©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Nov 18, 2025; 16(11): 110426
Published online Nov 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i11.110426
Published online Nov 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i11.110426
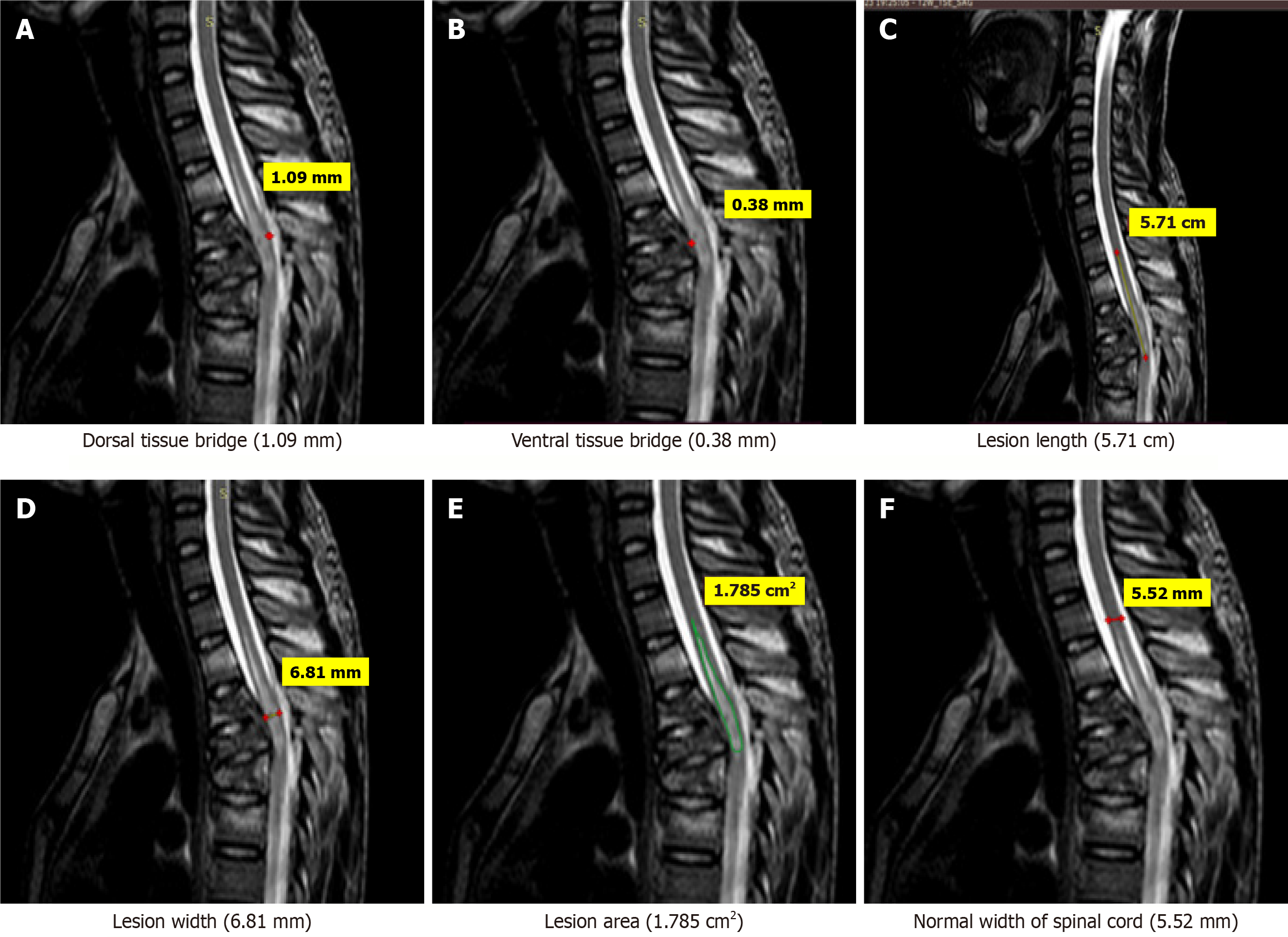
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging T2-weighted sagittal images of an 18-years-old patient who sustained trauma to thoracic spine (D10-D11) with ASIA grade C.
A: Dorsal tissue bridge (1.09 mm); B: Ventral tissue bridge (0.38 mm); C: The lesion length (5.71 cm); D: Lesion width (6.81 mm); E; Lesion area (1.785 cm2); F: Normal width of spinal cord (5.52 mm).
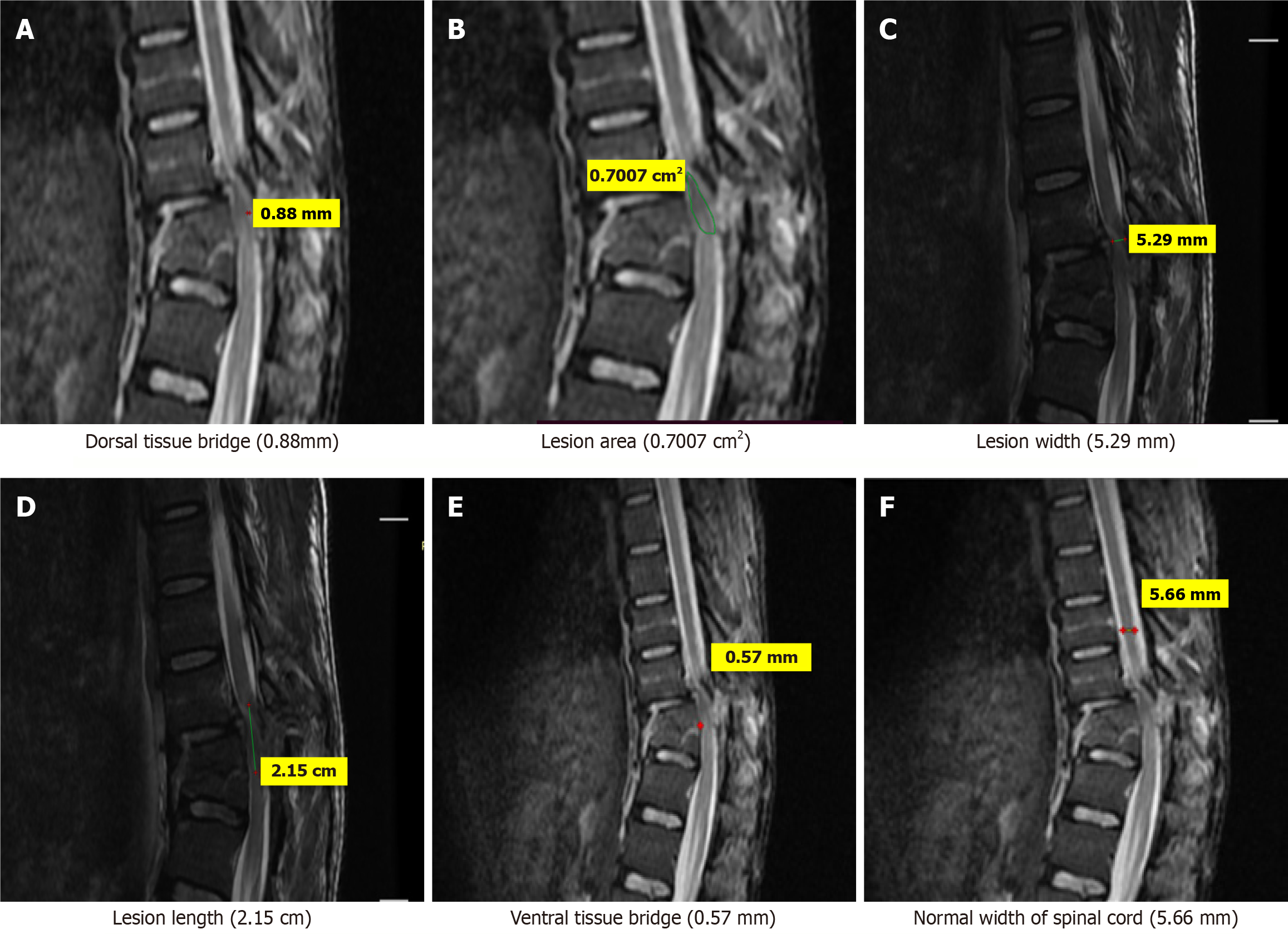
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging T2-weighted sagittal images of a 30-years old patient who sustained trauma to thoracic spine(D11) with ASIA grade C.
A: Dorsal tissue bridge (0.88 mm); B: Lesion area (0.7007 cm2); C: Lesion width (5.29 mm); D: Lesion length (2.15 cm); E: Ventral tissue bridge (0.57 mm); F: Normal width of spinal cord (5.66 mm).
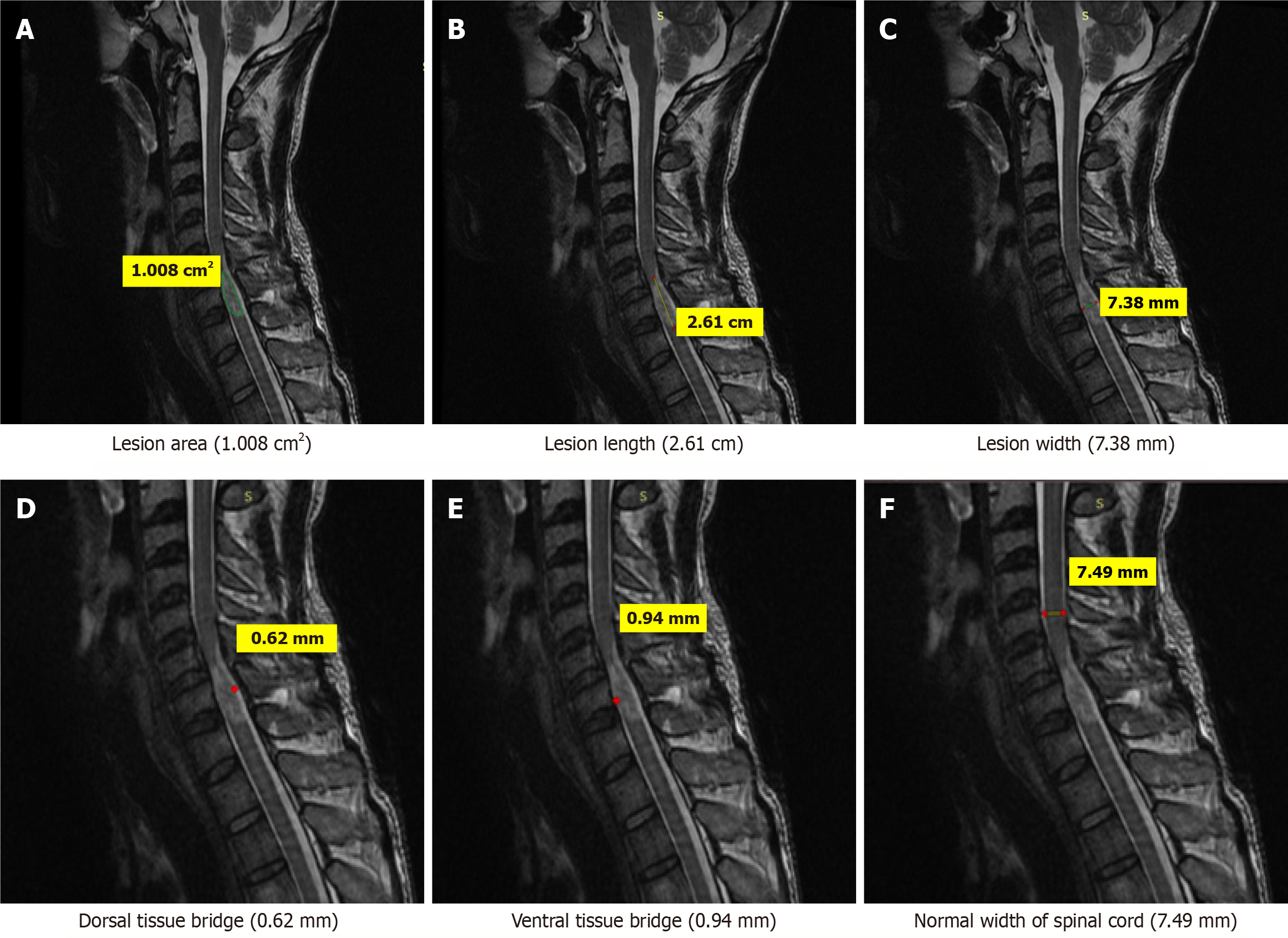
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance imaging T2-weighted sagittal images of a 39-years old patient who sustained trauma of cervical spine (C5-C6) with ASIA grade D.
A: Lesion area (1.008 cm2); B: Lesion length (2.61 cm); C: Lesion width (7.38 mm); D: Dorsal tissue bridge (0.62 mm); E: Ventral tissue bridge (0.94 mm); F: Normal width of spinal cord (7.49 mm).
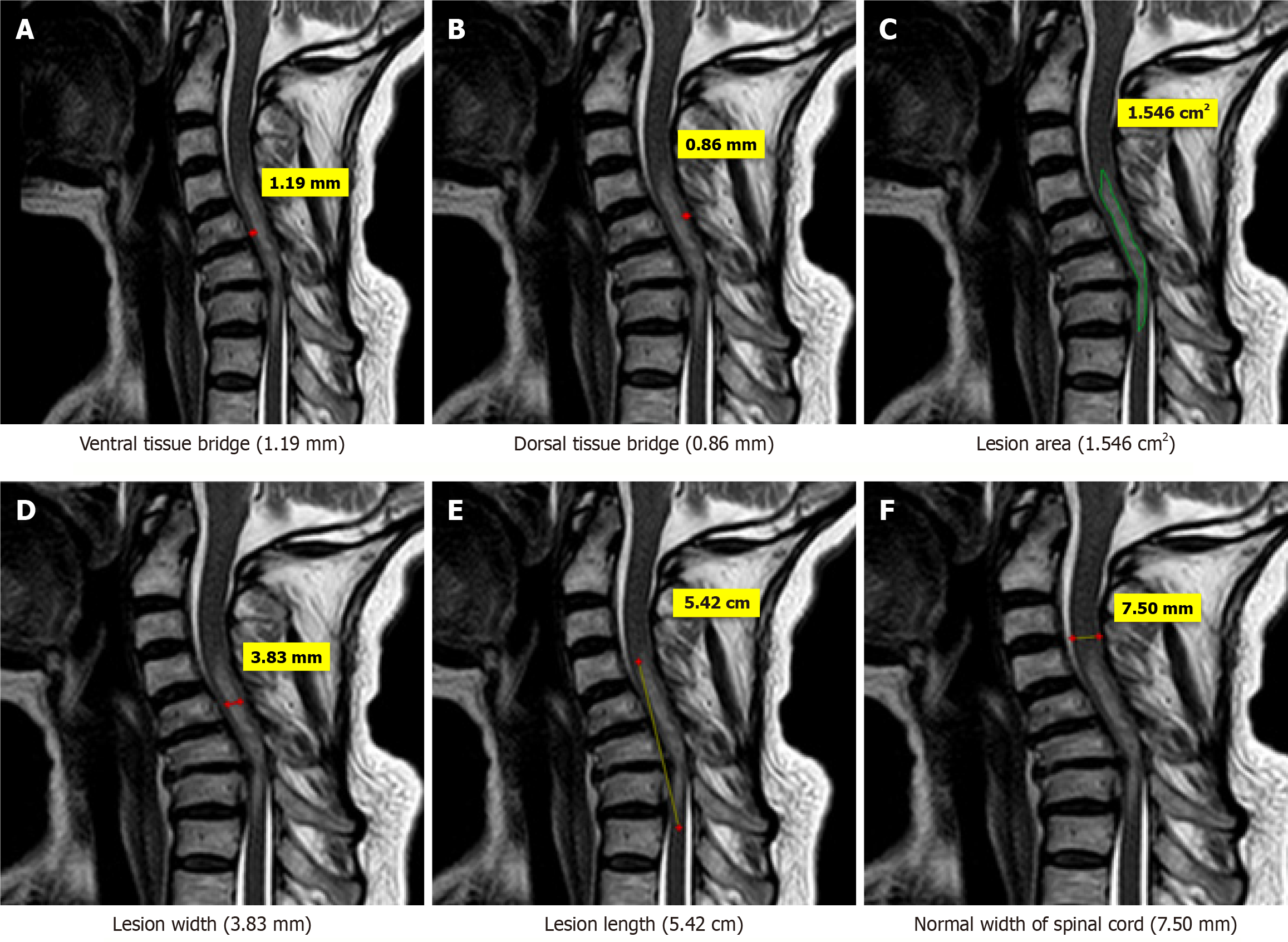
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging T2-weighted sagittal images of a 48-years old patient who sustained trauma of cervical spine (C5-C6) with ASIA grade C.
A: Ventral tissue bridge(1.19mm); B: Dorsal tissue bridge (0.86 mm); C: Lesion area (1.546 cm2); D: Lesion width (3.83 mm); E: Lesion length (5.42 cm); F: Normal width of spinal cord (7.50 mm).
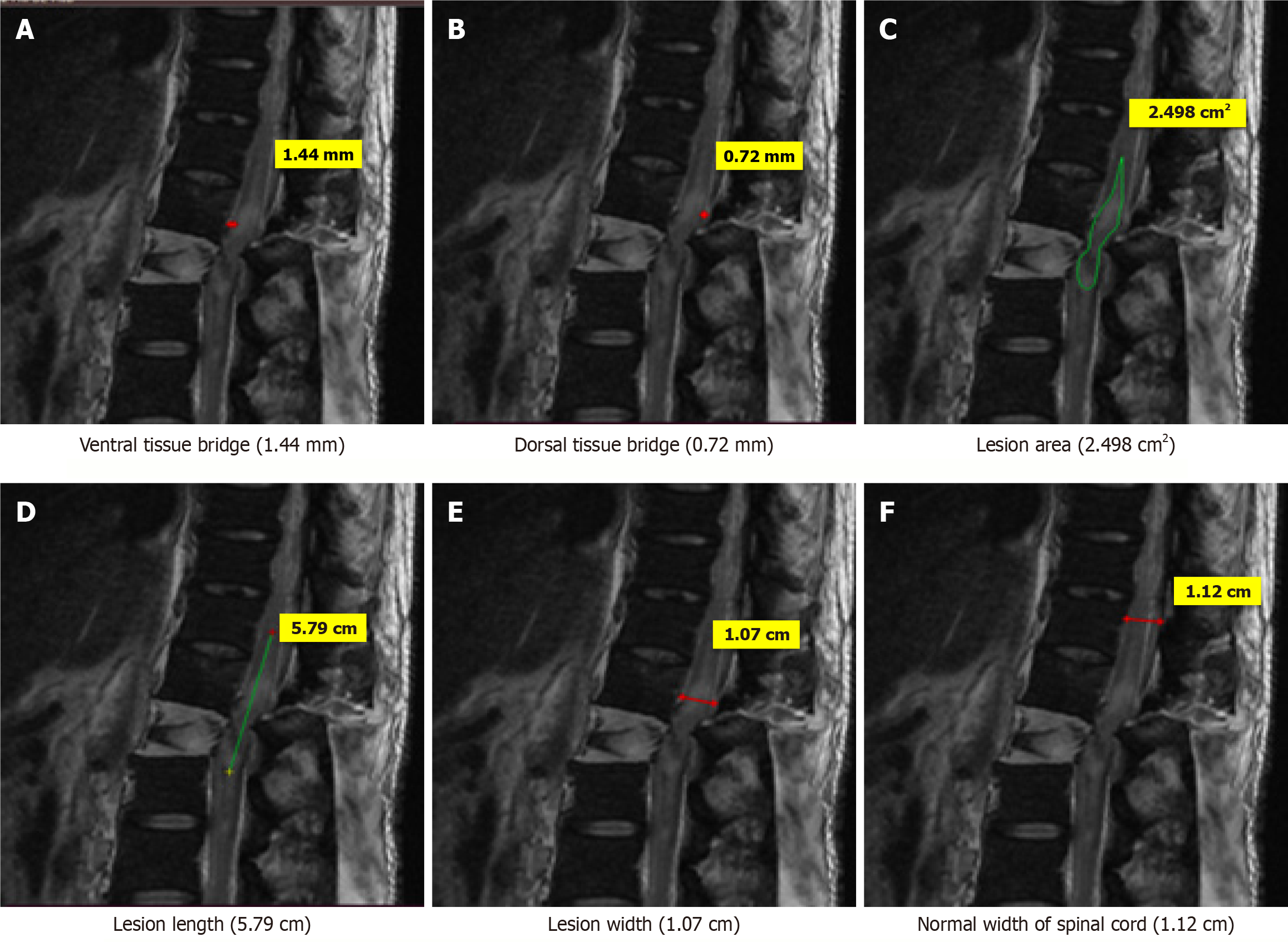
Figure 5 Magnetic resonance imaging T2-weighted sagittal image of a 34-years old patient who sustained trauma of thoracolumbar spine (D12-L1) with ASIA grade A.
A: Ventral tissue bridge (1.44 mm); B: Dorsal tissue bridge (0.72 mm); C: Lesion area (2.498 cm2); D: Lesion length (5.79 cm); E: Lesion width (1.07 cm); F: Normal width of spinal cord (1.12 cm).
- Citation: Singh R, Gautam S, Aggarwal S, Kaur S, Jain M. Correlation of magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers (tissue bridges) with neurological recovery following traumatic spinal cord injury. World J Orthop 2025; 16(11): 110426
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i11/110426.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i11.110426