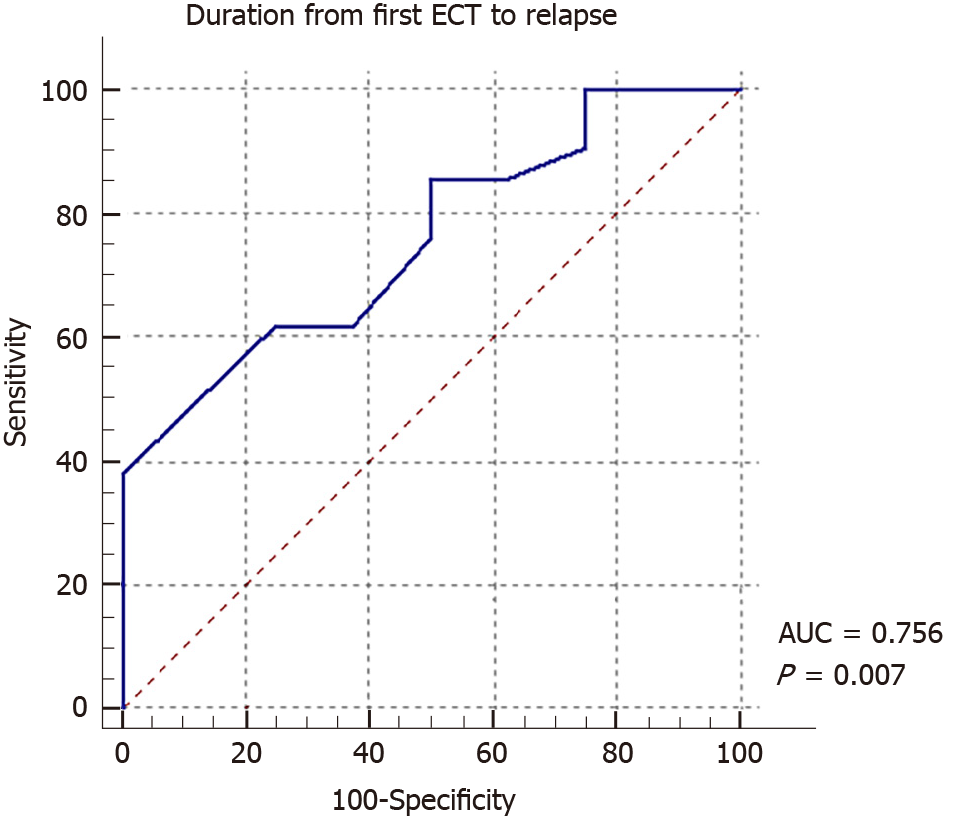
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristic analysis for determining the accuracy of the diagnosis based on the duration of the period until relapse.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of predicting diagnostic changes from major depressive disorder to Bipolar disorder from the duration between the first course of electroconvulsive therapy and relapse of depressive symptoms. The area under the ROC curve to for detecting diagnostic changes by based on relapse duration was 0.756 (95%CI: 0.562-0.895, P = 0.007).
- Citation: Kurimoto N, Inagaki T, Aoki T, Kadotani H, Kurimoto F, Kuriyama K, Yamada N, Ozeki Y. Factors causing a relapse of major depressive disorders following successful electroconvulsive therapy: A retrospective cohort study. World J Psychiatr 2021; 11(10): 841-853
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v11/i10/841.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i10.841