©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 10, 2014; 5(5): 1020-1027
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.1020
Published online Dec 10, 2014. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.1020
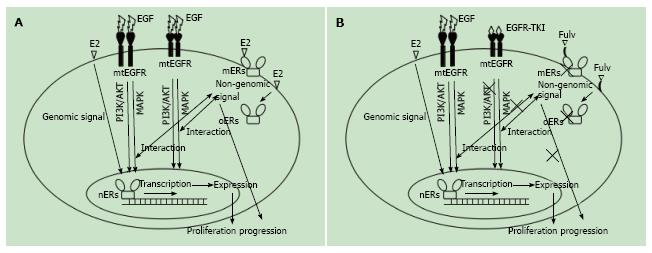
Figure 1 Intracellular estrogen receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.
A: Mechanisms of ER and EGFR signaling in NSCLC. E2 (17β-estradiol)-bound ER acts in part as a transcription factor in the nucleus. Once the ER binds to the DNA in the estrogen response element of a gene, it generally recruits co-activator complexes to modulate gene transcription (genomic signal). In addition, E2-bound ER also acts in the cytoplasm (non-genomic signal) by interacting with downstream mediators of EGFR signaling, such as MAPK and PI3K/AKT. EGFR is a cell membrane receptor tyrosine kinase that transmits a signal when it binds EGF; B: Mechanisms of combination therapy for NSCLC. The estrogen antagonist fulv binds to ERs and blocks estrogen signaling. EGFR-TKIs, such as gefitinib or erlotinib, bind to mtEGFR and inhibit EGFR signaling. Both treatments block the interaction between ER and EGFR signaling. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ER: Estrogen receptor; TKI: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
- Citation: Kawai H. Estrogen receptors as the novel therapeutic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5(5): 1020-1027
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v5/i5/1020.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i5.1020