©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Sep 24, 2025; 16(9): 111379
Published online Sep 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i9.111379
Published online Sep 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i9.111379
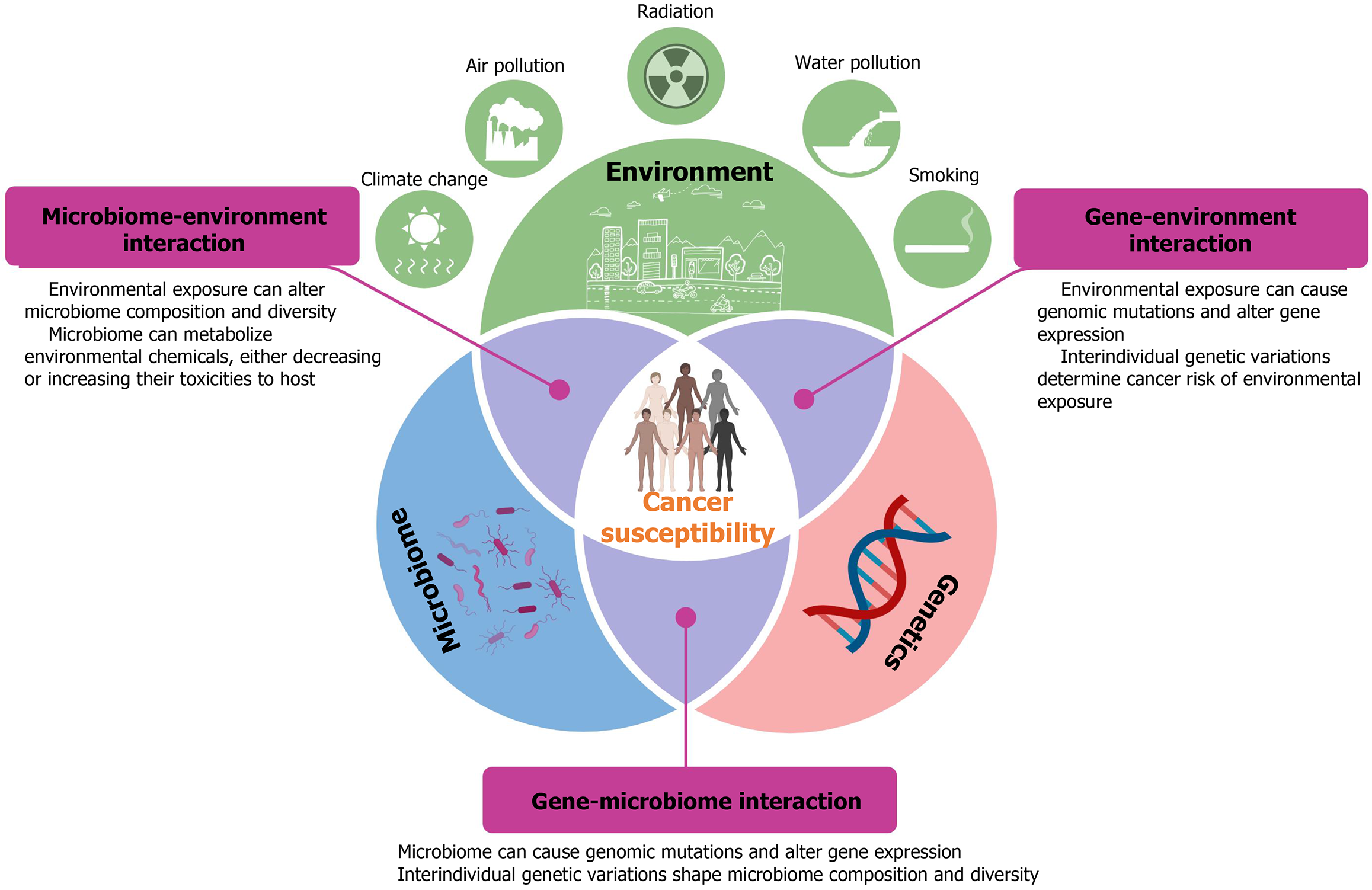
Figure 1 Contribution of host genetics, microbiome, environmental factors, and their bidirectional interactions to cancer susceptibility.
The host gene-environment, host gene-microbiome, and microbiome-environment bidirectional interactions play critical roles in cancer susceptibility.
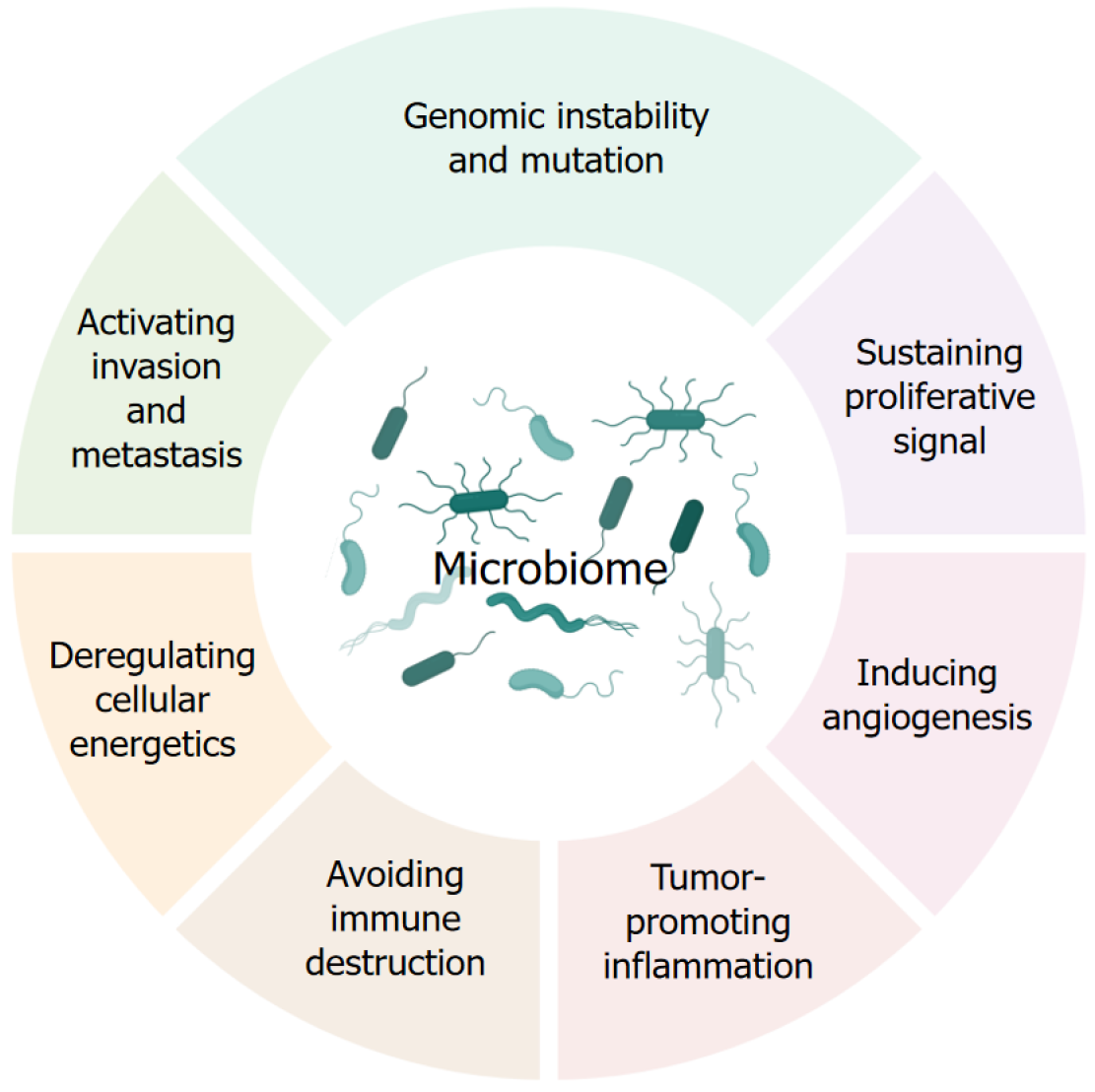
Figure 2 The microbiome and the hallmarks of cancer.
The microbiome modulates the majority of the hallmarks of cancer.
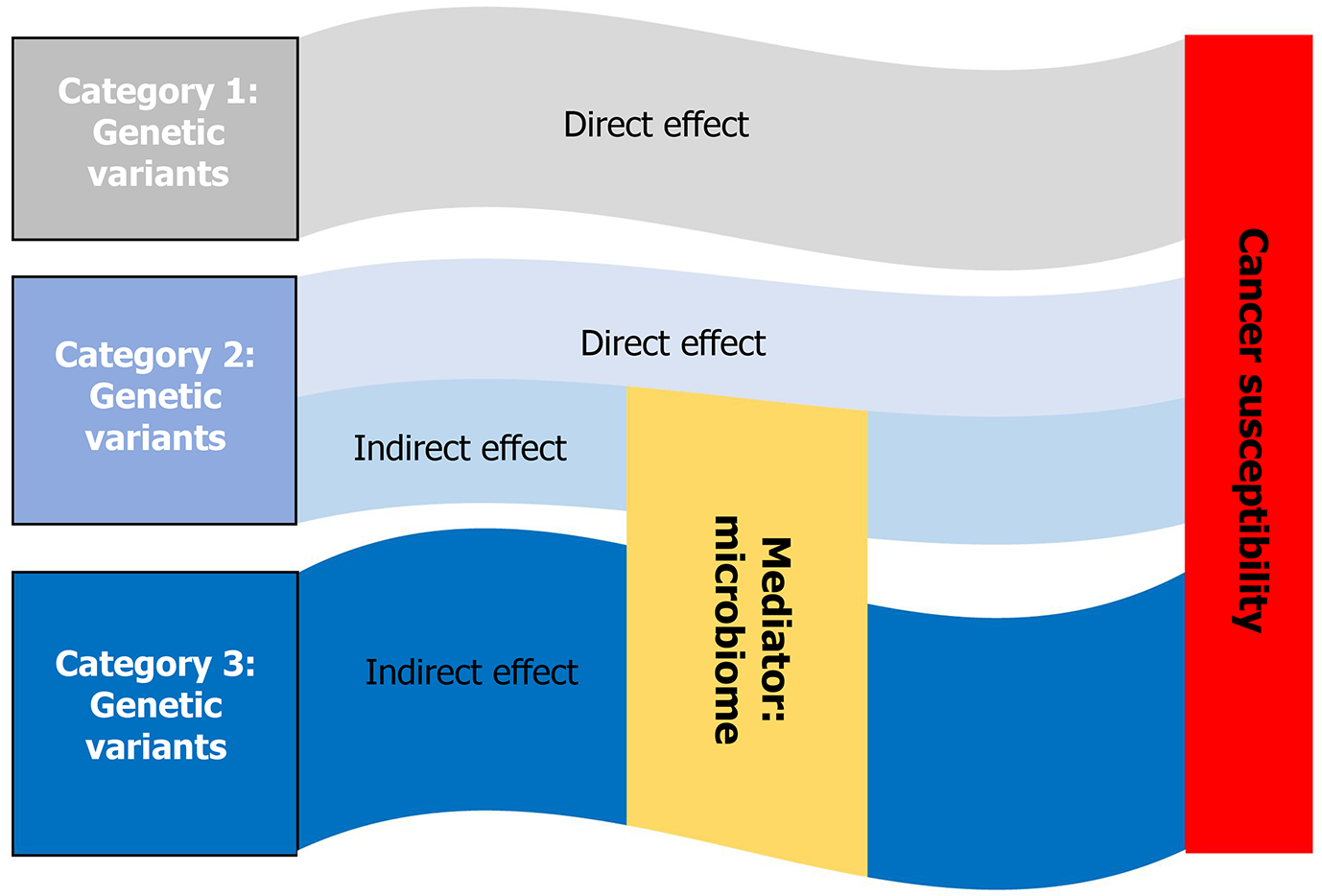
Figure 3 Direct and indirect genetic effect on cancer susceptibility.
The microbiome can serve as a mediator of genetic susceptibility.
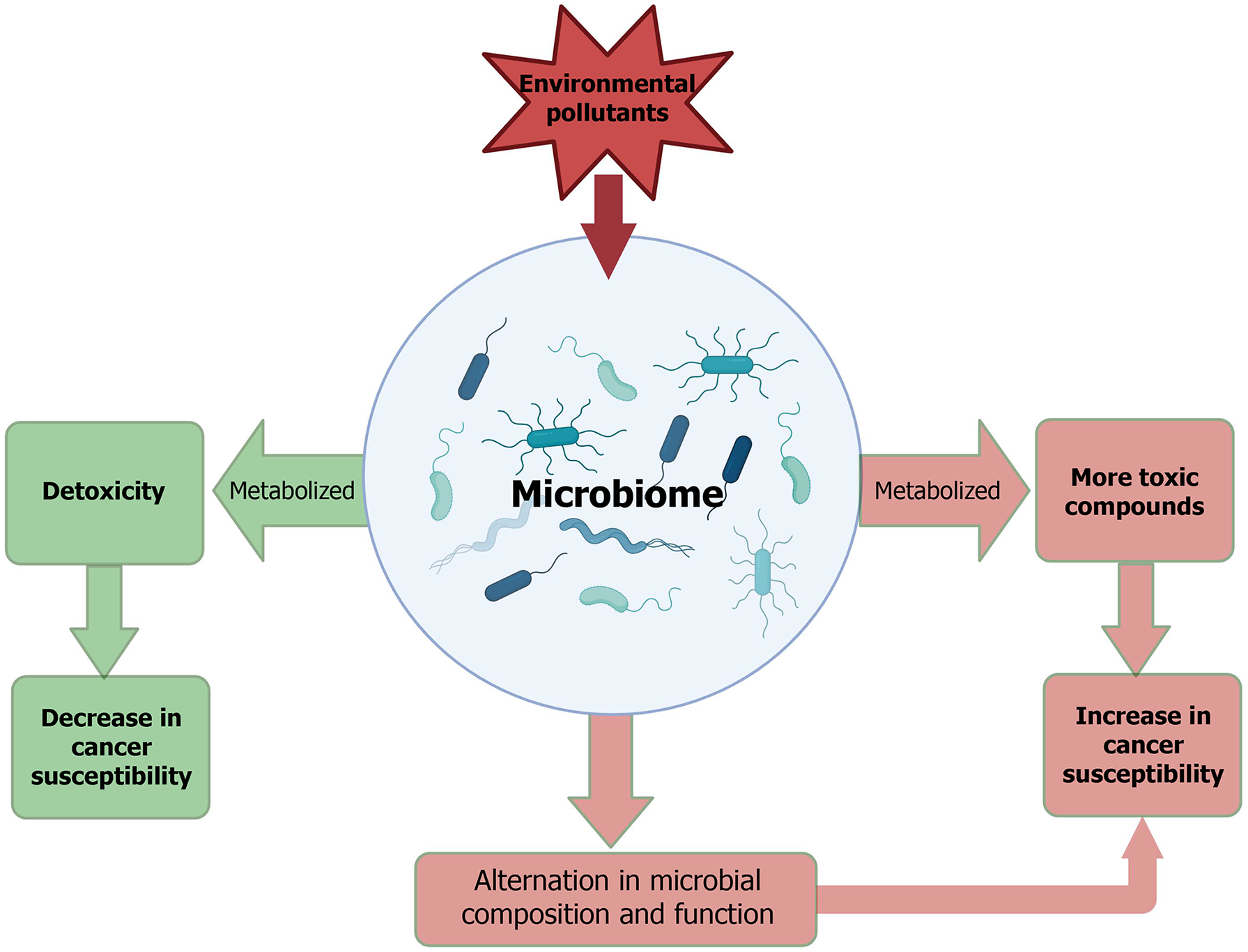
Figure 4 Bidirectional interactions between the microbiome and environmental pollutants and their contribution to cancer susceptibility.
The interactions between the microbiome and environmental pollutants modulate cancer susceptibility.
Figure 5
Analytical methods for microbiome-wide association study.
- Citation: Chang H, Perez-Losada J, Mao JH. Emerging multifaceted roles of the microbiome in cancer susceptibility. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(9): 111379
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i9/111379.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i9.111379